《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)热功转换及可用能
5.2 Translation between Work and Heat 5.2.1 The First Law of thermodynamics Conservation and transformation of energy Do the process according with the First Law can occur spontaneously spontaneous process: A process which can occur automatically without any outside effect In nature,the spontaneous processes exist direction
5.2.1 The First Law of thermodynamics Conservation and transformation of energy Do the process according with the First Law can occur spontaneously ? 5.2 Translation between Work and Heat spontaneous process: A process which can occur automatically without any outside effect In nature, the spontaneous processes exist direction

Produce heat by friction Power plant Work Heat Work Heat 100% 40% Spontaneous process exists direction, condition and bounds. How do we describe the dir ertion,conditions and bounds of Spontaneous prccess The Second Law of Thermodynamics
Spontaneous process exists direction, condition and bounds. Heat Power plant Work 40% Produce heat by friction Heat 100% Work How do we describe the direction, conditions and bounds of Spontaneous process The Second Law of Thermodynamics

5.2.2 The Second Law of thermodynamics Statements of the Second Law There are 60-70 statements of the Second Law in 1851 Kelvin-Planck Statement according to transformation of work and heat No apparatus can operate in such a way that its only effect is to convert heat absorbed by a system completely into work done by the system. im1850 Clausius statement according to heat transfer No process is possible which consists solely in the transfer of heat from one temperature level to a higher one
Statements of the Second Law There are 60-70 statements of the Second Law in 1850 Clausius statement according to heat transfer No process is possible which consists solely in the transfer of heat from one temperature level to a higher one 5.2.2 The Second Law of thermodynamics in 1851 Kelvin -Planck Statement according to transformation of work and heat No apparatus can operate in such a way that its only effect is to convert heat absorbed by a system completely into work done by the system

热力学第二定律 开尔文说法:不可能从单一热源吸热使之完全变为 有用的功而不引起其他变化。 ·克劳修斯说法:热不可能自动从低温物体传给高温 物体
热力学第二定律 • 开尔文说法:不可能从单一热源吸热使之完全变为 有用的功而不引起其他变化。 • 克劳修斯说法:热不可能自动从低温物体传给高温 物体

第二类永动机??? 如果三峡水电站用降温法发电,使水 温降低5C,发电能力可提高11.7倍。 设mkg水的位差为180米 重力势能转化为电能: 21000 E=mgh=1800m[J] 2=11.7 E 1800 mkg水降低5C放热: Q=cm△t=21000m[J]
第二类永动机??? 如果三峡水电站用降温法发电,使水 温降低 5 ° C,发电能力可提高11.7倍。 设m kg水的位差为180 米 重力势能转化为电能: E = = mgh m J 1800 [ ] mkg水降低 5 ° C放热: Q cm t m J = Δ= 21000 [ ] 21000 11.7 1800 Q m E m = =
两种表述的关系 开尔文一普朗克 克劳修斯表述: 表述 完全等效! 违反一种表述,必违反另一种表述!
两种表述的关系 开尔文-普朗克 表述 完全等效!!! 克劳修斯表述 : 违反一种表述 ,必违反另一种表述!!!

Spontaneous process exists direction, condition and bounds. 22 How much can the thermal efficiency achieve? What influence the thermal efficiency?
Spontaneous process exists direction, condition and bounds. How much can the thermal efficiency achieve? What influence the thermal efficiency?
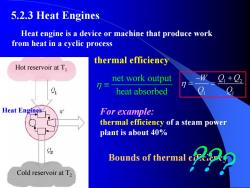
5.2.3 Heat Engines Heat engine is a device or machine that produce work from heat in a cyclic process thermal efficiency Hot reservoir at T net work output heat absorbed Heat Engines For example: thermal efficiency of a steam power plant is about 40% Bounds of thermal Cold reservoir at T2
For example: thermal efficiency of a steam power plant is about 40% 1 2 1 1 W Q Q Q Q η − + = = Hot reservoir at T1 Cold reservoir at T2 Heat Engines Heat engine is a device or machine that produce work from heat in a cyclic process thermal efficiency Bounds of thermal efficiency 5.2.3 Heat Engines net work output heat absorbed η ≡

5.2.4 Carnot's Theorem For two given heat reservoirs no engine can have a thermal efficiency higher than that of a Carnot engine.The thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine depends only on the temperature levels and not upon the working substance of the engine. Carnot efficiency -W 7= =1- T For two given heat reservoirs no engine can have a thermal efficiency higher than that of a Carnot engine. T
5.2.4 Carnot’s Theorem : For two given heat reservoirs no engine can have a thermal efficiency higher than that of a Carnot engine. The thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine depends only on the temperature levels and not upon the working substance of the engine. T1 T2 Rc Q1 Q2 W Carnot efficiency For two given heat reservoirs no engine can have a thermal efficiency higher than that of a Carnot engine. 1 2 1 1 T T Q W −= − η =

5.3 Entropy and Entropy Change 5.3.1 Entropy and theorem of entropy increasing This mathematical statement of the second law affirms that every proceeds in such a direction that the total entropy change associated with it is positive,the limiting value of zero being attained only by a reversible process.No process is possible for which the total entropy decreases. s≥ T for isolated system The entropy of an isolated system during a process always dS≥0 increase or,in the limiting case of a reversible process,remains theorem of entropy increasing constant
5.3 Entropy and Entropy Change 5.3.1 Entropy and theorem of entropy increasing T Q dS δ ≥ This mathematical statement of the second law affirms that every proceeds in such a direction that the total entropy change associated with it is positive, the limiting value of zero being attained only by a reversible process. No process is possible for which the total entropy decreases. dS ≥ 0 for isolated system theorem of entropy increasing The entropy of an isolated system during a process always increase or, in the limiting case of a reversible process, remains constant
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)溶液热力学原理 Solution thermodynamics:Theory.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)热动力 Production of Power from Heat.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)流体热力学性质 Thermodynamic properties of fluids.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)纯流体性质 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第8章 化学反应平衡(含答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第5章 非均相体系热力学性质计算(无答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第4章 非均相封闭体系热力学(选择题带答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第2章 流体的P-V-T关系(含答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第1章 绪言(无答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 13 Chemical-Reaction Equilibria.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 12 Solution Thermodynamics:Application.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 11 Solution thermodynamics - Theory.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 9 Refrigeration and Liquefaction.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 7 Application of Thermodynamics to Flow Processes.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 6 Thermodynamic properties of fluids.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 5 The Second Law of Thermodynamics.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 3 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 2 The First Law and Other Basic Concepts.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学大纲 Thermodynamics of chemical engineering(新疆大学:黄雪莉).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论 Chemical Engineering thermodynamics.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 流体的p-V-T关系.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 化工过程的能量分析.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 相平衡.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 流体的热力学性质.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第六章 蒸汽动力循环与制冷循环.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十章 化学反应平衡.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 流体混合物的热力学性质.ppt
- 《化工原理》课程教学大纲 Principles of Chemical Engineering B.pdf
- 《化学反应工程》课程教学标准B.doc
- 山东理工大学:《化学反应工程》课教学大纲B.doc
- 《化工安全与环保》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)物质性质、物化原理与安全.pdf
- 《化学反应工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第3章 釜式及均相管式反应器.ppt
- 《化学反应工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第4章 反应器中的混合及对反应的影响.ppt
- 《化学反应工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第5章 固定床气-固相催化反应工程.ppt
- 《化学反应工程》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 气-固相催化反应本征及宏观动力学.pdf
- 《化学反应工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第1章 应用化学反应动力学.ppt
- 《化工安全与环保》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第11章 化工环境保护技术.pdf
- 《化工安全与环保》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 化工厂安全操作与维护.pdf
- 《化工安全与环保》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 化工厂设计和装置安全.pdf
