上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140924
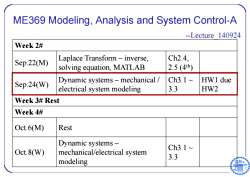
ME369 Modeling,Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture 140924 Week 2# Laplace Transform-inverse, Ch2.4, Sep.22(M) solving equation,MATLAB 2.5(4th) Dynamic systems-mechanical Ch3.1~ HW1 due Sep.24(W) electrical system modeling 3.3 HW2 Week 3#Rest Week 4# 0ct.6M)) Rest Dynamic systems- Ch3.1~ Oct.8(W) mechanical/electrical system 3.3 modeling
ME369 Modeling, Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture_140924 Week 2# Sep.22(M) Laplace Transform – inverse, solving equation, MATLAB Ch2.4, 2.5 (4th ) Sep.24(W) Dynamic systems – mechanical / electrical system modeling Ch3.1 ~ 3.3 HW1 due HW2 Week 3# Rest Week 4# Oct.6(M) Rest Oct.8(W) Dynamic systems – mechanical/electrical system modeling Ch3.1 ~ 3.3

Problems of HW2 ·Refer to the ftp site. ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn ·User:yuanjj ·Password:public DUE:Oct.13(M)
Problems of HW2 • Refer to the ftp site. • ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn • User: yuanjj • Password: public DUE: Oct. 13 (M)
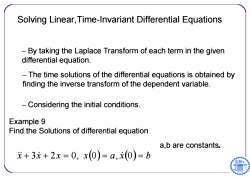
Solving Linear,Time-Invariant Differential Equations By taking the Laplace Transform of each term in the given differential equation. The time solutions of the differential equations is obtained by finding the inverse transform of the dependent variable. -Considering the initial conditions. Example 9 Find the Solutions of differential equation a,b are constants. 求+3元+2x=0,x(0)=a,(0)=b
– By taking the Laplace Transform of each term in the given differential equation. – The time solutions of the differential equations is obtained by finding the inverse transform of the dependent variable. – Considering the initial conditions. Example 9 Find the Solutions of differential equation x 3x 2x 0, x0 a, x0 b a,b are constants. Solving Linear,Time-Invariant Differential Equations

Example 10 Find the Solutions of differential equation: 求+2x+5x=3,x(0)=0,x(0)=0
Example 10 Find the Solutions of differential equation: x 2x 5x 3, x0 0, x 0 0
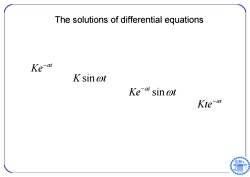
The solutions of differential equations Ke-a K sin @t Kea sin wt Kte-at
The solutions of differential equations at Ke K sin t sin at Ke t at Kte

Mechanical system modeling Translation mass-spring -damper(viscous friction coefficient),force Rotation moment of inertia-torsional spring damper,torque mass M spring K damper B +x(0 →xz(0 →x(t) →(0 →2(0 一→10 →(0 +x1() +v(0 →(0 f.(() f() 8M 6- f() fe(t) fa(t) 71 K B fo(1)=Blv (1)-v2(1)=Bv(t) f()=K()-x2()]=Kx() =K(-v.( =B () (t) d d2 dt dt .0=m市0=m =KJv(dr =B( dt
Mechanical system modeling Translation : mass – spring – damper (viscous friction coefficient), force Rotation : moment of inertia – torsional spring – damper, torque mass M spring K damper B
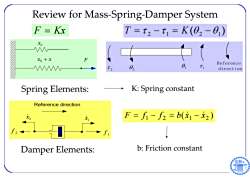
Review for Mass-Spring-Damper System F=Kx T=t2-t1=K(02-0) Xo Xo+x F 02 0、 Reference direction Spring Elements: K:Spring constant Reference direction F=f-f2=b(x1-x2) f Damper Elements: b:Friction constant
Review for Mass‐Spring‐Damper System 0 x x x 0 F Spring Elements: K: Spring constant ( ) 2 1 2 1 F Kx T K 2 1 2 1 1 x2 x 1 2 f f ( ) 1 2 1 2 F f f b x x Damper Elements: b: Friction constant

Review for Mass-Spring-Damper System Newton's second law ma=∑F Ja=∑T F=the vector sum of all forces applied to each body in a system,newtons (N)or pounds (lb) a the vector acceleration of each body with respect to an inertial reference frame.m/sec2 or ft/sec2 m=mass of the body.Kg or slug
Newton’s second law ma F J T F = the vector sum of all forces applied to each body in a system, newtons (N) or pounds (lb) a = the vector acceleration of each body with respect to an inertial reference frame. m/sec2 or ft/sec2 m = mass of the body. Kg or slug Review for Mass-Spring-Damper System
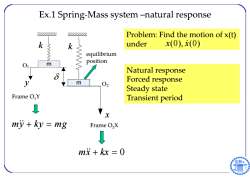
Ex.1 Spring-Mass system-natural response Problem:Find the motion of x(t) k k under x(0),x(0) equilibrium m position Natural response m 02 Forced response Steady state Frame OY Transient period L x my +ky =mg Frame O2X ↓ mx+kx=0
Ex.1 Spring‐Mass system –natural response equilibrium position Frame O1Y k k x y my ky mg Frame O2X m x kx 0 Problem: Find the motion of x(t) under x(0), x(0) Natural response Forced response Steady state Transient period
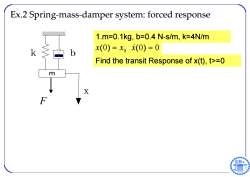
Ex.2 Spring-mass-damper system:forced response 1.m=0.1kg,b=0.4N-s/m,k=4N/m k b x(0)=x(0)=0 Find the transit Response of x(t),t>=0 m X
1.m=0.1kg, b=0.4 N-s/m, k=4N/m Ex.2 Spring ‐mass ‐damper system: forced response 0 0 0 x ( ) x 0 x( ) Find the transit Response of x(t), t>=0 F
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140922.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140917.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140915.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源_电气工程基础(二)课程导学与习题集.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)空气间隙放电实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)电缆波过程实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)沿面放电实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统过电压.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统绝缘.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统波过程(线路和绕组中的波过程).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)高电压技术概论(张君).pdf
- 中华人民共和国国家标准:GB/T 16927.1 - 2011(代替GB/T 16927.1 - 1997)《高电压试验技术》第1部分:一般定义及试验要求 High-voltage test techniques-Part 1:General definitions and test requirements(IEC60060-1:2010,MOD).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)高电压的测量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)冲击高电压及大电流的产生.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)稳态高电压试验设备.pdf
- 《高电压工程》课程教学资源(参考书籍)《电力系统过电压》(朱子述).pdf
- 《高电压工程》课程教学资源(参考书籍)《High Voltage Engineering Test》Chapter 2 Generation of high voltages Chapter 3 Measurement of high voltages.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源[09]homework03_solution.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源[19]2014至2015学年第1学期期末考-答案.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源[19]2014至2015学年第1学期期末考-A卷.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140928.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141008.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141013.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141015.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141020.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141027.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141029.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141103.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141105.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141110.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141112.pdf
- 《电气与电子测量技术》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第一章 测量及测量系统基础、第二章 误差的基本理论.pdf
- 《电气与电子测量技术》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第三章 常用传感器及其调理电路、第四章 集成运放与模拟调理电路分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)绪论、第一章 测量技术概述(罗利文).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第七章 虚拟仪器LABVIEW.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第三章 常用传感器及其调理电路.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第二章 误差的基本理论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第五章 电气测量技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第八章 电气测量中的抗干扰技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第六章 数字化测量技术(数字化电气测量系统设计).pdf
