上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141015
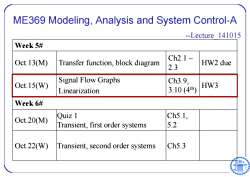
ME369 Modeling,Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture 141015 Week 5# Ch2.1~ Oct.13(M) Transfer function,block diagram HW2 due 2.3 Signal Flow Graphs Ch3.9, Oct.15(W) Linearization 3.10(4h) HW3 Week 6# Oct.20(M) Quiz 1 Ch5.1, Transient,first order systems 5.2 Oct.22(W) Transient,second order systems Ch5.3
ME369 Modeling, Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture_141015 Week 5# Oct.13(M) Transfer function, block diagram Ch2.1 ~ 2.3 HW2 due Oct.15(W) Signal Flow Graphs Linearization Ch3.9, 3.10 (4th ) HW3 Week 6# Oct.20(M) Quiz 1 Transient, first order systems Ch5.1, 5.2 Oct.22(W) Transient, second order systems Ch5.3

Problems of HW3 ·Refer to the ftp site. ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn ·User:yuanjj ·Password:public DUE:Oct.25(F)
Problems of HW3 • Refer to the ftp site. • ftp://public.sjtu.edu.cn • User: yuanjj • Password: public DUE: Oct. 25 (F)
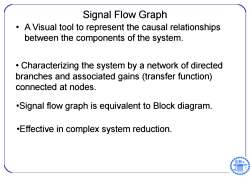
Signal Flow Graph A Visual tool to represent the causal relationships between the components of the system. Characterizing the system by a network of directed branches and associated gains (transfer function) connected at nodes. .Signal flow graph is equivalent to Block diagram. .Effective in complex system reduction
Signal Flow Graph • A Visual tool to represent the causal relationships between the components of the system. • Characterizing the system by a network of directed branches and associated gains (transfer function) connected at nodes. •Signal flow graph is equivalent to Block diagram. •Effective in complex system reduction
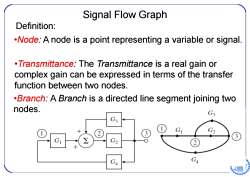
Signal Flow Graph Definition: .Node:A node is a point representing a variable or signal. Transmittance:The Transmittance is a real gain or complex gain can be expressed in terms of the transfer function between two nodes. .Branch:A Branch is a directed line segment joining two nodes. G3 G G2 GA GA 日96
Signal Flow Graph Definition: •Node : A node is a point representing a variable or signal. •Branch: A Branch is a directed line segment joining two nodes. •Transmittance : The Transmittance is a real gain or complex gain can be expressed in terms of the transfer function between two nodes
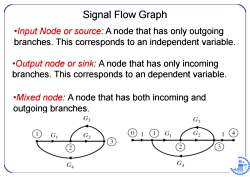
Signal Flow Graph .Input Node or source:A node that has only outgoing branches.This corresponds to an independent variable. .Output node or sink:A node that has only incoming branches.This corresponds to an dependent variable. .Mixed node:A node that has both incoming and outgoing branches. G3 G GA GA 日96
Signal Flow Graph •Input Node or source : A node that has only outgoing branches. This corresponds to an independent variable. •Output node or sink: A node that has only incoming branches. This corresponds to an dependent variable. •Mixed node: A node that has both incoming and outgoing branches
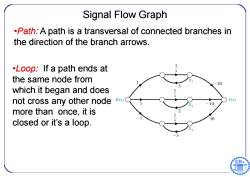
Signal Flow Graph .Path:A path is a transversal of connected branches in the direction of the branch arrows. Loop:If a path ends at the same node from 20 which it began and does not cross any other node R(s) Y(s) 10 more than once,it is 30 closed or it's a loop
Signal Flow Graph •Path : A path is a transversal of connected branches in the direction of the branch arrows. •Loop: If a path ends at the same node from which it began and does not cross any other node more than once, it is closed or it’s a loop
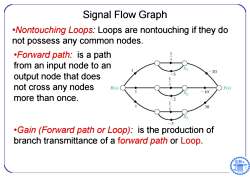
Signal Flow Graph .Nontouching Loops:Loops are nontouching if they do not possess any common nodes. .Forward path:is a path from an input node to an 20 output node that does not cross any nodes R(s) Y(s) more than once. 30 .Gain (Forward path or Loop):is the production of branch transmittance of a forward path or Loop
Signal Flow Graph •Nontouching Loops: Loops are nontouching if they do not possess any common nodes. •Forward path: is a path from an input node to an output node that does not cross any nodes more than once. •Gain (Forward path or Loop): is the production of branch transmittance of a forward path or Loop
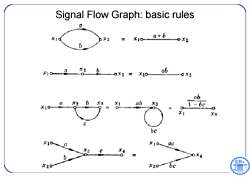
Signal Flow Graph:basic rules Q X2=10 a+6 XE x10-26 0x3=x10 ab 0Y月 ab ab x3 1-bc 0 1 X3 be ¥10 b 0X4 X20 ¥2gbc 日6
Signal Flow Graph: basic rules
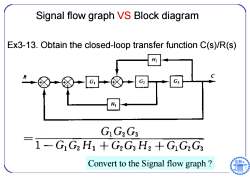
Signal flow graph VS Block diagram Ex3-13.Obtain the closed-loop transfer function C(s)/R(s) He G2 G H GG2Gs 1-GG2 H1+G2G3 H2 +GG2Gs Convert to the Signal flow graph
Signal flow graph VS Block diagram Ex3-13. Obtain the closed-loop transfer function C(s)/R(s) Convert to the Signal flow graph ?
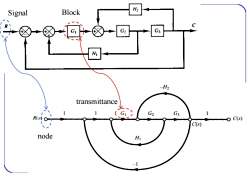
Signal Block H G H -H2 transmittance G2 G R(s) C(s) C(s) node H -1
node Signal transmittance Block
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141013.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141008.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140928.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140924.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140922.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140917.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_140915.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源_电气工程基础(二)课程导学与习题集.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)空气间隙放电实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)电缆波过程实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(试验报告)沿面放电实验.doc
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统过电压.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统绝缘.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)电力系统波过程(线路和绕组中的波过程).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)高电压技术概论(张君).pdf
- 中华人民共和国国家标准:GB/T 16927.1 - 2011(代替GB/T 16927.1 - 1997)《高电压试验技术》第1部分:一般定义及试验要求 High-voltage test techniques-Part 1:General definitions and test requirements(IEC60060-1:2010,MOD).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)高电压的测量.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)冲击高电压及大电流的产生.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高电压工程》课程教学资源(电气工程基础)稳态高电压试验设备.pdf
- 《高电压工程》课程教学资源(参考书籍)《电力系统过电压》(朱子述).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141020.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141027.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141029.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141103.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141105.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141110.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《系统模型、分析与控制 Modeling、Analysis and Control》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lecture_141112.pdf
- 《电气与电子测量技术》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第一章 测量及测量系统基础、第二章 误差的基本理论.pdf
- 《电气与电子测量技术》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第三章 常用传感器及其调理电路、第四章 集成运放与模拟调理电路分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)绪论、第一章 测量技术概述(罗利文).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第七章 虚拟仪器LABVIEW.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第三章 常用传感器及其调理电路.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第二章 误差的基本理论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第五章 电气测量技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第八章 电气测量中的抗干扰技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第六章 数字化测量技术(数字化电气测量系统设计).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017课件讲稿)第四章 集成运放与模拟调理电路分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017版教材)习题答案.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017版教材)第二章 误差的基本理论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电气与电子测量技术》精品课程教学资源(2017版教材)第五章 电气测量技术.pdf
