南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 Hashes and Message Digests

Hashes and Message Digests Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
Hashes and Message Digests Haipeng Dai haipengdai@nju.edu.cn 313 CS Building Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
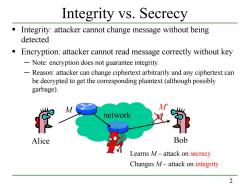
Integrity vs.Secrecy Integrity:attacker cannot change message without being detected Encryption:attacker cannot read message correctly without key -Note:encryption does not guarantee integrity. Reason:attacker can change ciphertext arbitrarily and any ciphertext can be decrypted to get the corresponding plaintext(although possibly garbage). M network Alice Bob Learns M-attack on secrecy Changes M-attack on integrity 2
2 Integrity vs. Secrecy Integrity: attacker cannot change message without being detected Encryption: attacker cannot read message correctly without key ─ Note: encryption does not guarantee integrity. ─ Reason: attacker can change ciphertext arbitrarily and any ciphertext can be decrypted to get the corresponding plaintext (although possibly garbage). network Learns M – attack on secrecy Alice Bob M M Changes M – attack on integrity M’
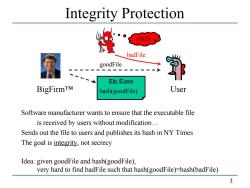
Integrity Protection VIRUS badFile goodFile ①小e①ites BigFirmTM hash(goodFile) User Software manufacturer wants to ensure that the executable file is received by users without modification... Sends out the file to users and publishes its hash in NY Times The goal is integrity,not secrecy Idea:given goodFile and hash(goodFile), very hard to find badFile such that hash(goodFile)-hash(badFile) 3
3 Integrity Protection Software manufacturer wants to ensure that the executable file is received by users without modification… Sends out the file to users and publishes its hash in NY Times The goal is integrity, not secrecy Idea: given goodFile and hash(goodFile), very hard to find badFile such that hash(goodFile)=hash(badFile) goodFile BigFirm™ User VIRUS badFile The Times hash(goodFile)
Authentication Authenticity is identification and assurance of origin of information -We'll see many specific examples in different scenarios network 第 4
4 Authentication Authenticity is identification and assurance of origin of information ─ We’ll see many specific examples in different scenarios network
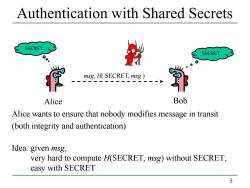
Authentication with Shared Secrets SECRET SECRET msg,H(SECRET,msg) Alice Bob Alice wants to ensure that nobody modifies message in transit (both integrity and authentication) Idea:given msg, very hard to compute H(SECRET,msg)without SECRET; easy with SECRET 5
5 Authentication with Shared Secrets Alice wants to ensure that nobody modifies message in transit (both integrity and authentication) Idea: given msg, very hard to compute H(SECRET, msg) without SECRET; easy with SECRET msg, H( SECRET, msg ) Alice Bob SECRET SECRET
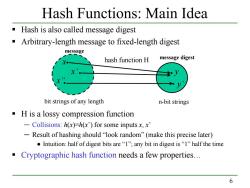
Hash Functions:Main Idea Hash is also called message digest Arbitrary-length message to fixed-length digest message hash function H message digest bit strings of any length n-bit strings H is a lossy compression function -Collisions:h(x)=h(x)for some inputs x,x' -Result of hashing should "look random"(make this precise later) ●Intuition:half of digest bits are“I',any bit in digest is“l”half the time Cryptographic hash function needs a few properties... 6
6 Hash Functions: Main Idea Hash is also called message digest Arbitrary-length message to fixed-length digest H is a lossy compression function ─ Collisions: h(x)=h(x’) for some inputs x, x’ ─ Result of hashing should “look random” (make this precise later) ● Intuition: half of digest bits are “1”; any bit in digest is “1” half the time Cryptographic hash function needs a few properties… bit strings of any length n-bit strings . . . . . x’ x’’ x y’ y hash function H message digest message

Hashes and Message Digest One-wayness:given h(x),hard to find x -Also called“pre-image resistance” Collision resistance:hard to find x,x'such that h(x)=h(x') -Also called "strong collision resistance" -Brute-force collision search is only O(2n/2),not 2n -Birthday Paradox -n needs to be at least 128 ■ Weak collision resistance:given x,hard to find x'such that h(x)=h(x') -Also called“second pre-image resistance” -Brute-force attack requires O(2m)time 7
7 Hashes and Message Digest One-wayness: given h(x), hard to find x ─ Also called “pre-image resistance” Collision resistance: hard to find x, x’ such that h(x)=h(x’) ─ Also called “strong collision resistance” ─ Brute-force collision search is only O(2n/2), not 2n ─ Birthday Paradox ─ n needs to be at least 128. Weak collision resistance: given x, hard to find x’ such that h(x)=h(x’) ─ Also called “second pre-image resistance” ─ Brute-force attack requires O(2n) time

One-Wayness Intuition:hash should be hard to invert -"Preimage resistance" -Leth(x)=y∈{0,l}for a random x' -Given y,it should be hard to find x such that h(x)= ▣How hard? -Brute-force:try every possible x,see if h(x)=y -SHA-1 (common hash function)has 160-bit output .Assuming 264 trials per second,can do 289 trials per year Will take 271 years to invert SHA-1 on a random image 8
8 One-Wayness Intuition: hash should be hard to invert ─ “Preimage resistance” ─ Let h(x’) = y ∈{0,1}n for a random x’ ─ Given y, it should be hard to find x such that h(x)=y How hard? ─ Brute-force: try every possible x, see if h(x)=y ─ SHA-1 (common hash function) has 160-bit output ● Assuming 264 trials per second, can do 289 trials per year ● Will take 271 years to invert SHA-1 on a random image

Collision Resistance (CR) Should be hard to find x,x'such that h(x)h(x) -Brute-force collision search is only O(22),not O(2") -For SHA-1,this means O(280)vs.O(2160) 9
9 Collision Resistance (CR) Should be hard to find x, x’ such that h(x)=h(x’) ─ Brute-force collision search is only O(2n/2), not O(2n) ─ For SHA-1, this means O(280) vs. O(2160)
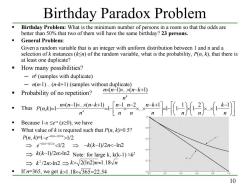
Birthday Paradox Problem Birthday Problem:What is the minimum number of persons in a room so that the odds are better than 50%that two of them will have the same birthday?23 persons. General Problem: Given a random variable that is an integer with uniform distribution between 1 and n and a selection of k instances(ksn)of the random variable,what is the probability,P(n,k),that there is at least one duplicate? How many possibilities? -nk(samples with duplicate) n(n-1)...(n-k+1)(samples without duplicate) Probability of no repetition? nx(n-1)x.×(n-k+l) n ·msw。三卧】 Because 1-x 0.5? P(n,k)-1-e-k(k-by2n>1/2 →e-2mln2Note:for large k,kk-l)≈k2 →k2/2>ln2→k>√2ln2)n≈l.18vn 0.2 Ifn=365,we get k>1.18x√365=22.54 02 04 0.6 0.8 10
10 Birthday Paradox Problem Birthday Problem: What is the minimum number of persons in a room so that the odds are better than 50% that two of them will have the same birthday? 23 persons. General Problem: Given a random variable that is an integer with uniform distribution between 1 and n and a selection of k instances (k≤n) of the random variable, what is the probability, P(n, k), that there is at least one duplicate? How many possibilities? ─ nk (samples with duplicate) ─ n(n-1)…(n-k+1) (samples without duplicate) Probability of no repetition? Thus Because 1-x ≤e-x (x≥0), we have What value of k is required such that P(n, k)>0.5? P(n, k)= ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ Note: for large k, k(k-1) ≈k2 ⇒ ⇒ If n=365, we get k n n×(n−1)×...×(n−k+1) − × × − × − = − − − + × × − × − = − × − × × − + = − n k n n n n k n n n n n n n n k P n k k 1 ... 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 ... 1 2 1 ( 1) ... ( 1) ( , ) 1 1 1/2 ( 1)/2 − > −k k− n e 1/2 ( 1)/2 ln2 /2 ln2 2 k n> k> 2(ln2)n≈1.18 n k>1.18× 365=22.54
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 Number Theory.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 Asymmetric Key Cryptography.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Advanced Encryption Standard(AES).pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 Symmetric Key Cryptography.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 Security Principles.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 Introduction(戴海鹏).pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 09 图形用户界面的设计与实现.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 08 数据结构与算法.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 07 Java 工具类.pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 06 继承与多态.pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 05 Java 类.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 05 Java 类.pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 04 Java 语言基础.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 03 Java 编程入门.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 03 Java 编程入门.pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 02 Java 概述.ppt
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 10 Java 高级编程.pdf
- 南京大学:《Java语言程序设计 Programming in Java》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 01 面向对象软件开发概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《Linux操作系统内核技术 The Linux Kernel Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四讲 内核模块不可调试之谜.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《Linux操作系统内核技术 The Linux Kernel Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三讲 指针存储之谜.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)08 Authentication Using Asymmetric Keys.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)09 Authentication Using Symmetric Keys.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)10 Kerberos.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)11 Public-Key Infrastructure.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)12 Secure Socket Layer(SSL)、TLS(Transport Layer Security).pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)13 Human Authentication.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)14 Buffer Overflow Attacks.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)15 Bloom Filters and its Variants.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)16 Bloom Filter for Network Security.pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)17 Web Security(Cookies and Cross Site Scripting,XSS).pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)18 Web Security(SQL Injection and Cross-Site Request Forgery).pdf
- 南京大学:《网络安全与入侵检测 Network Security and Intrusion Detection》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)19 Firewall Design Methods.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)MPI A Message-Passing Interface Standard(Version 2.2).pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)An Asymmetric Distributed Shared Memory Model for Heterogeneous Parallel Systems.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Software and the Concurrency Revolution.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Some Computer Organizations and Their Effectiveness.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Optimization Principles and Application Performance Evaluation of a Multithreaded GPU Using CUDA.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Program Optimization Space Pruning for a Multithreaded GPU.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)Single-pass Parallel Prefix Scan with Decoupled Look-back.pdf
- 《GPU并行编程 GPU Parallel Programming》课程教学资源(参考文献)NVIDIA Parallel Prefix Sum(Scan)with CUDA(April 2007).pdf
