厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论 Marine Planktology(主讲:曹文清、郭东晖)

REFERENCES Zheng Zhong, Li Shaojing, Xu Zhenzu, 1989. Marine Planktology China Ocean Press & Springer-Verlag 郑重, 李少菁, 许振祖, 1984. 海洋浮游生物学 海洋出版社; 1992 繁体 字版 台湾水产出版社; 1996 修订再版 台湾水产出版社 金德祥, 1991. 海洋硅藻学 厦门大学出版社 Bougis P., 1976. Marine Plankton Ecology Raymont J. E. G., 1980, 1983. Plankton and Productivity in the Oceans Vol. I, II Miller C. B., 2004. Biological Oceanography 金德祥等, 1965. 中国海洋浮游硅藻类 郑重, 1986. 海洋浮游生物生态学文集 郑重, 曹文清, 1987. 海洋枝角类生物学 郑重, 李少菁, 连光山, 1992. 海洋桡足类生物学 郑重, 1993. 郑重文集(续) 中国动物志, 中国海藻志, 海洋学报, 海洋与湖沼 Journal Plankton Research, Journal Marine Biological Association, Marine Biology
REFERENCES Zheng Zhong, Li Shaojing, Xu Zhenzu, 1989. Marine Planktology China Ocean Press & Springer-Verlag 郑重, 李少菁, 许振祖, 1984. 海洋浮游生物学 海洋出版社; 1992 繁体 字版 台湾水产出版社; 1996 修订再版 台湾水产出版社 金德祥, 1991. 海洋硅藻学 厦门大学出版社 Bougis P., 1976. Marine Plankton Ecology Raymont J. E. G., 1980, 1983. Plankton and Productivity in the Oceans Vol. I, II Miller C. B., 2004. Biological Oceanography 金德祥等, 1965. 中国海洋浮游硅藻类 郑重, 1986. 海洋浮游生物生态学文集 郑重, 曹文清, 1987. 海洋枝角类生物学 郑重, 李少菁, 连光山, 1992. 海洋桡足类生物学 郑重, 1993. 郑重文集(续) 中国动物志, 中国海藻志, 海洋学报, 海洋与湖沼 Journal Plankton Research, Journal Marine Biological Association, Marine Biology

INTRODUCTION 1. Definition 2. The Relation Between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines of Oceanography 3. Ecological Groups of Plankton 4. Economic Importance 5. Brief History and Prospects
INTRODUCTION 1. Definition 2. The Relation Between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines of Oceanography 3. Ecological Groups of Plankton 4. Economic Importance 5. Brief History and Prospects

1 Definition Plankton (planktos, Victor Hensen, 1887): drifters of the open ocean Nekton = free swimmers of the sea Benthos = dwellers of the sea floor Planktology: the science of studying the life and activities of plankton
1 Definition Plankton (planktos, Victor Hensen, 1887): drifters of the open ocean Nekton = free swimmers of the sea Benthos = dwellers of the sea floor Planktology: the science of studying the life and activities of plankton

Introduction 1. Definition 2. The Relation Between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines of Oceanography 3. Ecological Groups of Plankton 4. Economic Importance 5. Brief History and Prospects
Introduction 1. Definition 2. The Relation Between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines of Oceanography 3. Ecological Groups of Plankton 4. Economic Importance 5. Brief History and Prospects

2 Relationship Planktology: morphology, taxonomy, ecology, physiology, biochemistry Marine Biology Biological Oceanography Relation between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines Biology Oceanography Aquaculture Fishery Meteorology Marine Sedimentology (Marine Geology) Environmental Science
2 Relationship Planktology: morphology, taxonomy, ecology, physiology, biochemistry Marine Biology Biological Oceanography Relation between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines Biology Oceanography Aquaculture Fishery Meteorology Marine Sedimentology (Marine Geology) Environmental Science

Phytoplankton Zooplankton 25 Fe CO 22
Phytoplankton Zooplankton 25 Fe CO 22

Introduction 1. Definition 2. The Relation Between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines of Oceanography 3. Ecological Groups of Plankton 4. Economic Importance 5. Brief History and Prospects
Introduction 1. Definition 2. The Relation Between Marine Planktology and Other Disciplines of Oceanography 3. Ecological Groups of Plankton 4. Economic Importance 5. Brief History and Prospects

3 Ecological Groups 3.1 Type of Nutrition Phytoplankton: autotrophic bacteria and unicellular algae (Bacillariophyta, Pyrrophyta, Chlorophyta, Cyanophyta, Chrysophyta, Xanthophyta, Cryptophyta and Euglenophyta) Zooplankton: heterotrophic Protozoa, medusae, Rotifera, Crustacea, Chaetognatha, pelagic Mollusca, Tunicata, larvae of invertebrate and lower chordates
3 Ecological Groups 3.1 Type of Nutrition Phytoplankton: autotrophic bacteria and unicellular algae (Bacillariophyta, Pyrrophyta, Chlorophyta, Cyanophyta, Chrysophyta, Xanthophyta, Cryptophyta and Euglenophyta) Zooplankton: heterotrophic Protozoa, medusae, Rotifera, Crustacea, Chaetognatha, pelagic Mollusca, Tunicata, larvae of invertebrate and lower chordates

Phytoplankton 1: Diatom
Phytoplankton 1: Diatom
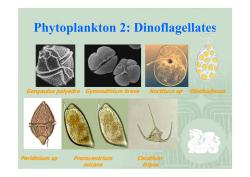
Phytoplankton 2: Dinoflagellates Gonyaulax polyedra Gymnodinium breve Noctiluca sp Olisthodiscus Peridinium sp Ceratium tripos Prorocentrium micans
Phytoplankton 2: Dinoflagellates Gonyaulax polyedra Gymnodinium breve Noctiluca sp Olisthodiscus Peridinium sp Ceratium tripos Prorocentrium micans
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第09章 毛颚动物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第08章 浮游软体动物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第7节 樱虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第6节 端足类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第5节 糠虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第4节 磷虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第3节 桡足类 2/2.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第3节 桡足类 1/2.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第2节 枝角类.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第1节 绪论.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第06章 栉水母.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第05章 腔肠动物.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第04章 原生动物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第03章 其他海洋浮游植物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第02章 甲藻门.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第01章 硅藻门.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第18章 Plankton and Fishery.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第17章 Diurnal vertical migration(DVM).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第16章 vertical distribution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第15章 geographic distribution.ppt
- 齐鲁工业大学(山东轻工业学院):《生物工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 生物工艺学概论 biotechnologh.ppt
- 齐鲁工业大学(山东轻工业学院):《生物工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 生物工业菌种.ppt
- 齐鲁工业大学(山东轻工业学院):《生物工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 厌氧发酵机制.ppt
- 齐鲁工业大学(山东轻工业学院):《生物工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 好氧发酵机制.ppt
- 齐鲁工业大学(山东轻工业学院):《生物工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 生物工艺学过程控制.ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(主讲:周传云).ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 微生物分类与鉴定.ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 食品中微生物来源及主要种类.ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 食品中微生物及其产物的测定.ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 微生物在食品发酵工业中的应用.ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 微生物生态与生态工程.ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 微生物与食品的腐败变质.ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物与食品中毒.ppt
- 湖南农业大学:《高级微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 食品安全的微生物指标与质量管理控制.ppt
- 山西师范大学:《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 生态系统中的能量流动.ppt
- 山西师范大学:《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 生态系统的物质循环.ppt
- 山西师范大学:《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(主讲:毕润成).ppt
- 山西师范大学:《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 生物与环境.ppt
- 山西师范大学:《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 种群.ppt
- 山西师范大学:《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 种群生活史.ppt
