斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 12 PHARMACEUTICALS AND THE ECONOMICS OF INNOVATION

CHAPTER 12 PHARMACEUTICALS AND THE ECONOMICS OF INNOVATION
CHAPTER 12 PHARMACEUTICALS AND THE ECONOMICS OF INNOVATION

Intro The pharmaceutical industry got its start in 1899, when Bayer,a German chemical company, introduced a painkiller called aspirin Today,the pharmaceutical industry is massive but tightly regulated This industry is an ideal setting to study both the economics of innovation and the economics of regulation. Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Intro The pharmaceutical industry got its start in 1899, when Bayer, a German chemical company, introduced a painkiller called aspirin Today, the pharmaceutical industry is massive but tightly regulated This industry is an ideal setting to study both the economics of innovation and the economics of regulation

THE LIFE CYCLE OF A DRUG Ch 12 I Pharmaceuticals and the economics of innovation
Ch 12 | Pharmaceuticals and the economics of innovation THE LIFE CYCLE OF A DRUG

The life cycle of a drug Find chemical compound that might treat a disease Then,test it on animals to show it is not toxic Then,test on humans in three phases Phase 1:low dose to healthy individuals(-2 years) Phase 2:dose to unhealthy individuals(-2 years) Phase 3:test effectiveness in preventing disease or medical conditions(~-3-4 years) Get approved for sale by FDA or similar body Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics The life cycle of a drug Find chemical compound that might treat a disease Then, test it on animals to show it is not toxic Then, test on humans in three phases Phase 1: low dose to healthy individuals (~2 years) Phase 2: dose to unhealthy individuals (~2 years) Phase 3: test effectiveness in preventing disease or medical conditions(~3-4 years) Get approved for sale by FDA or similar body

The life cycle of a drug Once the drug is approved for sale,the drug company has a temporary legal monopoly protected by a patent(17 years in the US) This is the company's chance to recoup the millions of dollars spent on testing After that time is up,other companies can produce the same drug cheaply and profits decrease sharply Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics The life cycle of a drug Once the drug is approved for sale, the drug company has a temporary legal monopoly protected by a patent (17 years in the US) This is the company’s chance to recoup the millions of dollars spent on testing After that time is up, other companies can produce the same drug cheaply and profits decrease sharply

DRUG DEVELOPMENT Ch 12 Pharmaceuticals and the economics of innovation
Ch 12 | Pharmaceuticals and the economics of innovation DRUG DEVELOPMENT

Drug development is costly Hard to find a promising chemical in the first place Only 21.5%of drugs that enter Phase I pass to Phase Ill The whole process can cost $500 million or more to bring a drug to the point of approval Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics Drug development is costly Hard to find a promising chemical in the first place Only 21.5% of drugs that enter Phase I pass to Phase III The whole process can cost $500 million or more to bring a drug to the point of approval

PATENTS Ch 12 Pharmaceuticals and the economics of innovation
Ch 12 | Pharmaceuticals and the economics of innovation PATENTS

How do we induce companies to make these costly investments? Patents create a legal monopoly and hence the opportunity for monopoly profits In practice,only the top 30%of drugs pay for themselves Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics How do we induce companies to make these costly investments? Patents create a legal monopoly and hence the opportunity for monopoly profits In practice, only the top 30% of drugs pay for themselves
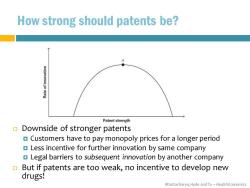
How strong should patents be? Patent strength Downside of stronger patents Customers have to pay monopoly prices for a longer period Less incentive for further innovation by same company Legal barriers to subsequent innovation by another company But if patents are too weak,no incentive to develop new drugs! Bhattacharya,Hyde and Tu-HealthEconomics
Bhattacharya, Hyde and Tu – Health Economics How strong should patents be? Downside of stronger patents Customers have to pay monopoly prices for a longer period Less incentive for further innovation by same company Legal barriers to subsequent innovation by another company But if patents are too weak, no incentive to develop new drugs!
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 11 MORAL HAZARD.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 10 ADVERSE SELECTION IN REAL MARKETS.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 01 WHY HEALTH ECONOMICS?.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 9 Adverse Selection - The Rothschild-Stiglitz Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 8 Adverse Selection - Akerlof’s Market for Lemons.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 7 Demand for Insurance.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 6 The Hospital Industry.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 5 The Labor Market for Physicians.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 4 Socioeconomic Disparities in Health.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 3 Demand for Health:The Grossman Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 24 Time Inconsistency and Health.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 23 Prospect Theory.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 22 Obesity.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 21 Economic Epidemiology.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 20 The Economics of Health Externalities.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 2 Demand for Health Care.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 19 Population Aging and the Future of Health Policy.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 18 The American Model.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 17 The Bismarck Model - Social Health Insurance.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,英文版)课后判断题及答案 Ch 16 The Beveridge Model - Nationalized Health Care.pdf
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 13 TECHNOLOGY AND THE PRICE OF HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 14 HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 15 THE HEALTH POLICY CONUNDRUM.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 16 THE BEVERIDGE MODEL - NATIONALIZED HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 17 THE BISMARCK MODEL - SOCIAL HEALTH INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 18 THE AMERICAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 19 POPULATION AGING AND THE FUTURE OF HEALTH POLICY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 02 DEMAND FOR HEALTH CARE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 20 THE ECONOMICS OF HEALTH EXTERNALITIES.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 21 ECONOMIC EPIDEMIOLOGY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 22 OBESITY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 23 PROSPECT THEORY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 24 TIME INCONSISTENCY AND HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 03 CHAPTER 3 DEMAND FOR HEALTH:THE GROSSMAN MODEL.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 04 SOCIOECONOMIC DISPARITIES IN HEALTH.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 05 THE PHYSICIAN LABOR MARKET.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 06 THE HOSPITAL INDUSTRY.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 07 DEMAND FOR INSURANCE.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 08 ADVERSE SELECTION - AKERLOF’S MARKET FOR LEMONS.ppt
- 斯坦福卫生经济学教材(Health Economics)杰伊·巴塔查里亚《健康经济学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 09 ADVERSE SELECTION - THE ROTHSCHILD-STIGLITZ MODEL.ppt
