斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 02 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE

CHAPTER 2 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE
CHAPTER 2 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE
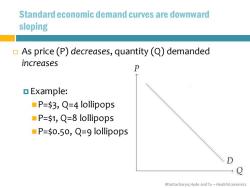
Standard economic demand curves are downward sloping As price(P)decreases,quantity (Q)demanded increases ▣Example: ■P=3,Q=4 lollipops ■P=$1,Q=8 lollipops P=50.50,Q=9 lollipops Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Standard economic demand curves are downward sloping As price (P) decreases, quantity (Q) demanded increases Example: ◼P=$3, Q=4 lollipops ◼P=$1, Q=8 lollipops ◼P=$0.50, Q=9 lollipops
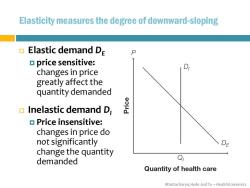
Elasticity measures the degree of downward-sloping Elastic demand DE a price sensitive: changes in price greatly affect the quantity demanded Inelastic demand D Price insensitive: changes in price do not significantly DE change the quantity demanded Q Quantity of health care Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Elasticity measures the degree of downward-sloping Elastic demand DE price sensitive: changes in price greatly affect the quantity demanded Inelastic demand DI Price insensitive: changes in price do not significantly change the quantity demanded

Does the demand curve for health care slope downward? Are people sensitive to the price of health care? Is demand for vaccines such that... ■P=5100,Q=1,000 ■P=51,Q=1,000 i.e.demand is inelastic? Is demand for band-aids such that... ■P=$100,Q=1 ■P=$1,Q=30 i.e.demand is elastic? If people always obey their doctors,then demand should be inelastic! Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Does the demand curve for health care slope downward? Are people sensitive to the price of health care? Is demand for vaccines such that… ◼ P = $100, Q=1,000 ◼ P = $1, Q=1,000 ◼ i.e. demand is inelastic? Is demand for band-aids such that… ◼ P = $100, Q = 1 ◼ P = $1, Q = 30 ◼ i.e. demand is elastic? If people always obey their doctors, then demand should be inelastic!

Need randomized experiments Randomized experiments: Definition:a study that assigns treatments randomly to different groups of study participants Includes: A control group(no treatment) ■Placebo group Helps generate experimental groups that are statistically similar to each other Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Need randomized experiments Randomized experiments: Definition: a study that assigns treatments randomly to different groups of study participants Includes: ◼A control group (no treatment) ◼Placebo group Helps generate experimental groups that are statistically similar to each other
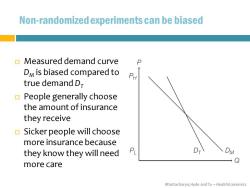
Non-randomized experiments can be biased Measured demand curve P DM is biased compared to PH true demand D People generally choose the amount of insurance they receive Sicker people will choose more insurance because they know they will need PL DM Q more care Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Non-randomized experiments can be biased Measured demand curve DM is biased compared to true demand DT People generally choose the amount of insurance they receive Sicker people will choose more insurance because they know they will need more care

Evidence from Randomized Experiments
Evidence from Randomized Experiments

Two Randomized Experiments RAND Health Insurance Experiment (HIE) Oregon Medicaid Experiment Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Two Randomized Experiments RAND Health Insurance Experiment (HIE) Oregon Medicaid Experiment

RAND HIE Randomly assigned 2,o00 families from six US cities to different insurance coverage plans Copayments groups: ■Free,25%,50%,and95% Tracked utilization of health care (Q)in each copayment plan(P) Copayment acts as the marginal cost that each family faces when buying care Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics RAND HIE Randomly assigned 2,000 families from six US cities to different insurance coverage plans Copayments groups: ◼Free, 25%, 50%, and 95% Tracked utilization of health care (Q) in each copayment plan (P) Copayment acts as the marginal cost that each family faces when buying care

Oregon Medicaid Experiment Compared two groups of low-income adults Medicaid lottery winners vs.lottery losers Lottery winners got to apply for public health insurance through Medicaid So they faced lower out-of-pocket prices for care Lottery losers could not get Medicaid (but might have purchased outside insurance) Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Oregon Medicaid Experiment Compared two groups of low-income adults Medicaid lottery winners vs. lottery losers Lottery winners got to apply for public health insurance through Medicaid So they faced lower out-of-pocket prices for care Lottery losers could not get Medicaid (but might have purchased outside insurance)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 19 POPULATION AGING AND THE FUTURE OF HEALTH POLICY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 18 THE AMERICAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 17 THE BISMARCK MODEL - SOCIAL HEALTH INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 16 THE BEVERIDGE MODEL - NATIONALIZED HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 15 THE HEALTH POLICY CONUNDRUM.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 14 HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 13 TECHNOLOGY AND THE PRICE OF HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 12 PHARMACEUTICALS AND THE ECONOMICS OF INNOVATION.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 11 MORAL HAZARD.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 10 ADVERSE SELECTION IN REAL MARKETS.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 01 WHY HEALTH ECONOMICS?.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 9 Adverse Selection - The Rothschild-Stiglitz Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 8 Adverse Selection - Akerlof’s Market for Lemons.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 7 Demand for Insurance.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 6 The Hospital Industry.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 5 The Labor Market for Physicians.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 4 Socioeconomic Disparities in Health.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 3 Demand for Health:The Grossman Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 24 Time Inconsistency and Health.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 23 Prospect Theory.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 20 THE ECONOMICS OF HEALTH EXTERNALITIES.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 21 ECONOMIC EPIDEMIOLOGY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 22 OBESITY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 23 PROSPECT THEORY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 24 TIME INCONSISTENCY AND HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 03 CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH:THE GROSSMAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 04 SOCIOECONOMIC DISPARITIES IN HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 05 THE PHYSICIAN LABOR MARKET.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 06 THE HOSPITAL INDUSTRY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 07 DEMAND FOR INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 08 ADVERSE SELECTION - AKERLOF’S MARKET FOR LEMONS.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 09 ADVERSE SELECTION - THE ROTHSCHILD-STIGLITZ MODEL.ppt
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(教案大纲)教学大纲 Microeconomics(负责人:李新文).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(教案大纲)微观经济学授课教案(打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(案例分析)微观经济学教学案例(打印版).pdf
- 《微观经济学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)西方经济学名著选读.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)微观经济学各章习题库及参考答案(打印版,共十一章).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)微观经济学试题(A卷)试卷(打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)微观经济学试卷(A卷)答案(打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第一章 导论(负责人:李新文).pdf
