《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)14.Gestational Trophoblastic Diseases(GTDs)

Gestational Trophoblastic Diseases(GTDs) Dong xiaojing
Gestational Trophoblastic Diseases (GTDs) Dong xiaojing
Introduction Encompass a spectrum of neoplastic disorders that arise from placental trophoblastic tissue after abnormal fertilization The first and only disseminated solid tumors Highly curable by chemotherapy Unique and characteristic tumor marker:hCG Characters: lack of a fetus,trophoblastic cell hyperplasia,edema of villous stroma,loss of normal villous blood vessels
Introduction Encompass a spectrum of neoplastic disorders that arise from placental trophoblastic tissue after abnormal fertilization The first and only disseminated solid tumors Highly curable by chemotherapy Unique and characteristic tumor marker:hCG Characters: ²lack of a fetus, trophoblastic cell hyperplasia, edema of villous stroma, loss of normal villous blood vessels

Classification Benign- hydatidiform mole (HM) GTDs invasive mole (chorioadenoma Gestational destruens) Throphoblastic choriocarcinoma tumor (GTT) placental site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT)
Classification invasive mole (chorioadenoma destruens) choriocarcinoma placental site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT) GTDs Benign- hydatidiform mole (HM) Gestational Throphoblastic tumor (GTT)
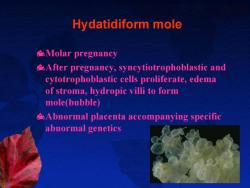
Hydatidiform mole Molar pregnancy After pregnancy,syncytiotrophoblastic and cytotrophoblastic cells proliferate,edema of stroma,hydropic villi to form mole(bubble) Abnormal placenta accompanying specific abnormal genetics
Hydatidiform mole Molar pregnancy After pregnancy, syncytiotrophoblastic and cytotrophoblastic cells proliferate, edema of stroma, hydropic villi to form mole(bubble) Abnormal placenta accompanying specific abnormal genetics

Complete chorionic villi are converted into a mass of clear vesicles Size of vesicles are variable in diameter,hang in clusters from thin pedicles,like grape Incomplete Focal change,fetus or at least an amnionic sac Avascular villi swelling
Complete ²chorionic villi are converted into a mass of clear vesicles ²Size of vesicles are variable in diameter, hang in clusters from thin pedicles, like grape Incomplete ²Focal change, fetus or at least an amnionic sac ²Avascular villi swelling

1.Incidence and epidemiology Incidence varies dramatically in different regions of the world In USA or Europe,1 in 1500 pregnancies In Mexico,1 in 125 In Far East and Southeast Asian,5 to 15 fold than in USA Complete is more often than incomplete
1. Incidence and epidemiology Incidence varies dramatically in different regions of the world ²In USA or Europe, 1 in 1500 pregnancies ²In Mexico, 1 in 125 ²In Far East and Southeast Asian, 5 to 15 fold than in USA Complete is more often than incomplete

High risk factors women≤20and>40 years Low economic status Nutrition:diets deficient in protein and folic acid,carotene deficiency Particular ABO blood groups Cell heredity:abnormal fertilization of ovum and sperm,enucleate egg,triploid, especially the abnormal of sperm
High risk factors ²women 40 years ²Low economic status ²Nutrition: diets deficient in protein and folic acid, carotene deficiency ²Particular ABO blood groups ²Cell heredity: abnormal fertilization of ovum and sperm, enucleate egg, triploid, especially the abnormal of sperm
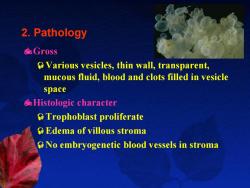
2.Pathology Gross Various vesicles,thin wall,transparent, mucous fluid,blood and clots filled in vesicle space Histologic character Trophoblast proliferate Edema of villous stroma No embryogenetic blood vessels in stroma
2. Pathology Gross ²Various vesicles, thin wall, transparent, mucous fluid, blood and clots filled in vesicle space Histologic character ²Trophoblast proliferate ²Edema of villous stroma ²No embryogenetic blood vessels in stroma
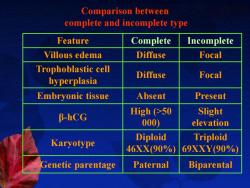
Comparison between complete and incomplete type Feature Complete Incomplete Villous edema Diffuse Focal Trophoblastic cell Diffuse Focal hyperplasia Embryonic tissue Absent Present Slight B-hCG High (>50 000) elevation Diploid Triploid Karyotype 46XX(90%) 69XXY(90%) Genetic parentage Paternal Biparental
Comparison between complete and incomplete type Feature Complete Incomplete Villous edema Diffuse Focal Trophoblastic cell hyperplasia Diffuse Focal Embryonic tissue Absent Present β-hCG High (>50 000) Slight elevation Karyotype Diploid 46XX(90%) Triploid 69XXY(90%) Genetic parentage Paternal Biparental

Theca-lutein cysts Surface is smooth,yellowish and lined with luteal cells,diameter from 10cm to more, thin wall,multichamber in section Overstimulation of luteal elements by large amounts of chorionic gonadotropin secreted by proliferated trophoblast Often occurred in both side and in complete (30%-50%)
Theca-lutein cysts ²Surface is smooth, yellowish and lined with luteal cells, diameter from 10cm to more, thin wall, multichamber in section ²Overstimulation of luteal elements by large amounts of chorionic gonadotropin secreted by proliferated trophoblast ²Often occurred in both side and in complete (30%~50%)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)16.Abnormal uterine bleeding(AUB).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)8.dystocia.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)6.3 Abnormal anmiotic fluid volume.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)3.1 Hos DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY & ANTENATAL CARE.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)placenta previa(showed).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)6.2 Postterm pregnancy.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)6.1 Preterm labor.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Hypertensive states of pregnancy.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)normal labor & delivery.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程作业练习题(无答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程教学实习大纲.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(英文)fetal distress.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(英文)endometriosis.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(英文)Physiology of menstruation.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(英文)pelvic pain and endometriosis.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(英文)Disorders of menstruation.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(英文)cervical neoplasia.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(英文)The normal labor & delivery.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(英文)abortion and ectopic pregnancy.doc
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)01 妊娠生理(重庆医科大学第二临床学院:刘建).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)02 异位妊娠 ectopic pregnancy.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)03 正常分娩.ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)04 异常分娩(Dystocia).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)05 妊娠期高血压病(hypertensive disorder complicating pregnancy).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)06 前置胎盘 placenta previa(重庆医科大学:曾建华).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)07 产后出血(postpartum hemorrhage).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)08 宫颈癌(cervical cancer).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)09 子宫内膜癌(Carcinoma of endometrium).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)10 闭经(重庆医科大学:熊正爱).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)11 子宫内膜异位症(endometriosis).ppt
- 《妇产科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)12 计划生育(contraception/family planning).ppt
- 《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一讲 概论 Laboratory Diagnotics、临床血液学检查(1/2).pdf
- 《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(作业习题)绪论(含答案).doc
- 《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二讲 临床血液学检查(2/2).pdf
- 《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(作业习题)血液一般检查(含答案).doc
- 《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三讲 骨髓、血型血库.pdf
- 《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(作业习题)血型鉴定与交叉配血(含答案).doc
- 《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(作业习题)骨髓细胞学检查(含答案).doc
- 《实验诊断学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四讲 血栓与止血检测.pdf
