上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 8 chemical equilibrium

Contents of Today S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Review previous /Quiz Equlibrium Thermodynamic activity Chemical equilibrium Gaseous equilibrium Solid-vapor equilibrium Sources of information on Chemical equilibrium and adiabatic flame temperature etc. Science research is an adventure,is an interest-driving learning process. It takes more time to think than to do.-Ke Lu SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Contents of Today Review previous / Quiz Equlibrium Science research is an adventure, is an interest-driving learning process. It takes more time to think than to do. – Ke Lu Thermodynamic activity Chemical equilibrium Gaseous equilibrium Solid-vapor equilibrium Sources of information on Chemical equilibrium and adiabatic flame temperature etc

Review previous lecture (1) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Condition of equilibrium Phase equilibrium相平衡/化学反应的平衡 8W,en1>2=0 4,2=41G2=G1 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Review previous lecture (1) Condition of equilibrium Phase equilibrium相平衡/化学反应的平衡 Wrev.1→2 = 0 i,2 i,1 Gi,2 = Gi,1 =

恒温下(aAG/aP)r=△V关系式的应用 S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 在298K和1atm下,石墨为稳定态 298K 石墨(G)->金刚石(D) 已知:石墨和金刚石的标准生产热和标准熵为 0,1900J.mol1,5.73J.mol1.K-1,2.43J.mo1.K-1 298K下石墨和金刚石密度为:2.22g.cm-3,3.515g.cm3 V,=12/3.515=3.414cm3.mol1 'c=5.405cm3.mol1 Diamond ↑ g △2Gnm(298K,1atm)=△Hm-T△S,m Graphite 7=Constant =1900-298(2.43-5.73)=2883J.mo1>0 Po Equilibrium pressure O△G Pressure-> =AV='o-'c<0 op Figure 4.3 Specific Gibbs free energy versus pressure at con- stant temperature for graphite and diamond. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018.J.Jin Lecture 8 Cnemical equllonur
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium 恒温下 (∂ΔG/∂P)T =ΔV 关系式的应用 在298K和1atm下,石墨为稳定态 已知:石墨和金刚石的标准生产热和标准熵为 0,1900 J.mol-1 , 5.73 J.mol-1 .K-1 , 2.43 J.mol-1 .K-1 298K下石墨和金刚石密度为:2.22 g.cm-3 , 3.515 g.cm-3 = = − 0 D G T V V V p G 298K 石墨(G) -> 金刚石(D) 1900 298(2.43 5.73) 2883 0 (298 ,1 ) 1 = − − = = − − J mol Gm K atm Hm T Sm D G 3 1 12 /3.515 3.414 − V = = cm mol D 3 1 5.405 − V = cm mol G

Review previous lecture (2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Clapeyron equation in vapor equilibria Clapeyron equation pand Talong this line △H Teg△V B Change of the melting point of tin resulting from a pressure change of 500 atm 人 AH 7196 T Figure 4.4 Pressure-temperature relationship Teg△V 505×4.39×10-7 for equilibrium between phases A and B. △p9=500atm△Teg=+1.58K SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Review previous lecture (2) Clapeyron equation in vapor equilibria T V H dT dp e q e q e q = Clapeyron equation Change of the melting point of tin resulting from a pressure change of 500 atm 7 505 4.39 10 7196 − = = T V H T p e q e q e q p atm T K e q e q = 500 = +1.58

Variation of vapor pressure with particle size S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The pressure on a small droplet is the sum of the imposed gas pressure and the internal pressure generated by the surface tension of the material 2mY=m2△p △p= π ViPT RTIn Figure 4.7 The force holding two hemispheres together is 2mry:the force pushing them apart is AP, RTI- where△P=2ylr. The vapor pressure above the small particles is greater than the vapor pressure I=Y (2x above the large particles.Material would RT then move through the gas phase from Coarsening SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials small particles to largerones..Coar Spring 2018
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Variation of vapor pressure with particle size The pressure on a small droplet is the sum of the imposed gas pressure and the internal pressure generated by the surface tension of the material r = r p 2 2 r p 2 = e Vl pT RT = ln e l RT r V ln 2 = = RT r V l e 2 ln The vapor pressure above the small particles is greater than the vapor pressure above the large particles. Material would then move through the gas phase from small particles to larger ones. Coarsening

Second-order transition S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications First derivatives of G with respect to T and p are continuous and the second derivatives of G with respect to T and P are discontinuous SA=SB S=S(T,p) dS dT+ dp T dS= d7- C。=T T dp n SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Second-order transition First derivatives of G with respect to T and p are continuous and the second derivatives of G with respect to T and P are discontinuous S A = S B S = S(T, p) dp p S dT T S dS p T + = dp T V dT T C d S p p = − p p T S C T =

Second-order transition(2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications ds=dt-ar T dp ds,=dsB dsas。-0-CsC≥rm-eas-ra,p Teq VA=VR=V ACp The thermal expansion dTeg VTe△a coefficient does change! dp △ dTeg △B SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Second-order transition (2) dp T V dT T C d S p p = − dS A = dS B ( ) e q B B A A e q e q p B p A A B dT V V dp T C C dS dS − − − − = = , , 0 V A =V B =V = e q p e q e q VT C dT dp The thermal expansion coefficient does change! = e q e q dT dp
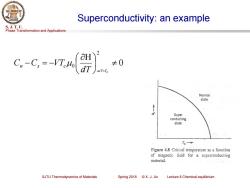
Superconductivity:an example S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 2 C,-C.=-VTMh dr ≠0 atT-Tc Normal state Super conducting state Tc→ Figure 4.8 Critical temperature as a function of magnetie field for a superconducting material. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Superconductivity: an example 0 2 0 − = − d T atT=Tc Cn Cs VTc

Index of nomenclature S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Activity:活度 Fugacity:逸度 Reference state/standard state:参考态/标准态 Equilibrium constant:平衡常数 Ellingham diagrams:Ellingham SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Index of nomenclature Activity:活度 Fugacity:逸度 Reference state / standard state:参考态 / 标准态 Equilibrium constant:平衡常数 Ellingham diagrams: Ellingham图

Introduction S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Physical equilibrium. Chemical equilibrium. Activity Fugacity dG=VdrdG=-SdT+Vdp,withdT=O) dG=RTP RTdln P P SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Introduction Physical equilibrium. Chemical equilibrium. Activity Fugacity dG =VdP(dG = −SdT +VdP,withdT = 0) RTd P P dP dG = R T = ln
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 7 equilibrium.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 6 property relation II.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 5 property relation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料热力学》教学资源_2018 lecture 4 second law II.pdf
- 《力学改变生活》课程教学资源(文献资料)Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger.pdf
- 《力学改变生活》课程教学资源(文献资料)The First Sounds of Merging Black Holes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)生物力学的发展前景.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)运动生物力学及组织损伤机理、计算机辅助手术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)心血管生物力学及其在疾病诊疗方面的应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)人体生物力学概论(梁夫友).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_静平衡条件说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_运动学计算流程图.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_运动学上机_运动学计算流程图.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_双摆动力学逆问题说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_双摆动力学仿真说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学附加题.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_静平衡条件说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_双摆动力学逆问题说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_双摆动力学仿真说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example2.doc
- 西安交通大学:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一部分 基本变形(共六章,主讲:殷民).pdf
- 西安交通大学:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二部分 组合变形(共三章,主讲:殷民).pdf
- 西安交通大学:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三部分 专题讨论(共四章,主讲:殷民).pdf
- 东莞理工学院:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 东南大学土木工程学院:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学资源(考核要求).pdf
- 上海交通大学材料科学与工程学院:《材料力学 Mechanics of Materials》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(发展简史,主讲:曹志翔).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(学科体系).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(课件教案与部分讲义)绪论、结构的几何组成、静定梁.pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教学单元教案,共十二章).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《结构力学》课程教学资源(求解器简介).pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(教学大纲,含思政元素).docx
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第一章 电磁现象的普遍规律.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第二章 静电场.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第三章 静磁场.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第四章 电磁波的传播.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第五章 电磁波的辐射.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(习题解答,打印版)第六章 狭义相对论.pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版)绪论(负责人:郑伟).pdf
- 运城学院:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版)第一章 电磁现象的普遍规律.pdf
