斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 10 ADVERSE SELECTION IN REAL MARKETS

CHAPTER 10 ADVERSE SELECTION IN REAL MARKETS
CHAPTER 10 ADVERSE SELECTION IN REAL MARKETS

Intro Recall our example:a man walks into the office of a life insurance company. He wants to buy a $1 million life insurance policy for a term of one day.Your company will have to pay $1 million to his heirs if and only if he dies tomorrow. You know nothing else about this man. How much do you charge? Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Intro Recall our example: a man walks into the office of a life insurance company. He wants to buy a $1 million life insurance policy for a term of one day. Your company will have to pay $1 million to his heirs if and only if he dies tomorrow. You know nothing else about this man. How much do you charge?

PREDICTIONS OF ASYMMETRIC INFORMATION MODELS Ch 10|Adverse selection in real markets
Ch 10 | Adverse selection in real markets PREDICTIONS OF ASYMMETRIC INFORMATION MODELS

Asymmetric information models make three predictions about these markets )Positive correlation between risk and coverage 2 Bulk markups 3) Adverse selection death spiral Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Asymmetric information models make three predictions about these markets 1) Positive correlation between risk and coverage 2) Bulk markups 3) Adverse selection death spiral
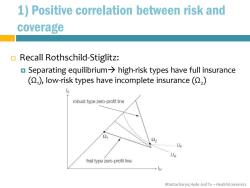
1)Positive correlation between risk and coverage Recall Rothschild-Stiglitz: Separating equilibrium>high-risk types have full insurance (Q,),low-risk types have incomplete insurance() robust type zero-profit line 22 ------.UE UR frail type zero-profit line Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics 1) Positive correlation between risk and coverage Recall Rothschild-Stiglitz: Separating equilibrium→ high-risk types have full insurance (Ω1 ), low-risk types have incomplete insurance (Ω2 )

2)Bulk markups Bulk discounts-a lower per-unit price for a large purchase of a commodity Bulk markups-a higher per-unit price for large purchases of a commodity Insurance companies use bulk markups to protect themselves from risk customers who want a lot of insurance This is exactly what the Rothschild-Stiglitz model predicts Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics 2) Bulk markups Bulk discounts– a lower per-unit price for a large purchase of a commodity Bulk markups– a higher per-unit price for large purchases of a commodity Insurance companies use bulk markups to protect themselves from risk customers who want a lot of insurance This is exactly what the Rothschild-Stiglitz model predicts
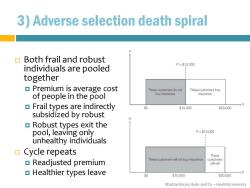
3)Adverse selection death spiral Both frail and robust P=s10.000 individuals are pooled together Premium is average cost These customere do not These customers buy of people in the pool buy insurance insurance Frail types are indirectly X $0 $10.000 $20,000 subsidized by robust Robust types exit the pool,leaving only P=$15,000 unhealthy individuals Cycle repeats These customers Readjusted premium These customers will not buy insurance st训w面 Healthier types leave $10,000 s20.000 Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics 3) Adverse selection death spiral Both frail and robust individuals are pooled together Premium is average cost of people in the pool Frail types are indirectly subsidized by robust Robust types exit the pool, leaving only unhealthy individuals Cycle repeats Readjusted premium Healthier types leave

ADVERSE SELECTION IN HEALTH INSURANCE Ch 10 Adverse Selection in Real Markets
Ch 10 | Adverse Selection in Real Markets ADVERSE SELECTION IN HEALTH INSURANCE

Empirical evidence foradverse selection in health insurance markets G RAND HIE Individuals are able to predict their health care costs for the year to a good degree of accuracy Specifically,they are able to predict health care costs more accurately than insurance companies Families with high predicted costs were more likely to want supplemental insurance Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Empirical evidence for adverse selection in health insurance markets RAND HIE Individuals are able to predict their health care costs for the year to a good degree of accuracy Specifically, they are able to predict health care costs more accurately than insurance companies Families with high predicted costs were more likely to want supplemental insurance

Empirical evidence foradverse selection in health insurance markets Several studies find a positive risk-coverage correlation in various markets Brown and Finkelstein 2009(elderly US Medicare beneficiaries) Van de Ven and van Vliet 1995(Dutch supplemental private insurance) Cutler and Zeckhauser 1998(Harvard professors) Spenkuch 2012(low-income Mexican families) Cardon and Hendel 2001(young graduates joining US workforce) Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Empirical evidence for adverse selection in health insurance markets Several studies find a positive risk-coverage correlation in various markets Brown and Finkelstein 2009 (elderly US Medicare beneficiaries) Van de Ven and van Vliet 1995 (Dutch supplemental private insurance) Cutler and Zeckhauser1998 (Harvard professors) Spenkuch 2012 (low-income Mexican families) Cardon and Hendel 2001 (young graduates joining US workforce)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 01 WHY HEALTH ECONOMICS?.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 9 Adverse Selection - The Rothschild-Stiglitz Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 8 Adverse Selection - Akerlof’s Market for Lemons.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 7 Demand for Insurance.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 6 The Hospital Industry.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 5 The Labor Market for Physicians.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 4 Socioeconomic Disparities in Health.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 3 Demand for Health:The Grossman Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 24 Time Inconsistency and Health.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 23 Prospect Theory.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 22 Obesity.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 21 Economic Epidemiology.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 20 The Economics of Health Externalities.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 2 Demand for Health Care.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 19 Population Aging and the Future of Health Policy.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 18 The American Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 17 The Bismarck Model - Social Health Insurance.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 16 The Beveridge Model - Nationalized Health Care.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 15 The Health Policy Conundrum.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 14 Health Technology Assessment.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 11 MORAL HAZARD.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 12 PHARMACEUTICALS AND THE ECONOMICS OF INNOVATION.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 13 TECHNOLOGY AND THE PRICE OF HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 14 HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 15 THE HEALTH POLICY CONUNDRUM.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 16 THE BEVERIDGE MODEL - NATIONALIZED HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 17 THE BISMARCK MODEL - SOCIAL HEALTH INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 18 THE AMERICAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 19 POPULATION AGING AND THE FUTURE OF HEALTH POLICY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 02 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 20 THE ECONOMICS OF HEALTH EXTERNALITIES.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 21 ECONOMIC EPIDEMIOLOGY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 22 OBESITY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 23 PROSPECT THEORY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 24 TIME INCONSISTENCY AND HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 03 CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH:THE GROSSMAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 04 SOCIOECONOMIC DISPARITIES IN HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 05 THE PHYSICIAN LABOR MARKET.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 06 THE HOSPITAL INDUSTRY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 07 DEMAND FOR INSURANCE.ppt
