南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)12 Secure Socket Layer(SSL)、TLS(Transport Layer Security)

Secure Socket Layer (SSL)/ TLS (Transport Layer Security) Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) / TLS (Transport Layer Security) Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University

SSL/TLS By far,SSL/TLS is the dominant security technology on the web Provide transport layer security -Any TCP/IP application can be protected by using SSL.For example, FTP communication or Telnet or HTTP communication can be protected by using SSL. -HTTPS is HTTP over SSL Responsible for the emergence of e-commerce,other security sensitive services on the web Beneficiary of several years of public scrutiny 2
2 SSL/TLS By far, SSL/TLS is the dominant security technology on the web Provide transport layer security ─ Any TCP/IP application can be protected by using SSL. For example, FTP communication or Telnet or HTTP communication can be protected by using SSL. ─ HTTPS is HTTP over SSL Responsible for the emergence of e-commerce, other security sensitive services on the web Beneficiary of several years of public scrutiny
SSL/TLS in the Real World Wells Fargo Account Summary -Microsoft Internet Explorer ×☒ Eile Edit Yiew Favorites Iools Help 中Back·→,⑧Favorites固} Address https://online.wellsfargo.com/mn1__on/cgi-bin/session.cgi7sessargs-coAn76ax52xitPxBuoCTrRBfMMdidxGo LinksYahoo mapsMapblastDictionary Home Help Center|Cortact Us Locations I Ste Map I Apply I Sign off T写 FARGO 物 Account Summary Last Log On:January 06,2004 >Account Summary Brokerage Wells Fargo Accounts OneLook Accounts Bill Pay Transfer Tip:Select an account's balance to access the Account History. Account Services 前roS鱼 My Message Center My Message Center Cash Accounts Account Account Number Available Balance Stay organized Checking色d Bll Pey with FREE 24/7 Total access to Online To end your session,be sure to Sign Om. Statements. Sign up today. Account Summary Brokerage Bill Pay Transfer I My Message Center Sign Otf Sign up for the Home Help Center Cortact Us Locations I Ste Map Apply Wells Fargo Rewards" program and get 1995-2003 Wells Fargo.All rights reserved. 2,500 points. Learn More. 3
3 SSL / TLS in the Real World

History of the Protocol ■SSL1.0 -Internal Netscape design.Never deployed. The idea was proposed in Thomas Y.C.Woo,Raghuram Bindignavle,Shaowen Su, and Simon S.Lam,"SNP:An Interface for Secure Network Programming," USENIX 1994. ■SSL2.0 Published by Netscape,November 1994 Several weaknesses Microsoft improved upon SSL v2,and call it PCT(Private Communication Technology). ■SSL3.0 Designed by Netscape and Paul Kocher,November 1996 SSL v3 is deployed in nearly every Web browser. TLS(Transport Layer Security)1.0 by IETF. Internet standard based on SSL 3.0,January 1999 -Not interoperable with SSL 3.0 4
4 History of the Protocol SSL 1.0 ─ Internal Netscape design. Never deployed. ─ The idea was proposed in Thomas Y. C. Woo, Raghuram Bindignavle, Shaowen Su, and Simon S. Lam, "SNP: An Interface for Secure Network Programming," USENIX 1994. SSL 2.0 ─ Published by Netscape, November 1994 ─ Several weaknesses Microsoft improved upon SSL v2, and call it PCT (Private Communication Technology). SSL 3.0 ─ Designed by Netscape and Paul Kocher, November 1996 ─ SSL v3 is deployed in nearly every Web browser. TLS (Transport Layer Security) 1.0 by IETF. ─ Internet standard based on SSL 3.0, January 1999 ─ Not interoperable with SSL 3.0

RFC:Request for Comments Network protocols are usually disseminated in the form of an RFC TLS version 1.0 is described in RFC 2246 Intended to be a self-contained definition of the protocol -Describes the protocol in sufficient detail for readers who will be implementing it and those who will be doing protocol analysis -Mixture of informal prose and pseudo-code 5
5 RFC: “Request for Comments” Network protocols are usually disseminated in the form of an RFC TLS version 1.0 is described in RFC 2246 Intended to be a self-contained definition of the protocol ─ Describes the protocol in sufficient detail for readers who will be implementing it and those who will be doing protocol analysis ─ Mixture of informal prose and pseudo-code

Why SSL?SSL Provides Confidentiality (Privacy) Data integrity (Tamper-proofing) -done as part of digital signing. ■ Server authentication(Proving a server is what it claims it is) Used in typical B2C transactions Optional client authentication -Would be required in B2B(or Web services environment in which program talks to program) Why not B2C:server use passwords to authenticate clients,not certificates.Clients normally do not have certificates. 6
6 Why SSL? SSL Provides ... Confidentiality (Privacy) Data integrity (Tamper-proofing) ─ done as part of digital signing. Server authentication (Proving a server is what it claims it is) Used in typical B2C transactions Optional client authentication ─ Would be required in B2B (or Web services environment in which program talks to program) ─ Why not B2C: server use passwords to authenticate clients, not certificates. Clients normally do not have certificates

TLS Basics TLS consists of two protocols ■Handshake protocol -Use public-key cryptography to establish a shared secret key between the client and the server Record protocol -Use the secret key established in the handshake protocol to protect communication between the client and the server We will focus on the handshake protocol 7
7 TLS Basics TLS consists of two protocols Handshake protocol ─ Use public-key cryptography to establish a shared secret key between the client and the server Record protocol ─ Use the secret key established in the handshake protocol to protect communication between the client and the server We will focus on the handshake protocol

TLS Handshake protocol Two parties:client and server Negotiate version of the protocol and the set of cryptographic algorithms to be used -Interoperability between different implementations of the protocol Authenticate server and client (optional) Use digital certificates to learn each other's public keys and verify each other's identity Use public keys to establish a shared secret 8
8 TLS Handshake Protocol Two parties: client and server Negotiate version of the protocol and the set of cryptographic algorithms to be used ─ Interoperability between different implementations of the protocol Authenticate server and client (optional) ─ Use digital certificates to learn each other’s public keys and verify each other’s identity Use public keys to establish a shared secret
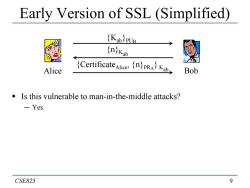
Early Version of SSL (Simplified) (KabpUp njKab Alice CertificateliceKab Bob Is this vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks? -Yes. CSE825 9
9 Early Version of SSL (Simplified) Is this vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks? ─ Yes. CSE825 Alice Bob {n}Kab {CertificateAlice, {n}PRA} Kab {Kab}PUB
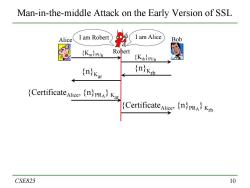
Man-in-the-middle Attack on the Early Version of SSL Alice I am Robert I am Alice Bob (KarPUR Robert {Krb}PUB (nKar nK CertificateAlicenRKat Certificatelicen CSE825 10
10 Man-in-the-middle Attack on the Early Version of SSL CSE825 {Kar}PUR Alice Bob Robert I am Robert I am Alice {Krb}PUB {n}K {n}K rb ar {CertificateAlice, {n}PRA} Kar {CertificateAlice, {n}PRA} Krb
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)11 Public-Key Infrastructure.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)10 Kerberos.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)09 Authentication Using Symmetric Keys.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)08 Authentication Using Asymmetric Keys.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 Hashes and Message Digests.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 Number Theory.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 Asymmetric Key Cryptography.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Advanced Encryption Standard(AES).pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 Symmetric Key Cryptography.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 Security Principles.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 Introduction(戴海鹏).pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 09 图形用户界面的设计与实现.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 08 数据结构与算法.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 07 Java 工具类.pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 06 继承与多态.pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 05 Java 类.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 05 Java 类.pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 04 Java 语言基础.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 03 Java 编程入门.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 03 Java 编程入门.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)13 Human Authentication.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)14 Buffer Overflow Attacks.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)15 Bloom Filters and its Variants.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)16 Bloom Filter for Network Security.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)17 Web Security(Cookies and Cross Site Scripting,XSS).pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)18 Web Security(SQL Injection and Cross-Site Request Forgery).pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)19 Firewall Design Methods.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)MPI A Message-Passing Interface Standard(Version 2.2).pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)An Asymmetric Distributed Shared Memory Model for Heterogeneous Parallel Systems.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Software and the Concurrency Revolution.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Some Computer Organizations and Their Effectiveness.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Optimization Principles and Application Performance Evaluation of a Multithreaded GPU Using CUDA.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Program Optimization Space Pruning for a Multithreaded GPU.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Single-pass Parallel Prefix Scan with Decoupled Look-back.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)NVIDIA Parallel Prefix Sum(Scan)with CUDA(April 2007).pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Methods of conjugate gradients for solving linear systems.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)NVIDIA CUDA C Programming Guide(Design Guide,June 2017).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introduction To Cuda C.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 CUDA PARALLELISM MODEL.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 MEMORY AND DATA LOCALITY.pdf
