上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141103
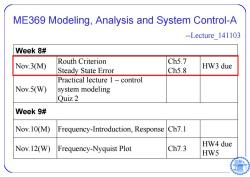
ME369 Modeling,Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture 141103 Week 8# Routh Criterion Ch5.7 Nov.3(M) HW3 due Steady State Error Ch5.8 Practical lecture 1-control Nov.5(W) system modeling Quiz 2 Week 9# Nov.10(M) Frequency-Introduction,Response Ch7.1 HW4 due Now.12(W)) Frequency-Nyquist Plot Ch7.3 HW5
ME369 Modeling, Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture_141103 Week 8# Nov.3(M) Routh Criterion Steady State Error Ch5.7 Ch5.8 HW3 due Nov.5(W) Practical lecture 1 – control system modeling Quiz 2 Week 9# Nov.10(M) Frequency-Introduction, Response Ch7.1 Nov.12(W) Frequency-Nyquist Plot Ch7.3 HW4 due HW5
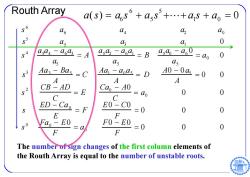
Routh Array a(s)=a,s6+a5s5+…+as+a0=0 06 ao a 43 a 0 S 4 aa4-a6凸 二A asaasa=B 0 as as as Aa3- BasC Aaaoas=D A0-0a=0 0 A A A 2 CB-AD =E Cao-40 S 二do 0 0 C ED E0-C0 S -Cao=F =0 0 0 E F Fao F0-E0 0 0 0 F F The number of sign changes of the first column elements of the Routh Array is equal to the number of unstable roots
Routh Array s 6 a 6 a 4 a2 a 0 s 5 a 5 a 3 a1 0 s 4 a 5 a 4 a 6 a 3 a 5 A a 5 a2 a 6 a1 a 5 B a 5 a 0 a 6 0 a 5 a 0 0 s 3 Aa 3 Ba 5 A C Aa1 a 0 a 5 A D A 0 0 a 5 A 0 0 s 2 CB AD C E Ca 0 A 0 C a 0 0 0 s ED Ca 0 E F E 0 C 0 F 0 00 s 0 Fa 0 E 0 F a 0 F 0 E 0 F 0 00 The number of sign changes of the first column elements of the Routh Array is equal to the number of unstable roots. a ( s ) a 6 s 6 a 5 s 5 a 1 s a 0 0

Example--Verification (s-1)2(s+2)(s+3)=s4+3s3-3s2-7s+6 1 -3 6 3 -7 0 -2 6 3 0 S 20 0 S 6 Examine 1st column,of sign changes= 日96
Example--Verification ( s 1) 2 ( s 2)( s 3) s 4 3 s 3 3 s 2 7 s 6 4 3 2 0 1 36 3 70 s s s s s 2 3 6 20 0 6 0 Examine 1st column, # of sign changes=
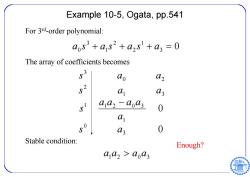
Example 10-5,Ogata,pp.541 For 3d-order polynomial: a0s3+a1s2+a2s+a3=0 The array of coefficients becomes s ao 02 a 03 a az -aoa3 0 1 s° a 0 Stable condition: Enough? a az aa;
Example 10-5, Ogata, pp.541 3 0 1 2 2 1 3 a 0 s a s a s a For 3rd-order polynomial: 0 0 3 0 1 1 1 2 0 3 1 3 2 0 2 3 s a a a a a a s s a a s a a The array of coefficients becomes Stable condition: 1 2 0 3 a a a a Enough?
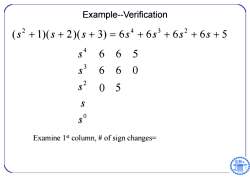
Example--Verification (s2+1)(s+2)(s+3)=6s4+6s3+6s2+6s+5 665 6 6 5 S 5O Examine 1st column,of sign changes= 6
Example--Verification 2 432 ( 1)( 2)( 3) 6 6 6 6 5 s s s ssss 4 3 2 0 665 660 s s s s s 0 5 Examine 1st column, # of sign changes=

Special Case 1 When one of the terms in the first column is zero, that indicates there may be pole(s)on RHP. ·These“zero”can be replaced by a small positive number“e”and continue the process. See the two examples in Ogata,pp.542
Special Case 1 • When one of the terms in the first column is zero, that indicates there may be pole(s) on RHP. • These “zero” can be replaced by a small positive number “” and continue the process. See the two examples in Ogata, pp.542
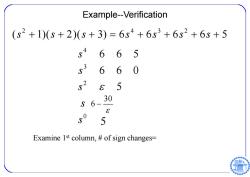
Example--Verification (s2+1)(s+2)(s+3)=6s4+6s3+6s2+6s+5 6 65 6 6 E 5 30 S E 5 5 Examine 1st column,of sign changes= 6
Example--Verification 2 432 ( 1)( 2)( 3) 6 6 6 6 5 s s s ssss 4 3 2 0 665 660 5 s s s s s 30 6 5 Examine 1st column, # of sign changes=
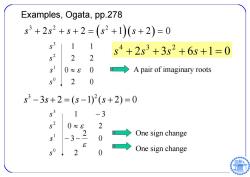
Examples,Ogata,pp.278 s3+2s2+s+2=(s2+1)(s+2)=0 s3 1 s4+2s3+3s2+6s+1=0 s2 2 2 s 0 0 A pair of imaginary roots 2 s3-3s+2=(s-1)2(s+2)=0 1 -3 s2 0≈8 2 -3 2 0 →One sign change → 2 One sign change
2 0 0 0 2 2 1 1 0 1 2 3 s s s s 32 2 s ss s s 2 2 1 20 Examples, Ogata, pp.278 2 0 0 2 3 0 2 1 3 0 1 2 3 s s s s A pair of imaginary roots One sign change One sign change 2 3 6 1 0 4 3 2 s s s s 3 2 ss s s 3 2 ( 1) ( 2) 0

Special Case 2 If all the coefficients in any row become all zero, that indicate poles in mirror image with respect to the origin. The evaluation can be continued by forming an auxiliary polynomial,by taking the coefficients of the last non-zero row. The all-zero row is then replaced by the coefficients of the derivative of the auxiliary polynomial
Special Case 2 • If all the coefficients in any row become all zero, that indicate poles in mirror image with respect to the origin. • The evaluation can be continued by forming an auxiliary polynomial, by taking the coefficients of the last non-zero row. • The all-zero row is then replaced by the coefficients of the derivative of the auxiliary polynomial
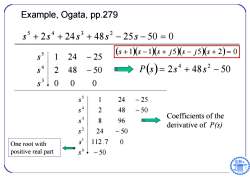
Example,Ogata,pp.279 s5+2s4+24s3+48s2-255-50=0 1 24-25 (6+10s-1s+j5s-j5g+2)=0 2 48-50 →P(s)=2s4+48s2-50 53 ,0 0 0 1 24 -25 2 48 -50 Coefficients of the 8 96 derivative of P(s) 24 -50 One root with 112.7 0 positive real part 50 -50
Example, Ogata, pp.279 2 24 48 25 50 0 5 4 3 2 s s s s s 0 0 0 2 48 50 1 24 25 3 4 5 s s s 2 48 50 4 2 P s s s 50 112.7 0 24 50 8 96 2 48 50 1 24 25 0 1 2 3 4 5 s s s s s s Coefficients of the derivative of P(s) One root with positive real part s 1 s 1 s j 5 s j 5 s 2 0
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141029.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141027.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141020.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141015.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141013.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141008.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140928.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140924.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140922.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140917.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140915.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源_电气工程基础(二)课程导学与习题集.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)空气间隙放电实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)电缆波过程实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)沿面放电实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统过电压.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统绝缘.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统波过程(线路和绕组中的波过程).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)高电压技术概论(张君).pdf
- 中华人民共和国国家标准:GB/T 16927.1 - 2011(代替GB/T 16927.1 - 1997)《高电压试验技术》第1部分:一般定义及试验要求 High-voltage test techniques-Part 1:General definitions and test requirements(IEC60060-1:2010,MOD).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141105.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141110.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141112.pdf
- 《电气与电子测量技术》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第一章 测量及测量系统基础、第二章 误差的基本理论.pdf
- 《电气与电子测量技术》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第三章 常用传感器及其调理电路、第四章 集成运放与模拟调理电路分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)绪论、第一章 测量技术概述(罗利文).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第七章 虚拟仪器LABVIEW.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第三章 常用传感器及其调理电路.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第二章 误差的基本理论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第五章 电气测量技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第八章 电气测量中的抗干扰技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第六章 数字化测量技术(数字化电气测量系统设计).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第四章 集成运放与模拟调理电路分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017版教材)习题答案.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017版教材)第二章 误差的基本理论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017版教材)第五章 电气测量技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017版教材)第八章 电气测量中的抗干扰技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论、第一章 测量技术概述(罗利文).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 虚拟仪器LABVIEW.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 常用传感器及其调理电路.pdf
