上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture6 Vector fundamentals for kinematic analysis

图 上海文通大¥ e2b口 HAa ILAO ToNr:UNpan LECTURE 6 ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Vector fundamentals and Velocity analysis Covered:Ch4~6-in Design of Machinery SH 1 国 上海文通大学 OUTLINE Why kinematic analysis ©Motion as vectors Instantaneous velocity center Applications of Instant Centers 1
1 Vector fundamentals and Velocity analysis LECTURE 6 ME371/ME337 DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Covered:Ch4~6- in Design of Machinery OUTLINE Why kinematic analysis Motion as vectors Instantaneous velocity center Applications of Instant Centers
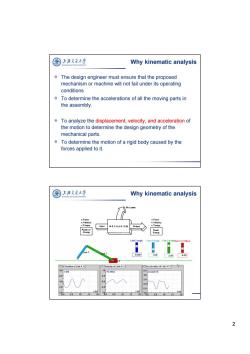
图 上泽久通大学 Why kinematic analysis The design engineer must ensure that the proposed mechanism or machine will not fail under its operating conditions To determine the accelerations of all the moving parts in the assembly. To analyze the displacement,velocity,and acceleration of the motion to determine the design geometry of the mechanical parts. To determine the motion of a rigid body caused by the forces applied to it. 国 上潘久大学 Why kinematic analysis 某Force x Force Velocity x Velocity x Torque Input MECHANISM Dutput x Torque Link 2 angle Link 2 length Link 3 lengtlslot 13 Y-Ofset ◆ 54.00 1.64 330 -0.26 X-Position of Link 4 11 Acceleration of Link 411 8.0 x同 10vx (m/s) 6.Txm2 5.0 00叶 2.0 15 1% 4 5.0 10 15 20 2
2 The design engineer must ensure that the proposed mechanism or machine will not fail under its operating conditions To determine the accelerations of all the moving parts in the assembly. To analyze the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of the motion to determine the design geometry of the mechanical parts. To determine the motion of a rigid body caused by the forces applied to it. Why kinematic analysis Why kinematic analysis

园 上海文通大学 Kinematic analysis Aa ILAO ToNr:UNpin © Displacement analysis to determine the output displacement and check if it meets the requirements. to find the stroke or output workspace to avoid space interferences. ©Velocity analysis the basis for further analysis to find the velocity characteristics of the output,then check if it meets the requirements.(such as quick return mechanism...) Acceleration analysis >to find the inertial forces to determine the dynamic performances of the output. 国 上潘久大学 Method of Kinematic analysis ©Graphical approach: >IC Instant Center) >Graphical method based on vectors(Vector graphic method) Derive the general equations of motion >analytical expressions suited to use computers to solve Complex vector method and Matrix method ® Present and derive analytical solutions to the position analysis problem for various planar mechanisms Discuss graphical solutions which are useful for checking analytical results 3
3 Displacement analysis to determine the output displacement and check if it meets the requirements. to find the stroke or output workspace. to avoid space interferences. Velocity analysis the basis for further analysis to find the velocity characteristics of the output, then check if it meets the requirements. (such as quick return mechanism…) Acceleration analysis to find the inertial forces to determine the dynamic performances of the output. Kinematic analysis Graphical approach : IC ( Instant Center) Graphical method based on vectors ( Vector graphic method) Derive the general equations of motion analytical expressions suited to use computers to solve Complex vector method and Matrix method Present and derive analytical solutions to the position analysis problem for various planar mechanisms. Discuss graphical solutions which are useful for checking analytical results Method of Kinematic analysis

图 上泽文通大¥ Space of motion G从AO TONE时真材 130mm 150m Curvilinear translation General plane motion Rectilinear translation Rotation about a fixed axis 6a2g 国上泽支大半 Motion Types Type of Rigid-Body Plane Motion Example (a) Rectilinear translation Rocket test aled near Parallel-link swinging plate Compound pendulum d 4
4 Space of motion Motion Types

图上泽通大学 Motion Curves GH TONG NR AMALYSIS OF THE FOUR R LINKAGE 国 上潘久大学 OUTLINE Why kinematic analysis ©Motion as vectors ® Position analysis of linkages Instantaneous velocity center Applications of Instant Centers 5
5 Motion Curves OUTLINE Why kinematic analysis Motion as vectors Position analysis of linkages Instantaneous velocity center Applications of Instant Centers
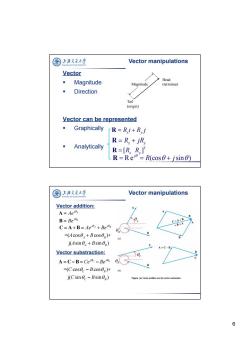
国 上海文通大学 Vector manipulations TON Vector Magnitude Head Magnitude (terminus) Direction Tail (origin) Vector can be represented Graphically R=Ri+Ryj R=R+jRy ◆ Analytically R=[R.RT R=Rei=R(cos0+jsine) 国上泽支大半 Vector manipulations Vector addition: A=Aeio A B=Beia C=A+B C=A+B=Aei+Bei0a =B+A 0 =(Acos0,+Bcoseg)+ (a) j(Asin+Bsineg) A=C-B Vector substraction: A=C-B=Ceic-Beio =(Ccosec-Bcos0g)+ j(Csinec-Bsine) Figure(Vee 6
6 Vector manipulations Vector Magnitude Direction Vector can be represented Graphically Analytically Head Magnitude (terminus) Tail (origin) R R jR x y R e (cos sin ) j R j R [ ]T R R x y R R Ri R j x y Vector manipulations Figure (a) Vector addition and (b) vector subtraction. B A B C A j Ae A B j Be B =( cos cos )+ j( sin sin ) A B j j A B A B Ae Be A B A B CAB =( cos cos )+ j( sin sin ) C B j j C B C B Ce Be C B C B A CB Vector addition: Vector substraction:

圈上游文大学 Vector rotation: R=Reio R R'=Reio=Rei(o+o) 国上泽支大半 o=i2+j-1)+k4(rad1s). Vector cross product: r=i(-1)+j10+k2(mm), A=iA,jA,+kA. ii i j k D=@xr= B=iB:jBy+kB. -1102 =i(-2-40)+j-4-4)+k(20-1) i jk =i(-42)+j(-8)+k(19)mm/s A×B=AA,A B.B,B. AxB=i(A,B.-A.B)+j(A.B-A B.)+k(A,B-A,B. A×Bl=ABsin0 7
7 Vector rotation: j R e R ( ) 'e j j R e R R X Y O R R ' ω i2 j(1) k4 (rad / s). r i(1) j10 k2 (mm), mm s B B B A A A x y z x y z ( 42) ( 8) (19) / ( 2 40) ( 4 4) (20 1) 1 10 2 2 1 4 i j k i j k i j k i j k υ ω r ω r v Ax Ay Az A i j k Bx By Bz B i j k Vector cross product: x y z x y z B B B A A A i j k AB ( ) ( ) ( ) AyBz AzBy AzBx AxBz AxBy AyBx A B i j k A B ABsin

国上泽夫通大学 i Vector dot product: A-B=ABcos0 ixj=k jxi=-k jxk=i k×j=-i kxi=j ixk=-j i×i=j×j=k×k=0 i.i=j.j=k.k=1 i.j=j.k=k.i=0 ixi=-k j=k 国 上海文通大学 Some useful trigonometric identities: COS0=eten 2 .sing=-jen-em 2 1-tan2(3) 2tan() cos0 sin= 1+a3 cos(0±)=cos(0)cos(p)干sin(0)sin(p) sin(0±)=sin(g)cos()±cos(0)sin() 8
8 Vector dot product: A B ABcos 0 k i j i k j i i j j k k i j k j i k j k i k j i i.i j.j k.k 1 i.j j.k k.i 0 Some useful trigonometric identities: 2 2 2 cos ,sin 2 2 1 tan ( ) 2 tan( ) 2 2 cos ,sin 1 tan ( ) 1 tan ( ) 2 2 cos( ) cos( )cos( ) sin( )sin( ) sin( ) sin( )cos( ) cos( )sin( ) jj jj ee ee j

图上泽通大学 Differentiation of complex polar vectors: Let R=R ei represent the position of a point with respect to a fixed reference origin,then First order: d(RRe+R(j)-ke+Roje" Second order: (Re=Re+Rdje+(Ra+0je+RaUe°7间 d -Re0+20Rj er+Rj e-ROelo =(R-R02)ei0+(20R+0R)j ei 上潘久大学 Second order: (R)-Re(Re d' =e+20Re+8Re°-R0e° =(R-RO)e+(20R+0R)j e 20Rj e Rj e hen R ROe 0 9
9 Differentiation of complex polar vectors: j R e Let repres R ent the position of a point with respect to a fixed reference origin, then First order: ( ) ( )= d j jj j j R e Re R e j Re R j e dt 2 2 2 2 Second order: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = 2 =( ) +(2 ) jj j j j j j jj j d R e Re R j e R R j e R je j dt Re Rj e Rj e R e RR e R R j j e X Y O R j j e j Re j R j e j e j Re 2 j R e 2 j Rj e j Rj e P 2 2 2 2 Second order: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = 2 =( ) +(2 ) jj j j j j j jj j d R e Re R j e RR j e R je j dt Re Rj e Rj e R e RR e R R j j e
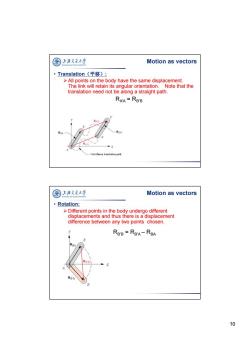
图 上海文通大¥ Motion as vectors ·Translation(平移): >All points on the body have the same displacement. The link will retain its angular orientation.Note that the translation need not be along a straight path. RAA=RBB R RBB RBA RBA RA Curvilinear translation path 国上泽支大半 Motion as vectors ·Rotation: >Different points in the body undergo different displacements and thus there is a displacement difference between any two points chosen. RBB=RBA-RBA RBA RB'B RBA 10
10 • Translation(平移): All points on the body have the same displacement. The link will retain its angular orientation. Note that the translation need not be along a straight path. RA’A = RB’B Motion as vectors • Rotation: Different points in the body undergo different displacements and thus there is a displacement difference between any two points chosen. RB’B = RB’A – RBA Motion as vectors
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture4 Electric Motors.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture12-I Gears.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture11 Cam Design.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture10 Belt Drives.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture-2 Kinematic Fundamentals.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture-1 Introduction to Design.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture-0 Course Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 7 Kinematic Analysis of Mechanisms.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 5 Graphical Linkage Synthesis.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 3 Planar Linkages.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 13 Bearings.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 12-III Gear design.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 12-II gear train.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《形象思维与工程语言》教学资源_教学课件_Lec08_02_Eng Lang_03基本表达方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《形象思维与工程语言》教学资源_教学课件_Lec08_01_Eng Lang_02组合体视图.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《形象思维与工程语言》教学资源_教学课件_Lec07_02_Eng Lang_01基本立体投影.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《形象思维与工程语言》教学资源_教学课件_Lec07_01_Eng Lang_Intro.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《形象思维与工程语言》教学资源_教学课件_Lec06_QFD02-new.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《形象思维与工程语言》教学资源_教学课件_Lec05_QFD01-new.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《形象思维与工程语言》教学资源_教学课件_Lec04_课程设计.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture8 Transmission Power Screws.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture9 Threaded Fasteners.pdf
- 《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资料:Potential Projects for Fall 2014.docx
- 上海交通大学:《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(讲义)Project Material Design ReviewI(for refer).pdf
- 《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资料:Reading material-Motors.pdf
- 《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(参考教材)《Design Of Machinery》(Robert Norton,2Nd Edition).pdf
- 《Design and manufacturing(ME371、ME337)》课程教学资源(参考教材)《Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design》(Richard G. Budynas、J. Keith Nisbett,Ninth Edition).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《自然界中的混沌与分岔》课程教学资源(实验指导书)混沌电路系统的设计与实验研究.doc
- 《自然界中的混沌与分岔》课程教学材料:武汉大学出版社《混沌及其应用》(第二版,共十一章).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《弹塑性力学》课程教学资源(讲义)绪论(胡永祥).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《弹塑性力学》课程教学资源(讲义)应力分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《弹塑性力学》课程教学资源(讲义)应变分析(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《弹塑性力学》课程教学资源(讲义)应变分析(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《弹塑性力学》课程教学资源(讲义)弹性与塑性应力应变关系.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《弹塑性力学》课程教学资源(讲义)弹性与塑性力学解题方法(1/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《弹塑性力学》课程教学资源(讲义)弹性与塑性力学解题方法(2/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《弹塑性力学》课程教学资源(讲义)弹性与塑性力学解题方法(3/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《制造工艺基础》课程教学资源(习题)第10章 复习思考题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《制造工艺基础》课程教学资源(习题)第01章 复习思考题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《制造工艺基础》课程教学资源(习题)第02章 复习思考题.pdf
