《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 09 & 10 Transistor Amplifier

Lab 9 Transistor Amplifier:part 1 cc Fig.1Basic common-emitter amplifying circuit. (a) (b) Fig.2 Voltage amplifier cl Fig.3 Cut-off distortion
Lab 9 Transistor Amplifier: part 1 Fig.1Basic common-emitter amplifying circuit. Fig.2 Voltage amplifier Fig.3 Cut-off distortion
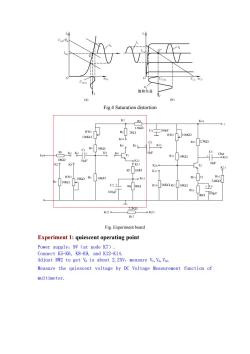
。 饱和失真 (a) (b) Fig.4 Saturation distortion K18 1.5K2 RW2 R5 C -200F RW3 100K I00K2 K106 C3 R13 2.7K2 K9 R4 K11。 10K2 RI Ks 10 C5 Ino K6 T R11 Ou 10K2 K20 10K2 o12 K49 9K13 10F K160- T2 I002 S1 K179 RWI 10K2 R3 10K2 oK14 R14 51 R16 R2 10K2 3.6K2 C2+ R10 B.6K2R12 +C6 R15 100F IK 100uF 2水☒工 K220 -o K23 R17 Fig.Experiment board Experiment 1:quiescent operating point Power supply:9V (at node K7). Connect K5-K6,K8-K9,and K12-K14. Adjust RW2 to get Va is about 2.25V,measure Vc,VE,Vce. Measure the quiescent voltage by DC Voltage Measurement function of multimeter
Fig.4 Saturation distortion Fig. Experiment board Experiment 1: quiescent operating point Power supply:9V(at node K7). Connect K5-K6, K8-K9, and K12-K14. Adjust RW2 to get VB is about 2.25V,measure VC,VE,VCE. Measure the quiescent voltage by DC Voltage Measurement function of multimeter
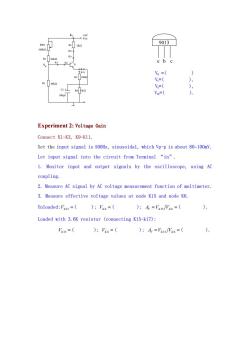
+9V RW2 9013 K5 K6 e b c K1 Va = ) 1002 V=( ), R3 V=( ), C2 Vo=( ) Experiment 2:Voltage Gain Connect K1-K3,K9-K11. Set the input signal is 500Hz,sinusoidal,which Vp-p is about 80~100mV. Let input signal into the circuit from Terminal "in". 1.Monitor input and output signals by the oscilloscope,using AC coupling. 2.Measure AC signal by AC voltage measurement function of multimeter. 3.Measure effective voltage values at node K15 and node K6. Unloaded:VKIs =)VKo=( ):A='k1s/Wk6=( ) Loaded with 3.6K resistor (connecting K15-k17): Vks=( ):Vk6=( ):A='xs/Wk6=( )
R4 10KΩ K5 K6 R3 10KΩ C2 100µF R8 1KΩ R7 100Ω K13 K12 K9 K8 R5 2KΩ + 100KΩ RW2 T1 +9V VCC VB K7 VB =( ) VC=( ), VE=( ), VCE=( ). Experiment 2: Voltage Gain Connect K1-K3, K9-K11. Set the input signal is 500Hz, sinusoidal, which Vp-p is about 80~100mV. Let input signal into the circuit from Terminal “in”. 1. Monitor input and output signals by the oscilloscope, using AC coupling. 2. Measure AC signal by AC voltage measurement function of multimeter. 3. Measure effective voltage values at node K15 and node K6. Unloaded:VK15 ( ); VK 6 ( ); AV V VKK 15 6 ( ). Loaded with 3.6K resistor (connecting K15-k17): VK15 ( ); VK 6 ( ); AV V VKK 15 6 ( )
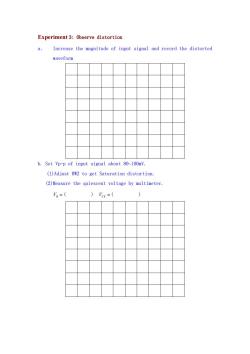
Experiment 3:Observe distortion a. Increase the magnitude of input signal and record the distorted waveform b.Set Vp-p of input signal about 80~100mV. (1)Adjust RW2 to get Saturation distortion. (2)Measure the quiescent voltage by multimeter. Va=( )'cE=(
Experiment 3: Observe distortion a. Increase the magnitude of input signal and record the distorted waveform b. Set Vp-p of input signal about 80~100mV. (1)Adjust RW2 to get Saturation distortion. (2)Measure the quiescent voltage by multimeter. VB ( ) VCE ( )

c.set Vp-p of input signal about 80~120mV. (2)Adjust RW2 to get Cut-off distortion. (3)Measure the quiescent voltage by multimeter. Va=( )'cE=(
c.set Vp-p of input signal about 80~120mV. (2)Adjust RW2 to get Cut-off distortion. (3)Measure the quiescent voltage by multimeter. VB ( ) VCE ( )

Lab 10 Transistor Amplifier:part 2 Experiment 1.Set quiescent operating point Power supply:9V (at node K7). Connect K5-K6,K8-K9,and K12-K14. Adjust RW2 to get Ve is about 2.25V, Experiment 2.Measure input resistance. Set the input signal is 500Hz,sinusoidal,which Vp-p is about 80~100mV. Let input signal into the circuit from Terminal "in". 1.Monitor input and output signals by the oscilloscope,using AC coupling. 2.Measure AC signal by AC voltage measurement function of multimeter. 3.Loaded with 3.6K resistor (connecting K15-k17) 4.Connect K1-K3,measure V=( ). Disconnect K1-K3 and connect K1-K4.Adjust Rpr to let Vx remain the same value. Disconnect Kl-K4,measure Rp1.Which is equal to the input resistance. Input resistance : ) Experiment 3.Calculate output resistance. Set the input signal is 500Hz,sinusoidal,which Vp-p is about 80-100mV. 1.Measure effective voltage values at node K15 Unloaded:v=(); Loaded with 3.6K Vo=( 0 2.Ro =(-1)XR Output resistance:
Lab 10 Transistor Amplifier: part 2 Experiment 1.Set quiescent operating point Power supply:9V(at node K7). Connect K5-K6, K8-K9, and K12-K14. Adjust RW2 to get VB is about 2.25V, Experiment 2.Measure input resistance. Set the input signal is 500Hz, sinusoidal, which Vp-p is about 80~100mV. Let input signal into the circuit from Terminal “in”. 1. Monitor input and output signals by the oscilloscope, using AC coupling. 2. Measure AC signal by AC voltage measurement function of multimeter. 3. Loaded with 3.6K resistor (connecting K15-k17) 4. Connect K1-K3, measure VK1 ( ). Disconnect K1-K3 and connect K1-K4. Adjust Rp1 to let VK1 remain the same value. Disconnect K1-K4,measure Rp1, Which is equal to the input resistance. Input resistance :( ) Experiment 3.Calculate output resistance. Set the input signal is 500Hz, sinusoidal, which Vp-p is about 80~100mV. 1. Measure effective voltage values at node K15 Unloaded: / O V =( ); Loaded with 3.6K : VO =( ) 2. RO =( O O V V / -1)×RL Output resistance:( )
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 07 & 08 filter、Function Generator.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 05 & 06 op-amp:adder、Integrator & Differentiator.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 04 counters.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 03 Edged-triggered Flip-Flops.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 02 Decoder and demultiplexer.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 12&13 Feedback amplifiers.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 11 OBJECTIVES.pdf
- 《Electronics Lab》课程教学资源:Lab 01 Combinational Logic.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《微电子学概论》课程教学资源_图灵奖下的人类智力延伸——-计算、集成电路及应用.pdf
- 《微电子学概论》课程教学资源:用十分鐘瞭解《圖靈獎得主》的學術貢獻.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_Novel Applications of Deep Learning Hidden Features for Adaptive Testing.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_IC design-for-test and testability features.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_Design, Manufacturing & Test of Integrated Circuits in the Nanotechnology Era.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_DESIGN AND TESTING OF COMBINATIONAL LOGIC CIRCUITS USING BUILT IN SELF TEST SCHEME FOR FPGAs.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_An introduction to IC testing.pdf
- 《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(阅读资料)IC testing_3D DFT challenges and solutions.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(课程实验)Lab #1:HSPICE Simulation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(课程实验)HSPICE SIMULATION.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《数字集成电路 Digital Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(讲义)Introduction(Semiconductor processing).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电路基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 电路分析的基本方法 §2.8 回路分析法 §2.9 节点分析法.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《通信原理与实验 Principles and Experiments of Communications》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)Intro.ppt
- 《通信原理与实验 Principles and Experiments of Communications》课程参考书:John G. Proakis Masoud Salehi《Fundamentals of Communication Systems》(Second Edition).pdf
- 《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(扩展知识)A Brief History of Measurement Systems.pdf
- 《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(扩展知识)Cross-Linked Gold Nanoparticles on Polyethylene:Resistive Responses to Tensile Strain and Vapors.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(扩展知识)Strain rate-dependent tensile properties and dynamic electromechanical response of carbon nanotube fibers.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(扩展知识)In the memorial of a great author.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Configuration and Functional Description.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 Generalized performance characteristics of instruments.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 Motion & Dimensional Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Force Torque and Shaft Power Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 Pressure and Sound Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 Flow Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Temperature and Heat-Flux Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Miscellaneous Measurements.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Manipulating Computing and Compensation Devices.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Measurement Systems:Application and Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Data Transmission and Instrument Connectivity.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》精品课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第1章 电路的基本概念与定律.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》精品课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第2章 电阻电路的一般分析方法.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》精品课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第3章 电路定理.ppt
