斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 03 CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH:THE GROSSMAN MODEL

CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH: THE GROSSMAN MODEL
CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH: THE GROSSMAN MODEL

Intro Previously... Demand for health care is downward sloping People choose amount of health care they receive based on price People choose their health care,but do they choose their own health? Is health somethingthat happens to us?Or do we choose it? We use the Grossman model to explore this question Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Intro Previously… Demand for health care is downward sloping People choose amount of health care they receive based on price People choose their health care, but do they choose their own health? Is health something that happens to us? Or do we choose it? We use the Grossman model to explore this question

The 3 Roles of Health (H) Health plays three roles in the Grossman model: 1.A consumption good 2.An input into production 3.A form of stock/capital (an investment) Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics The 3 Roles of Health (H) Health plays three roles in the Grossman model: 1. A consumption good 2. An input into production 3. A form of stock/capital (an investment)

Health as a consumption good
Health as a consumption good
Health as a direct input into utility Health as a consumption good enters directly into utility 口 Single-period Utility at time t U=U(Hy Z) H level of health ▣Zt=“home good” Everything non-health that contributes to utility E.g.video games,time with friends,movie tickets **Note:health health care Health care is not explicitly in the utility function i.e.Getting vaccines does not provide utility but staying healthy does Health as a consumption good Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Health as a direct input into utility Health as a consumption good enters directly into utility Single-period Utility at time t Ut= U(Ht , Zt ) Ht = level of health Zt= “home good” ◼ Everything non-health that contributes to utility ◼ E.g. video games, time with friends, movie tickets **Note: health ≠ health care Health care is not explicitly in the utility function ◼ i.e. Getting vaccines does not provide utility but staying healthy does Health as a consumption good

Time constraints in the Grossman model In a single period,there are only 24 hours in a day to contribute to your utility: Θ=24=TW+TZ+TH+TS Divide total time between: Working Tw Playing TZ Improving health TH Being sick TS Health as a consumption good Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Time constraints in the Grossman model In a single period, there are only 24 hours in a day to contribute to your utility: Θ = 24 = TW + TZ + TH + TS Divide total time Θ between: Working TW Playing TZ Improving health TH Being sick TS Health as a consumption good
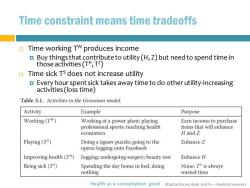
Time constraint means time tradeoffs 口 Time working TW produces income Buy things that contribute to utility(H,Z)but need to spend time in those activities(TH,TZ) Time sick TS does not increase utility Every hour spent sick takes away time to do other utility-increasing activities(loss time) Table 3.1.Activities in the Grossman model. Activity Example Purpose Working(TW) Working at a power plant;playing Earn income to purchase professional sports;teaching health items that will enhance economics H and Z Playing(TZ) Doing a jigsaw puzzle;going to the Enhance Z opera;logging onto Facebook Improving health(T#) Jogging;undergoing surgery;beauty rest Enhance H Being sick(TS) Spending the day home in bed,doing None;T's is always nothing wasted time Health as a consumption good Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Time constraint means time tradeoffs Time working TW produces income Buy things that contribute to utility (H, Z) but need to spend time in those activities (TH, TZ ) Time sick TS does not increase utility Every hour spent sick takes away time to do other utility-increasing activities (loss time) Health as a consumption good
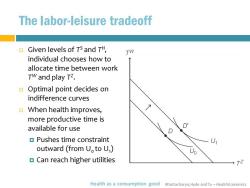
The labor-leisure tradeoff Given levels of TS and TH, Tw individual chooses how to allocate time between work TW and play TZ. Optimal point decides on indifference curves When health improves, more productive time is D available for use D Pushes time constraint U outward (from U.to U) Uo Can reach higher utilities TZ Health as a consumption good Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics The labor-leisure tradeoff Given levels of T S and T H , individual chooses how to allocate time between work T W and play T Z . Optimal point decides on indifference curves When health improves, more productive time is available for use Pushes time constraint outward (from U0 to U1 ) Can reach higher utilities Health as a consumption good

Health as an input into production
Health as an input into production

The three roles of health (H) Health plays three roles in the Grossman model: A consumption good 2.An input into production Of health(H) Of productive time(TP) 3.A form of stock/capital (an investment) Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics The three roles of health (H) Health plays three roles in the Grossman model: 1. A consumption good 2. An input into production Of health (H) Of productive time (TP ) 3. A form of stock/capital (an investment)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 24 TIME INCONSISTENCY AND HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 23 PROSPECT THEORY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 22 OBESITY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 21 ECONOMIC EPIDEMIOLOGY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 20 THE ECONOMICS OF HEALTH EXTERNALITIES.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 02 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 19 POPULATION AGING AND THE FUTURE OF HEALTH POLICY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 18 THE AMERICAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 17 THE BISMARCK MODEL - SOCIAL HEALTH INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 16 THE BEVERIDGE MODEL - NATIONALIZED HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 15 THE HEALTH POLICY CONUNDRUM.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 14 HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 13 TECHNOLOGY AND THE PRICE OF HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 12 PHARMACEUTICALS AND THE ECONOMICS OF INNOVATION.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 11 MORAL HAZARD.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 10 ADVERSE SELECTION IN REAL MARKETS.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 01 WHY HEALTH ECONOMICS?.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 9 Adverse Selection - The Rothschild-Stiglitz Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 8 Adverse Selection - Akerlof’s Market for Lemons.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 7 Demand for Insurance.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 04 SOCIOECONOMIC DISPARITIES IN HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 05 THE PHYSICIAN LABOR MARKET.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 06 THE HOSPITAL INDUSTRY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 07 DEMAND FOR INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 08 ADVERSE SELECTION - AKERLOF’S MARKET FOR LEMONS.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 09 ADVERSE SELECTION - THE ROTHSCHILD-STIGLITZ MODEL.ppt
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(教案大纲)教学大纲 Microeconomics(负责人:李新文).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(教案大纲)微观经济学授课教案(打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(案例分析)微观经济学教学案例(打印版).pdf
- 《微观经济学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)西方经济学名著选读.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)微观经济学各章习题库及参考答案(打印版,共十一章).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)微观经济学试题(A卷)试卷(打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)微观经济学试卷(A卷)答案(打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第一章 导论(负责人:李新文).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第二章 需求曲线和供给曲线以及均衡价格(供给需求和均衡价格).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第三章 效用论.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第四章 生产论.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第五章 成本论.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第七章 不完全竞争的市场.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《微观经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第八章 生产要素价格的决定.pdf
