《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 02 Decoder and demultiplexer
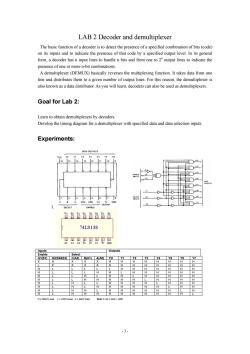
LAB 2 Decoder and demultiplexer The basic function of a decoder is to detect the presence of a specified combination of bits(code) on its inputs and to indicate the presence of that code by a specified output level.In its general form,a decoder has n input lines to handle n bits and from one to 2"output lines to indicate the presence of one or more n-bit combinations. A demultiplexer(DEMUX)basically reverses the multiplexing function.It takes data from one line and distributes them to a given number of output lines.For this reason,the demultiplexer is also known as a data distributor.As you will learn,decoders can also be used as demultiplexers. Goal for Lab 2: Learn to obtain demultiplexers by decoders. Develop the timing diagram for a demultiplexer with specified data and data selection inputs. Experiments: DATA OUTPUTS Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 16 1514131121110 G2A G2B G1 SELECT ENABLE t01246 同4国同团回可 74LS138 inputs Outputs Enable Select G1S1)G2(S2&S3)CA2)B(A1)A(A0) IYO Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7 X H X X X H H H H H H H X X H H H H H H H H H H H H H H L H H H H H H H H H H H H H L H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H L H H H H H H H H H H H H=HIGH Level L=LOW Level X=Don't Care Note 1:G2=G2A G2B -3-
- 3 - LAB 2 Decoder and demultiplexer The basic function of a decoder is to detect the presence of a specified combination of bits (code) on its inputs and to indicate the presence of that code by a specified output level. In its general form, a decoder has n input lines to handle n bits and from one to 2n output lines to indicate the presence of one or more n-bit combinations. A demultiplexer (DEMUX) basically reverses the multiplexing function. It takes data from one line and distributes them to a given number of output lines. For this reason, the demultiplexer is also known as a data distributor. As you will learn, decoders can also be used as demultiplexers. Goal for Lab 2: Learn to obtain demultiplexers by decoders. Develop the timing diagram for a demultiplexer with specified data and data selection inputs. Experiments: 1. inputs Enable Select Outputs G1(S1) G2(S2&S3) C(A2) B(A1) A(A0) YO Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7 X H X X X H H H H H H H H L X X X X H H H H H H H H H L L L L L H H H H H H H H L L L H H L H H H H H H H L L H L H H L H H H H H H L L H H H H H L H H H H H L H L L H H H H L H H H H L H L H H H H H H L H H H L H H L H H H H H H L H H L H H H H H H H H H H L H HIGH Level L LOW Level X Don’t Care Note 1: G2 G2A G2B

When inputs change from 000 to 111,the outputs are shown in Truth Table 2.Connect the circuit to it. Truth Table 2 inputs outputs C B A (A2) (A1) (A0) YO YI Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 (Only when S1=1,S2=0,S3=0, there are 0=A2AA,头1=A2A1A, 2=A2AA0… y,=AAA). Obtain demultiplexers by decoders Input signal:square wave,1KHz,Vp-p=5V 1.The input signal is at pin"S1".It is a square waveform,while S2S3=00 and A2A1A0=101 input signal: Then,the output signal at( Draw its waveform 2.The input signal is at pin“S2”and“S3”.It is a square waveform,while S1=land A2A1A0=010 Input signal Now,the output signal at Draw its waveform. Output signal -4-
- 4 - When inputs change from 000 to 111, the outputs are shown in Truth Table 2. Connect the circuit to it. Truth Table 2 inputs outputs C (A2) B (A1) A (A0) Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Y6 Y7 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 (Only when S1=1,S2=0,S3=0, there are 0 y = 2 A AA1 0 , 1 y = 2 1 A AA0 , 2 y = 2 0 AAA1 …… 7 y =AAA 210 ). Obtain demultiplexers by decoders Input signal: square wave , 1KHz ,Vp-p= 5V 1.The input signal is at pin “S1”. It is a square waveform, while S2S3=00 and A2A1A0=101 input signal : Then, the output signal at ( ) ) Draw its waveform. 2.The input signal is at pin “S2” and “S3” . It is a square waveform, while S1=1 and A2A1A0=010 Input signal: Now, the output signal at ( ) Draw its waveform. Output signal:
3.Let input signal at A2,A1A0=10,S1=1,S2=0,S3=0.Draw two output signals. Input signal (A2) Output signal 1:( Output signal 2:( 4.Let input signal at A2,A1A0=01,S1=1,S2=0,S3=0.Find two output signals Input signal :(A2) Now Output signal 1:( Output signal 2:( -5-
- 5 - 3.Let input signal at A2, A1A0=10, S1=1,S2=0,S3=0. Draw two output signals. Input signal :(A2) Output signal 1:( ) Output signal 2:( ) 4. Let input signal at A2, A1A0=01, S1=1,S2=0,S3=0. Find two output signals. Input signal :(A2) Now Output signal 1:( ) Output signal 2:( )
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 12&13 Feedback amplifiers.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 11 OBJECTIVES.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 01 Combinational Logic.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微电子学概论》课程教学资源_图灵奖下的人类智力延伸——-计算、集成电路及应用.pdf
- 《微电子学概论》课程教学资源:用十分鐘瞭解《圖靈獎得主》的學術貢獻.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_Novel Applications of Deep Learning Hidden Features for Adaptive Testing.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_IC design-for-test and testability features.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_Design, Manufacturing & Test of Integrated Circuits in the Nanotechnology Era.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_DESIGN AND TESTING OF COMBINATIONAL LOGIC CIRCUITS USING BUILT IN SELF TEST SCHEME FOR FPGAs.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_An introduction to IC testing.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_3D DFT challenges and solutions.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(课程实验)Lab #1:HSPICE Simulation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(课程实验)HSPICE SIMULATION.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(讲义)Introduction(Semiconductor processing).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电路基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 电路分析的基本方法 §2.8 回路分析法 §2.9 节点分析法.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《通信基本电路》课程教学资源(参考资料)Fundamental of Communication Circuits Lecture 1 Introduction.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《电路基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 电路定理 §3.4 互易定理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《电路基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 电路定理 §3.3 戴维宁定理和诺顿定理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《电路基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 电路定理 §3.1 替代定理 §3.2 叠加定理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《电路基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 电路分析的基本方法 §2.14 二端口电路的端口特性分析 §2.15 电路的对偶性.ppt
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 03 Edged-triggered Flip-Flops.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 04 counters.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 05 & 06 op-amp:adder、Integrator & Differentiator.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 07 & 08 filter、Function Generator.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 09 & 10 Transistor Amplifier.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《通信原理与实验 Principles and Experiments of Communications》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)Intro.ppt
- 《通信原理与实验 Principles and Experiments of Communications》课程参考书:John G. Proakis Masoud Salehi《Fundamentals of Communication Systems》(Second Edition).pdf
- 《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(扩展知识)A Brief History of Measurement Systems.pdf
- 《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(扩展知识)Cross-Linked Gold Nanoparticles on Polyethylene:Resistive Responses to Tensile Strain and Vapors.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(扩展知识)Strain rate-dependent tensile properties and dynamic electromechanical response of carbon nanotube fibers.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(扩展知识)In the memorial of a great author.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Configuration and Functional Description.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 Generalized performance characteristics of instruments.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 Motion & Dimensional Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Force Torque and Shaft Power Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 Pressure and Sound Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 Flow Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Temperature and Heat-Flux Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Miscellaneous Measurements.pdf
