斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 13 TECHNOLOGY AND THE PRICE OF HEALTH CARE

CH.13 TECHNOLOGY AND THE PRICE OF HEALTH CARE
CH. 13 TECHNOLOGY AND THE PRICE OF HEALTH CARE
Health care costs are rising Health care costs have increased faster than inflation for decades ▣1960: the typical American spent 1/20 of her income on medical care ▣2010: 1 in every 6 dollars of the American economy is spent on medical care This amounts to a total of $2.6 trillion and $8,402 per person Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Health care costs are rising Health care costs have increased faster than inflation for decades 1960: ◼ the typical American spent 1/20 of her income on medical care 2010: ◼ 1 in every 6 dollars of the American economy is spent on medical care ◼ This amounts to a total of $2.6 trillion and $8,402 per person
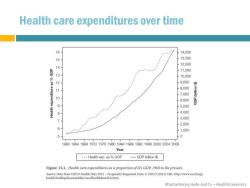
Health care expenditures over time 6 14.000 13.000 54821 12.000 11.000 10.000 9.000 8.000 7.000 098 6.000 5.000 4.000 3.000 7 2.000 1.000 0 1960196419681972197619801984198819921996200020042008 Year ---Health exp.as GDP -GDP (billion$周 Figure 13.1.Health care expenditures as a proportion ofUS GDP 1960 to the present Source:Data from OECD Health Data 2012-Frequently Requested Data.OECD(2012)URL:http://www.oecdong/ Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Health care expenditures over time

What are health care costs? When we speak of "health care costs,"we really mean total health expenditures Equation for medical expenditures E: E=P·Q E is expenditures on medical care P is the price of medical care Q is the quantity of medical care Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics What are health care costs? When we speak of “health care costs,” we really mean total health expenditures Equation for medical expenditures E: E = P · Q ◼ E is expenditures on medical care ◼ P is the price of medical care ◼ Q is the quantity of medical care

E=PXQ Hypotheses to explain rising expenditures: Prices have increased Quantity demanded has increased Technological innovations and technological overuse Rest of this chapter explores each one of these hypotheses Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics E = P x Q Hypotheses to explain rising expenditures: Prices have increased Quantity demanded has increased Technological innovations and technological overuse Rest of this chapter explores each one of these hypotheses

Quantity may be increasing An aging population people demand more health care as they age A richer population rising incomes lead to more health care consumption More insurance coverage More insurance reduces out-of-pocket prices to patients of obtaining medical care Increasing quality of medical care each dollar spent on health care generates a higher marginal health benefit,so demand for health care increases Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Quantity may be increasing An aging population people demand more health care as they age A richer population rising incomes lead to more health care consumption More insurance coverage More insurance reduces out-of-pocket prices to patients of obtaining medical care Increasing quality of medical care each dollar spent on health care generates a higher marginal health benefit, so demand for health care increases

Are rising costs a bad thing? If rising costs are due to rising demand rising health care costs is not necessarily a bad thing People are not necessarily worse off If rising costs are due to rising prices Rising costs does harm consumers Health is getting more expensive to produce,so people will either have to cut back on health care or spend more money to stay healthy Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Are rising costs a bad thing? If rising costs are due to rising demand rising health care costs is not necessarily a bad thing People are not necessarily worse off If rising costs are due to rising prices Rising costs does harm consumers Health is getting more expensive to produce, so people will either have to cut back on health care or spend more money to stay healthy

Prices may be rising,because... Increased resource costs Less competitive markets Hospital mergers may have made the market more monopolistic Expensive new technology if modern medical care routinely incorporates new, expensive technologies like MRI machines,the price of treating many ailments will rise Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Prices may be rising, because… Increased resource costs Less competitive markets Hospital mergers may have made the market more monopolistic Expensive new technology if modern medical care routinely incorporates new, expensive technologies like MRI machines, the price of treating many ailments will rise

Medical inflation A medical care consumer price index(CPI) measures changes in the price level for medical goods and services Medical inflation:a rise in the price level for medical goods and services A medical care CPI can tell us how much more it costs this year to buy the same things we bought last year Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Medical inflation A medical care consumer price index (CPI) measures changes in the price level for medical goods and services Medical inflation: a rise in the price level for medical goods and services A medical care CPI can tell us how much more it costs this year to buy the same things we bought last year
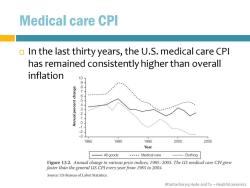
Medical care CPI In the last thirty years,the U.S.medical care CPl has remained consistently higher than overall inflation 10 9 8 65 4 0 2 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 Year All goods -----Medical care …Clothing Figure 13.2.Annual change in various price indices,1985-2003.The US medical care CPI grew faster than the general US CPI every year from 1985 to 2003. Source:US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Medical care CPI In the last thirty years, the U.S. medical care CPI has remained consistently higher than overall inflation
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 12 PHARMACEUTICALS AND THE ECONOMICS OF INNOVATION.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 11 MORAL HAZARD.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 10 ADVERSE SELECTION IN REAL MARKETS.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 01 WHY HEALTH ECONOMICS?.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 9 Adverse Selection - The Rothschild-Stiglitz Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 8 Adverse Selection - Akerlof’s Market for Lemons.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 7 Demand for Insurance.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 6 The Hospital Industry.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 5 The Labor Market for Physicians.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 4 Socioeconomic Disparities in Health.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 3 Demand for Health:The Grossman Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 24 Time Inconsistency and Health.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 23 Prospect Theory.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 22 Obesity.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 21 Economic Epidemiology.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 20 The Economics of Health Externalities.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 2 Demand for Health Care.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 19 Population Aging and the Future of Health Policy.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 18 The American Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 17 The Bismarck Model - Social Health Insurance.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 14 HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 15 THE HEALTH POLICY CONUNDRUM.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 16 THE BEVERIDGE MODEL - NATIONALIZED HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 17 THE BISMARCK MODEL - SOCIAL HEALTH INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 18 THE AMERICAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 19 POPULATION AGING AND THE FUTURE OF HEALTH POLICY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 02 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 20 THE ECONOMICS OF HEALTH EXTERNALITIES.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 21 ECONOMIC EPIDEMIOLOGY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 22 OBESITY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 23 PROSPECT THEORY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 24 TIME INCONSISTENCY AND HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 03 CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH:THE GROSSMAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 04 SOCIOECONOMIC DISPARITIES IN HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 05 THE PHYSICIAN LABOR MARKET.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 06 THE HOSPITAL INDUSTRY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 07 DEMAND FOR INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 08 ADVERSE SELECTION - AKERLOF’S MARKET FOR LEMONS.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 09 ADVERSE SELECTION - THE ROTHSCHILD-STIGLITZ MODEL.ppt
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(教案大纲)教学大纲 Microeconomics(负责人:李新文).pdf
