香港中文大学:Efficient protocols for generating bipartite classical distributions and quantum states

ioing biparite classical distributions and quantum states Rahul Jain,Yaoyun Shi,Zhaohui Wei,Shengyu Zhang
Rahul Jain, Yaoyun Shi, Zhaohui Wei, Shengyu Zhang

randomness/entanglement Shared randomness/entanglement is an important resource in distributive settings. Question:How hard to generate a bipartite classical distribution or quantum state?
randomness/entanglement • Shared randomness/entanglement is an important resource in distributive settings. • Question: How hard to generate a bipartite classical distribution or quantum state?

3 scenarios Distribution generation Distribution approximation Quantum state approximation
3 scenarios • Distribution generation • Distribution approximation • Quantum state approximation
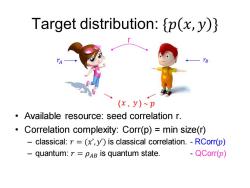
Target distribution:p(x,y)} TB (x,y)~p Available resource:seed correlation r. Correlation complexity:Corr(p)=min size(r) classical:r =(x',y')is classical correlation.-RCorr(p) 一 quantum:r =PAB is quantum state. QCorr(p)
Target distribution: {𝑝 𝑥, 𝑦 } • Available resource: seed correlation r. • Correlation complexity: Corr(p) = min size(r) – classical: 𝑟 = (𝑥’,𝑦’) is classical correlation. - RCorr(𝑝) – quantum: 𝑟 = 𝜌𝐴𝐵 is quantum state. - QCorr(𝑝) 𝑟𝐵 𝑥 𝑦 r ( , ) 𝑝 𝑟𝐴
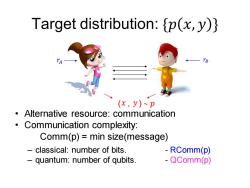
Target distribution:{p(x,y)} TB (x,y)~卫 Alternative resource:communication Communication complexity: Comm(p)=min size(message) classical:number of bits. RComm(p) quantum:number of qubits. QComm(p) -
Target distribution: {𝑝 𝑥, 𝑦 } • Alternative resource: communication • Communication complexity: Comm(p) = min size(message) – classical: number of bits. - RComm(p) – quantum: number of qubits. - QComm(p) 𝑟𝐵 (𝑥 , 𝑦 ) 𝑝 𝑟𝐴
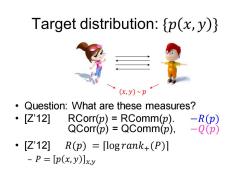
Target distribution:p(x,y)} (x,y)~卫 Question:What are these measures? ·[Z12] 88m8=&8m8.-89 ·[Z12] R(p)=flogrank+(P)] -P=[p(x,y)]xy
Target distribution: {𝑝 𝑥, 𝑦 } • Question: What are these measures? • [Z’12] RCorr(𝑝) = RComm(𝑝). −𝑅(𝑝) QCorr(𝑝) = QComm(𝑝), −𝑄(𝑝) • [Z’12] 𝑅(𝑝) = ⌈log 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘+(𝑃)⌉ – 𝑃 = 𝑝 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑥,𝑦 (𝑥, 𝑦) 𝑝
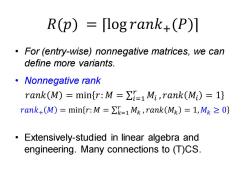
R(p)=logrank+(P) For (entry-wise)nonnegative matrices,we can define more variants. ·Nonnegative rank rank(M)=minfr:M=>=1Mi,rank(Mi)=13 rank+(M)=min{r:M =k=1Mk,rank(Mk)=1,Mk =0 Extensively-studied in linear algebra and engineering.Many connections to (T)CS
𝑅(𝑝) = ⌈log 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘+(𝑃)⌉ • For (entry-wise) nonnegative matrices, we can define more variants. • Nonnegative rank 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘 𝑀 = min 𝑟: 𝑀 = σ𝑖=1 𝑟 𝑀𝑖 , 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘 𝑀𝑖 = 1 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘+ 𝑀 = min 𝑟:𝑀 = σ𝑘=1 𝑟 𝑀𝑘 , 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘 𝑀𝑘 = 1,𝑀𝑘 ≥ 0 • Extensively-studied in linear algebra and engineering. Many connections to (T)CS
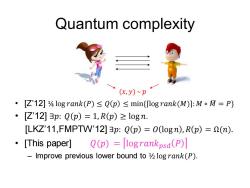
Quantum complexity (x,y)~p ·[Z12]4 log rank(P)≤Q(p)≤min{log rank(M):MoM=P} [Z'12]3p:Q(p)=1,R(p)=logn. [LKZ'11,FMPTW'12]3p:Q(p)=0(logn),R(p)=2(n). 。[This paper] Q(p)=logrankpsa(P) Improve previous lower bound to 12 log rank(P)
Quantum complexity • [Z’12] ¼ log 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘(𝑃) ≤ 𝑄 𝑝 ≤ min{⌈log 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘(𝑀)⌉: 𝑀 ∘ 𝑀ഥ = 𝑃} • [Z’12] ∃𝑝: 𝑄 𝑝 = 1, 𝑅 𝑝 ≥ log 𝑛. [LKZ’11,FMPTW’12] ∃𝑝: 𝑄 𝑝 = 𝑂 log 𝑛 , 𝑅 𝑝 = Ω(𝑛). • [This paper] 𝑄(𝑝) = log 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑝𝑠𝑑 𝑃 – Improve previous lower bound to ½ log 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘(𝑃). (𝑥, 𝑦) 𝑝
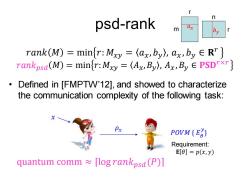
n psd-rank m ax rank(M)=minfr:Mxy (ax,by),ax,by E R"} rankpsd(M)=minfr:Mxy =(Ax,By),Ax,By E PSDrxr} o Defined in [FMPTW'12],and showed to characterize the communication complexity of the following task: Px POVM {E} Requirement: E[]=p(x,y) quantum comm flogrankpsa(P)]
psd-rank 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘 𝑀 = min 𝑟: 𝑀𝑥𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 , 𝑏𝑦 , 𝑎𝑥 , 𝑏𝑦 ∈ 𝐑 𝑟 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑝𝑠𝑑 𝑀 = min 𝑟:𝑀𝑥𝑦 = 𝐴𝑥,𝐵𝑦 , 𝐴𝑥 ,𝐵𝑦 ∈ 𝐏𝐒𝐃𝑟×𝑟 • Defined in [FMPTW’12], and showed to characterize the communication complexity of the following task: quantum comm ≈ ⌈log 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑘𝑝𝑠𝑑(𝑃)⌉ 𝑥 𝜌𝑥 𝑃𝑂𝑉𝑀 { 𝐸𝜃 𝑦 } Requirement: 𝐄 𝜃 = 𝑝(𝑥, 𝑦) m r r n 𝑎𝑥 𝑏𝑦
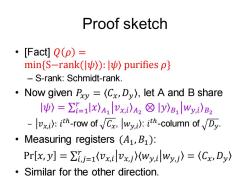
Proof sketch ·[Fact灯Q(p)= min{s-rank()):purifies p} -S-rank:Schmidt-rank. Now given Py =(Cx,Dy),let A and B share |〉=∑=1lx)A1vxi)A2☒ly)B1Wy,i)B2 -)ith-row ofCxwyi):ith-column ofDy. Measuring registers (A1,B1): Pr[x,y]=∑,j=1 VxiVxj)(Wy,iwy,)=(Cx,Dy〉 o Similar for the other direction
Proof sketch • [Fact] 𝑄 𝜌 = min{S−rank(|𝜓〉): |𝜓〉 purifies 𝜌} – S-rank: Schmidt-rank. • Now given 𝑃𝑥𝑦 = 〈𝐶𝑥,𝐷𝑦〉, let A and B share 𝜓 = σ𝑖=1 𝑟 𝑥 𝐴1 𝑣𝑥,𝑖 𝐴2 ⊗ 𝑦 𝐵1 𝑤𝑦,𝑖 𝐵2 – 𝑣𝑥,𝑖 : 𝑖 𝑡ℎ -row of 𝐶𝑥, 𝑤𝑦,𝑖 : 𝑖 𝑡ℎ -column of 𝐷𝑦. • Measuring registers (𝐴1,𝐵1): Pr 𝑥, 𝑦 = σ𝑖,𝑗=1 𝑟 〈𝑣𝑥,𝑖 𝑣𝑥,𝑗 〈𝑤𝑦,𝑖 𝑤𝑦,𝑗 = 𝐶𝑥,𝐷𝑦 • Similar for the other direction
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 香港中文大学:Fourier sparsity, spectral norm, and the Log-rank conjecture(long).pptx
- 香港中文大学:Fourier sparsity, spectral norm, and the Log-rank conjecture(short).pptx
- 香港中文大学:Fast quantum algorithms for Least Squares Regression and Statistic Leverage Scores.pptx
- 香港中文大学:Sensitivity Conjecture and Log-rank Conjecture for functions with small alternating numbers.pptx
- 香港中文大学:Networked Fairness in Cake Cutting.pptx
- 《金陵科技学院学报》:高形变二维码识别算法设计与实现.pdf
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末考试样题.doc
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)TSS示例程序.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)TSS软件栈 TSS-TCG Software Stack.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第6讲 可信启动.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第6章 TPM核心功能.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第6讲 可信计算基础.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第4讲 公钥基础设施(PKI).ppt
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三讲 认证技术与数字签名.ppt
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 密码学技术.ppt
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一章 概述(主讲:周福才).pptx
- 东北大学:《信息安全专业概论与职业发展》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一讲 浅析专业与兴趣(主讲:周福才).pptx
- 东北大学:《信息安全专业概论与职业发展》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三讲 信息安全专业规范.pptx
- 东北大学:《信息安全专业概论与职业发展》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二讲 信息安全概念、发展和现状.pptx
- 谷歌研究院(Google)数学之美与浪潮之巅.pdf
- 香港中文大学:On the complexity of trial and error.pptx
- 香港中文大学:A quantum protocol for sampling correlated equilibria unconditionally and without a mediator.pptx
- 香港中文大学:Quantum strategic game theory.ppt
- 香港中文大学:On the power of lower bound methods for quantum one-way communication complexity.ppt
- 香港中文大学:An Introduction to Quantum Computing in Theoretical Computer Science.ppt
- 香港中文大学:Random Walk on Graphs and its Algorithmic Applications.ppt
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Sample space and probability.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Sample space and probability.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Discrete random variables.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Discrete random variables.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Further Topics on Random Variables.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Further Topics on Random Variables.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)General random variables.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Limit Theorems.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Limit Theorems.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Bayesian Statistical Inference.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Bayesian Statistical Inference.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Classical Statistical Inference.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)General random variables.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Classical Statistical Inference.pptx
