香港中文大学:On the complexity of trial and error

On the Complexity of Trial and Error Shengyu Zhang Joint work with Xiaohui Bei and Ning Chen STOC'13,also at arXiv:1205.1183
Shengyu Zhang Joint work with Xiaohui Bei and Ning Chen STOC’13, also at arXiv:1205.1183

Motivating example:drug development Pandemic Consider an infectious disease outbreak due to an unknown virus. 。 Biochemists:find diagnosticreagents that have no serious side effects... ...as quickly as possible! PANDEMIC (Simplified)formulation Each side effect:certain combination of some ingredients Goal:find effective reagent/medicine without major side effect
Motivating example: drug development 2 • Consider an infectious disease outbreak due to an unknown virus. • Biochemists: find diagnostic reagents that have no serious side effects… … as quickly as possible! Pandemic • Each side effect: certain combination of some ingredients • Goal: find effective reagent/medicine without major side effect. (Simplified) formulation

Known vs.unknown If the virus(its DNA sequence,chemical composition,...) and its interactions to human body are known,then the reagent is much easier to find. Unfortunately,often the virus causing a pandemic is largely unidentified human body is too complicated a system to fully understand ●Learn it first?Efficiency! 3
If the virus (its DNA sequence, chemical composition, …) and its interactions to human body are known, then the reagent is much easier to find. Unfortunately, often the virus causing a pandemic is largely unidentified. human body is too complicated a system to fully understand Learn it first? Efficiency! 3 Known vs. unknown
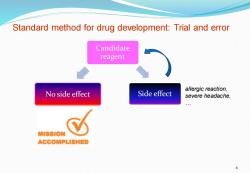
Standard method for drug development:Trial and error Candidate reagent allergic reaction, No side effect Side effect severe headache, MISSION ACCOMPLISHED 4
Candidate reagent No side effect Side effect 4 Standard method for drug development: Trial and error allergic reaction, severe headache, …

Phenomena Task:search for a solution (reagents)to satisfy a bunch of constraints(no side effect). Input(virus,human body):unknown. Allowed operations:solution testing. Approach:trial-and-error. Efficiency is crucial preferably better than learning the unknown input. ●Next:More examples. 5
Task: search for a solution (reagents) to satisfy a bunch of constraints (no side effect). Input (virus, human body): unknown. Allowed operations: solution testing. Approach: trial-and-error. Efficiency is crucial preferably better than learning the unknown input. Next: More examples. 5 Phenomena

Normal-Form Game Prisoner's Normal-form game dilemma Two (or more)players.Pi has a set Si of strategies. C D ·Joint strategy:s=(s1,S2)eS=S1×S2. C -1,-1 -10,0 ·Utility functions:ui:S→R. D 0,-10 -5,-5 Nash equilibrium A stable state where no player is willing to deviate her current strategy. Existence:(Mixed)Nash equilibrium alwaysexists.(vNM'44,N'51) Players have to Issue:In many scenarios,players do not know their payoffs. choose an action anyway Eg.:When a new business model appears,companies don't really know strategies will give how much payoff. 6
6 Normal-Form Game Issue: In many scenarios, players do not know their payoffs. • Eg.: When a new business model appears, companies don’t really know what strategies will give how much payoff. C D C -1, -1 -10, 0 D 0, -10 -5, -5 Prisoner’s dilemma • A stable state where no player is willing to deviate her current strategy. • Existence: (Mixed) Nash equilibrium always exists. (vNM’44, N’51) Nash equilibrium • Two (or more) players. 𝑃𝑖 has a set 𝑆𝑖 of strategies. • Joint strategy: 𝑠 = 𝑠1, 𝑠2 ∈ 𝑆 = 𝑆1 × 𝑆2. • Utility functions: 𝑢𝑖 : 𝑆 → ℝ. Normal-form game

Stable Matching Stable Matching Each individual has a preference over the agents of the other side Stable matching:no(m,w)preferring each other to their current ones 。 Gale-Shapley algorithm computes a stable matching Applications:hospital-intern allocation,school admission,... W1>W2>W3>W4 mi W1 m3>m1>m2>m4 W1>W2>W3>W4 1m2 W2 m3>m4>m1>m2 W2>W1>W3>W4 m3 W3 m1>m4>m2>m3 W3>W2>W4>W1 m4 W4 m4>m1>m3>m2 7
7 Stable Matching • Each individual has a preference over the agents of the other side • Stable matching: no (𝑚, 𝑤) preferring each other to their current ones • Gale-Shapley algorithm computes a stable matching • Applications: hospital-intern allocation, school admission, … Stable Matching 7 𝑚3 > 𝑚1 > 𝑚2 > 𝑚4 𝑚3 > 𝑚4 > 𝑚1 > 𝑚2 𝑚1 > 𝑚4 > 𝑚2 > 𝑚3 𝑚4 > 𝑚1 > 𝑚3 > 𝑚2 𝑤1 > 𝑤2 > 𝑤3 > 𝑤4 𝑚1 𝑤1 𝑤1 > 𝑤2 > 𝑤3 > 𝑤4 𝑤2 > 𝑤1 > 𝑤3 > 𝑤4 𝑤3 > 𝑤2 > 𝑤4 > 𝑤1 𝑚2 𝑚3 𝑚4 𝑤2 𝑤3 𝑤4

Stable Matching Stable Matching Issue:Individuals may not know their preferences exactly. Dating A man doesn't know how well a woman matches him as a wife until they are together for some time. Job market A candidate may not know precisely how much she likes the job. Also generally hard for recruiters to judge which candidates best fit the position. a systematic and continuous approach to fitting the right person to the An assignment right time has long been the Holy Grail of workforce organization." has to be ---McKinsey Quarterly,2003 determined 8
Stable Matching 8 Stable Matching Issue: Individuals may not know their preferences exactly. • A man doesn’t know how well a woman matches him as a wife until they are together for some time. Dating • A candidate may not know precisely how much she likes the job. • Also generally hard for recruiters to judge which candidates best fit the position. Job market “… a systematic and continuous approach to fitting the right person to the right job at the right time has long been the Holy Grail of workforce organization.” --- McKinsey Quarterly, 2003
In a broad sense Natural sciences Original Artist Reproduction rights.obtainable from www.CartoonStock.com- ·Hypothesis(theory) proposed.(Sometimes 2 predictions also made.) Experiment conducted to test it. If violation appears, reexamine the theory and propose new ones. 9
9 In a broad sense • Hypothesis (theory) proposed. (Sometimes predictions also made.) • Experiment conducted to test it. • If violation appears, reexamine the theory and propose new ones. Natural sciences

In a broad sense Natural Product design and sciences experiments ·Hypothesis(theory) Design and Analysis proposed.(Sometimes of Experiments predictions also made.) Experiment conducted to test it. If violation appears, reexamine the theory and ghih Edaio网 DOUGLAS C MONTGOMERY propose new ones. International Student Version 10
Product design and experiments 10 In a broad sense • Hypothesis (theory) proposed. (Sometimes predictions also made.) • Experiment conducted to test it. • If violation appears, reexamine the theory and propose new ones. Natural sciences
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 香港中文大学:Efficient protocols for generating bipartite classical distributions and quantum states.pptx
- 香港中文大学:Fourier sparsity, spectral norm, and the Log-rank conjecture(long).pptx
- 香港中文大学:Fourier sparsity, spectral norm, and the Log-rank conjecture(short).pptx
- 香港中文大学:Fast quantum algorithms for Least Squares Regression and Statistic Leverage Scores.pptx
- 香港中文大学:Sensitivity Conjecture and Log-rank Conjecture for functions with small alternating numbers.pptx
- 香港中文大学:Networked Fairness in Cake Cutting.pptx
- 《金陵科技学院学报》:高形变二维码识别算法设计与实现.pdf
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末考试样题.doc
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)TSS示例程序.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)TSS软件栈 TSS-TCG Software Stack.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第6讲 可信启动.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第6章 TPM核心功能.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第6讲 可信计算基础.pptx
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第4讲 公钥基础设施(PKI).ppt
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三讲 认证技术与数字签名.ppt
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 密码学技术.ppt
- 东北大学:《可信计算基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一章 概述(主讲:周福才).pptx
- 东北大学:《信息安全专业概论与职业发展》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一讲 浅析专业与兴趣(主讲:周福才).pptx
- 东北大学:《信息安全专业概论与职业发展》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三讲 信息安全专业规范.pptx
- 东北大学:《信息安全专业概论与职业发展》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二讲 信息安全概念、发展和现状.pptx
- 香港中文大学:A quantum protocol for sampling correlated equilibria unconditionally and without a mediator.pptx
- 香港中文大学:Quantum strategic game theory.ppt
- 香港中文大学:On the power of lower bound methods for quantum one-way communication complexity.ppt
- 香港中文大学:An Introduction to Quantum Computing in Theoretical Computer Science.ppt
- 香港中文大学:Random Walk on Graphs and its Algorithmic Applications.ppt
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Sample space and probability.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Sample space and probability.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Discrete random variables.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Discrete random variables.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Further Topics on Random Variables.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Further Topics on Random Variables.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)General random variables.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Limit Theorems.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Limit Theorems.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Bayesian Statistical Inference.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Bayesian Statistical Inference.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Classical Statistical Inference.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)General random variables.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Classical Statistical Inference.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 1:Sample Space and Probability 1.pdf
