《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 13 Chemical-Reaction Equilibria

Chapter 13 Chemical-Reaction Equilibria content 13.1 The Reaction Coordinate 13.2 Application of Equilibrium Criteria to Chemical Reactions 13.3 The Standard Gibbs-Energy Change and Equilibrium Constants 13.4 Effect of Temperature on EquilibriumConstants 13.5 Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants 13.6 Relation of Equilibrium Constant to Composition
Chapter 13 Chemical-Reaction Equilibria content 13.1 The Reaction Coordinate 13.2 Application of Equilibrium Criteria to Chemical Reactions 13.3 The Standard Gibbs-Energy Change and Equilibrium Constants 13.4 Effect of Temperature on EquilibriumConstants 13.5 Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants 13.6 Relation of Equilibrium Constant to Composition

13.1 The Reaction Coordinate The general chemical reaction A+A+.=4+A+. b,stoichiometric coefficient(化学计量系数) Positive(+)for products negative(-)for reactants For example CH4+H20→C0+3H2 veH,=-1H,0=-1H,=3ao=l dh_血_恤_恤-.=d血=dG :⅓V 典=s·血=吹 the reaction coordinate 4+4+.=4+l心A+. =v©-∫dm=jydc %=m°+yE0r△%=%-m°=y,E Summation over all species n=n+va The mole fractionyiyv nn+Ve Mutireaction stoichiomerry the stoichiometric number of species i in reactionj
13.1 The Reaction Coordinate The general chemical reaction 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 A A A A + + = + + i stoichiometric coefficient (化学计量系数 ) Positive(+) for products negative (-) for reactants For example CH4 + H2O →CO + 3H2 CH H O H CO 4 2 2 ν = − = − = = 1 1 3 1 ν ν ν 1 2 4 3 1 2 3 4 N N dn dn dn dn dn d = = = = = = i i dn d = → i i dn d = the reaction coordinate 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 A A A A + + = + + i i dn d = → 0 0 i i n i i n dn d = 0 i i i n n = + or 0 i i i i = − = n n n Summation over all species n n = + The mole fraction yi 0 i i i i n n y n n + = = + Mutireaction stoichiomerry i i,j j j 1 d ( ) n ν dε = = the stoichiometric number of species i in reaction j

Mutireaction stoichiomerry d血=∑)%=+∑F Summationoverall species=%+∑∑F Definition=∑,·n=%+∑"ys n+∑y) The mole fractionyi nn+∑ys 13.2 Application of Equilibrium Criteria to Chemical Reactions The direction of chemical reaction and equilibrium criteria is (dG)=0 The total Gibbs energy in relation to the reaction coordinate. At this equilibrium state [G]-0 Constant T and P G (dG')p=0 Ee The total Gibbs energy is a minimum
Mutireaction stoichiomerry i i,j j j 1 d ( ) n ν dε = = 0 i i i j j , j n n = + Summation over all species 0 ,i j j j i n n = + ↓ Definition j i j , i = → The mole fraction yi 0 i i j j , j i i j j j n n y n n + = = + 13.2 Application of Equilibrium Criteria to Chemical Reactions The direction of chemical reaction and equilibrium criteria is : ( ) , 0 t T P dG = The total Gibbs energy in relation to the reaction coordinate. At this equilibrium state , ( ) 0 t T P G = ( )T,P = 0 t dG Constant T and P ε G t e The total Gibbs energy is a minimum j j n n j = + 0
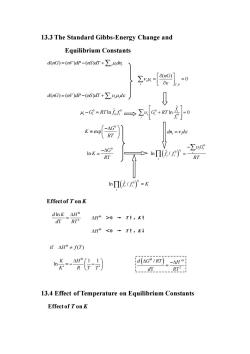
13.3 The Standard Gibbs-Energy Change and Equilibrium Constants dnG)=(nv)dP-(ns)dT+∑,4d d(nG)=(nV)dP-(nS)dT+>vuds 0 -AG° dn,=vds -△G -∑u,G RT oΠi1)° RT nΠi/e)=K Effect of Ton K △He>0→Tt,Kt △H<0+Tt,K if△H9≠fT) 炎}司 d(AGIRT-AH L.-.-RT2 13.4 Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Constants Effect of Ton K
13.3 The Standard Gibbs-Energy Change and Equilibrium Constants ( ) ( ) ( ) i i i d nG nV dP nS dT dn = − + , ( ) 0 i i i T P nG = = ( ) ( ) ( ) i i i d nG nV dP nS dT d = − + 0 0 / ˆ ln i i i i − = G RT f f 0 0 ˆ ln 0 i i i i i f G RT f + = 0 exp G K RT − i i dn d = 0 ln G K RT − = ( ) 0 ˆ 0 ln / i i i i i i i G f f RT − = ( ) ˆ 0 ln / i i i i f f K = Effect of T on K 2 ln T d K H d RT = >0 → T↑,K↑ <0 → T↑,K↓ 13.4 Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Constants Effect of T on K H H if ( ) H f T 1 1 ln K H K R T T = − − ( ) 2 / T d G RT H d RT − =
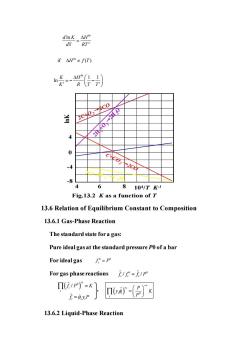
ifH≠fT) 火2c0/ y 2 -8 4 6 810/T1 Fig.13.2 K as a function of T 13.6 Relation of Equilibrium Constant to Composition 13.6.1 Gas-Phase Reaction The standard state for a gas: Pure ideal gas at the standard pressure P0 of a bar For idealgas/°-p For gas phase reactions=/p Π(i1P)°=K 广=0yP nIva- 13.6.2 Liquid-Phase Reaction
2 ln T d K H d RT = 2C+O2→2CO 2H2+O →2 2H2O C+CO2→2CO 2C+2H2→C2H4 lnK 104 /T K-1 0 -4 -8 4 4 6 8 Fig.13.2 K as a function of T 13.6 Relation of Equilibrium Constant to Composition 13.6.1 Gas-Phase Reaction The standard state for a gas: Pure ideal gas at the standard pressure P0 of a bar For ideal gas For gas phase reactions 13.6.2 Liquid-Phase Reaction if ( ) H f T 1 1 ln K H K R T T = − − 0 0 i f P = ˆ 0 0 ˆ / / i i i f f f P = ( ) ˆ 0 / i i i f P K = f ˆ i = ˆ i yiP ( ) 0 ˆ i v i i i P y K P − =
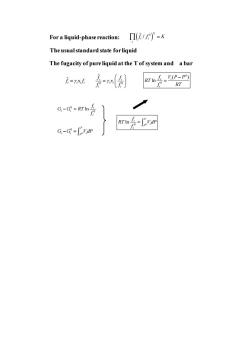
For a liquid-phase reaction::Πi/fW)P=K The usual standard state for liquid The fugacity of pure liquid at the T of system and a bar i-rxh 是月 RT G-G=会 Rrh片-可an G-G-S"vdP
For a liquid-phase reaction: The usual standard state for liquid The fugacity of pure liquid at the T of system and a bar ( ) ˆ 0 / i i i i f f K = ˆ i i i i f x f = 0 0 ˆ i i i i i i f f x f f = 0 0 ( ) ln i i i f V P P RT f RT − = 0 0 ln i i i i f G G RT f − = 0 0 P i i i P G G V dP − = 0 0 ln P i i P i f RT V dP f =
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 12 Solution Thermodynamics:Application.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 11 Solution thermodynamics - Theory.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 9 Refrigeration and Liquefaction.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 8 Production of Power from Heat.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 7 Application of Thermodynamics to Flow Processes.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 6 Thermodynamic properties of fluids.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 5 The Second Law of Thermodynamics.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 3 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程授课教案(讲义)Chapter 2 The First Law and Other Basic Concepts.doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学大纲 Thermodynamics of chemical engineering(新疆大学:黄雪莉).doc
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十章,负责人:刘钟馨、韩秀萍).docx
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)食品添加剂 Food additives.ppt
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)涂料(醇酸树脂涂料、丙烯酸树脂涂料).pptx
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)表面活性剂 surfactants.ppt
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)合成材料助剂.ppt
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)胶黏剂.ppt
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)绪论.ppt
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)涂料(环氧树脂涂料、聚氨酯树脂涂料).pptx
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)涂料(涂料的概念、作用和组成).pptx
- 海南大学:《精细化学品与工艺学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)涂料分类(涂料的分类和命名、溶剂型涂料、水性涂料).pptx
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第1章 绪言(无答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第2章 流体的P-V-T关系(含答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第4章 非均相封闭体系热力学(选择题带答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第5章 非均相体系热力学性质计算(无答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第8章 化学反应平衡(含答案).doc
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)纯流体性质 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)流体热力学性质 Thermodynamic properties of fluids.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)热动力 Production of Power from Heat.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)溶液热力学原理 Solution thermodynamics:Theory.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)热功转换及可用能.pdf
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论 Chemical Engineering thermodynamics.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 流体的p-V-T关系.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 化工过程的能量分析.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 相平衡.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 流体的热力学性质.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第六章 蒸汽动力循环与制冷循环.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十章 化学反应平衡.ppt
- 《化工热力学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 流体混合物的热力学性质.ppt
- 《化工原理》课程教学大纲 Principles of Chemical Engineering B.pdf
- 《化学反应工程》课程教学标准B.doc
