上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 4 second law II

Contents of Today S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Continue /Review previous Entropy 2nd law Heat engine etc. http://smse.sjtu.edu.cn/entropy SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II Contents of Today Continue / Review previous Entropy 2nd law Heat engine etc. http://smse.sjtu.edu.cn/entropy

Reversible Process(2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 功的计算、可逆过程和最大功 活塞上砝码同时取走三个,外压P,一 次降低到p2,并在p,外压下,气体体积 anag 19 由V,膨胀到V, 活塞上砝码分二次取走,外压由P,分 段经p;降到p2,气体由'分段经V‘; 膨胀到V, 膨胀过程中,外压始终比系统内压相 语 差无限小 (c) 图1-5不同途径下气体等温膨胀示意图 当系统以上述三种途径达到终态后,再各自以其相反的过程回到始态,这就构 成了与原过程方向相反的三种途径。今分别计算其正、逆过程的体积功,分析 比较,引入可逆过程的概念 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II Reversible Process (2) 功的计算、可逆过程和最大功 活塞上砝码同时取走三个,外压p1一 次降低到p2,并在p2外压下,气体体积 由V1膨胀到V2 活塞上砝码分二次取走,外压由p1分 段经 p‘; 降到p2,气体由V1分段经 V ‘; 膨胀到V2 膨胀过程中,外压始终比系统内压相 差无限小 当系统以上述三种途径达到终态后,再各自以其相反的过程回到始态,这就构 成了与原过程方向相反的三种途径。今分别计算其正、逆过程的体积功,分析 比较,引入可逆过程的概念

Reversible Process (7) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Annlications 表1-1不同途径功的比较 途 径 I及I 亚及I Ⅲ及四' W正 -1.87(I) -2.49正) -3,46() W/KJ W逆 +7.48(1)+4.99Ⅱ) +3.46(Ⅲ') W正+W递 +5.61 +2.50 0 由表可知系统由一个状态变化到另一状态,可以通过不同的途径来实现。 当系统状态变化后,再使系统恢复到始态,环境不一定能复原,只有途径 Ⅲ,当系统复原时环境中没有留下功变热的痕迹,此过程为可逆过程。而 另一种情况是系统经过途径、Ⅱ后,系统虽复原,但环境中留下功变热的 痕迹,途径I、Ⅱ为不可逆过程。 当系统由始态经过某一过程变到终态Ⅱ后,如能使系统再回到原态,同时 也消除了原过程对环境所产生的一切影响,则原来过程称为可逆过程。 反之,某过程进行后,如果用任何方法都不可能使系统和环境完全复原, 则此过程称为不可逆过程。 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II Reversible Process (7) 由表可知系统由一个状态变化到另一状态,可以通过不同的途径来实现。 当系统状态变化后,再使系统恢复到始态,环境不一定能复原,只有途径 III,当系统复原时环境中没有留下功变热的痕迹,此过程为可逆过程。而 另一种情况是系统经过途径I、II后,系统虽复原,但环境中留下功变热的 痕迹,途径I、II为不可逆过程。 当系统由始态I经过某一过程变到终态II后,如能使系统再回到原态,同时 也消除了原过程对环境所产生的一切影响,则原来过程称为可逆过程。 反之,某过程进行后,如果用任何方法都不可能使系统和环境完全复原, 则此过程称为不可逆过程
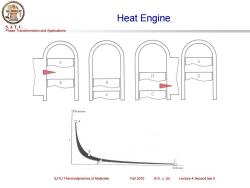
Heat Engine S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications A D D B B C Pressure B C Volume SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II Heat Engine
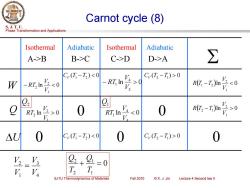
Carnot cycle(8) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Isothermal Adiabatic Isothermal Adiabatic A->B B->C C->D D->A ∑ C(T-T2)0 R(T-T2)I V2.0 V 9 RT2 In V2,0 V320 R(T-T) △U 0 Cr(T-T2)0 0 +9 =0 y Va L T SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II Carnot cycle (8) W ln 0 3 4 1 V V Q ln 0 RT 1 2 2 V V RT ln 0 1 2 − 2 V V RT U 0 A->B B->C C->D D->A 0 Isothermal Adiabatic Isothermal Adiabatic ln 0 3 4 − 1 V V RT 0 0 ( ) 0 CV T1 −T2 ( ) 0 CV T2 −T1 ( ) 0 CV T1 −T2 ( ) 0 CV T2 −T1 0 ( )ln 0 1 2 1 − 2 V V R T T ( )ln 0 1 2 2 − 1 V V R T T Q2 Q1 0 1 1 2 2 + = T Q T Q 4 3 1 2 V V V V =

Entropy as a State Function(3) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications B '-)〔号- )=〔号)-〔) 这一积分的数值与积分的途径无关,代表着某个状 态的改变量,定义为熵 For a close system the reversible heat flow divided by the absolute temperature of the system is a state or point function. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II Entropy as a State Function(3) = 0 + = A B r B A r r T Q T Q T Q = = − B A r A B r B A r T Q T Q T Q P V A B 这一积分的数值与积分的途径无关,代表着某个状 态的改变量,定义为熵 For a close system the reversible heat flow divided by the absolute temperature of the system is a state or point function

The Second Law S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The First Law:the conservation of energy and energy transfer in terms of heat and work. Energy is a state function. The Second Law:ENTROPY. Overview Heat engines,devices that convert thermal energy (heat)into mechanical energy (work). The first law places no limits on the amounts that can be converted. The second law is concerned with limits on the conversion of"heat"into work”by heat engines. 1824,a French engineer,Sadi Carnot,idealized heat engine. P.W.Atkins,The Second Law,Scientific American Books,1984 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II The Second Law The First Law: the conservation of energy and energy transfer in terms of heat and work. Energy is a state function. The Second Law: ENTROPY. Overview Heat engines, devices that convert thermal energy (heat) into mechanical energy (work). The first law places no limits on the amounts that can be converted. The second law is concerned with limits on the conversion of “heat” into “work” by heat engines. 1824, a French engineer, Sadi Carnot, idealized heat engine. P. W. Atkins, The Second Law, Scientific American Books, 1984
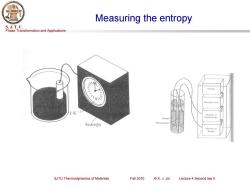
Measuring the entropy S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Display Microprocessor Monitor of Heater hermometer Entropy Thermometer Monitor of heater SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II Measuring the entropy

Review S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Entropy state function The second law is concerned with limits on the conversion of“heat"into“work”by heat engines. Through a consideration of an idealized heat engine operating between two heat reservoirs, Carnot found that not all the heat removed from a high temperature reservoir is converted into work. Entropy increase for an isolated system SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II Review • Entropy / state function • The second law is concerned with limits on the conversion of “heat” into “work” by heat engines. • Through a consideration of an idealized heat engine operating between two heat reservoirs, Carnot found that not all the heat removed from a high temperature reservoir is converted into work. • Entropy increase for an isolated system

热机:航空发动机 S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 4 Second law ll
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2010 © X. J. Jin Lecture 4 Second law II 热机:航空发动机
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《力学改变生活》课程教学资源(文献资料)Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger.pdf
- 《力学改变生活》课程教学资源(文献资料)The First Sounds of Merging Black Holes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)生物力学的发展前景.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)运动生物力学及组织损伤机理、计算机辅助手术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)心血管生物力学及其在疾病诊疗方面的应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)人体生物力学概论(梁夫友).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_静平衡条件说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_运动学计算流程图.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_运动学上机_运动学计算流程图.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_双摆动力学逆问题说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_双摆动力学仿真说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学附加题.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_静平衡条件说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_双摆动力学逆问题说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_双摆动力学仿真说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example2.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example1.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example 4.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Planar Dynamic Modeling and Analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 7_chap7-Numerical Methods in Dynamics.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 5 property relation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 6 property relation II.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 7 equilibrium.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 8 chemical equilibrium.pdf
- 西安交通大学:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一部分 基本变形(共六章,主讲:殷民).pdf
- 西安交通大学:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二部分 组合变形(共三章,主讲:殷民).pdf
- 西安交通大学:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三部分 专题讨论(共四章,主讲:殷民).pdf
- 东莞理工学院:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 东南大学土木工程学院:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学资源(考核要求).pdf
- 上海交通大学材料科学与工程学院:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(发展简史,主讲:曹志翔).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(学科体系).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(课件教案与部分讲义)绪论、结构的几何组成、静定梁.pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教学单元教案,共十二章).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(求解器简介).pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(教学大纲,含思政元素).docx
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第一章 电磁现象的普遍规律.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第二章 静电场.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第三章 静磁场.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第四章 电磁波的传播.pdf
