清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第九章 转录(Transcription)

Chapter 9 Transcription 清革大当
Chapter 9 Transcription

9.1 Introduction 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase 9.3 The transcription reaction has three stages 9.4 A stalled RNA polymerase can restart 9.5 RNA polymerase consists of multiple subunits 9.6 RNA Polymerase consists of the core enzyme and sigma factor 9.7 Sigma factor is released at initiation 9.8 Sigma factor controls binding to DNA 9.9 Promoter recognition depends on consensus sequences 9.10 Promoter efficiencies can be increased or decreased by mutation 9.11 RNA polymerase binds to one face of DNA 9.12 Supercoiling is an important feature of transcription 9.13 Substitution of sigma factors may control initiation 9.14 Sigma factors directly contact DNA 9.15 Sigma factors may be organized into cascades 9.16 Sporulation is controlled by sigma factors 9.17 Bacterial RNA polymerase has two modes of termination 9.18 There are two types of terminator in E.coli 9.19 How does rho factor work? 9.20 Antitermination is a regulatory event 9.21 Antitermination requires sites that are independent of the terminators 9.22 More subunits for RNA polymerase 情菜大当
9.1 Introduction 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase 9.3 The transcription reaction has three stages 9.4 A stalled RNA polymerase can restart 9.5 RNA polymerase consists of multiple subunits 9.6 RNA Polymerase consists of the core enzyme and sigma factor 9.7 Sigma factor is released at initiation 9.8 Sigma factor controls binding to DNA 9.9 Promoter recognition depends on consensus sequences 9.10 Promoter efficiencies can be increased or decreased by mutation 9.11 RNA polymerase binds to one face of DNA 9.12 Supercoiling is an important feature of transcription 9.13 Substitution of sigma factors may control initiation 9.14 Sigma factors directly contact DNA 9.15 Sigma factors may be organized into cascades 9.16 Sporulation is controlled by sigma factors 9.17 Bacterial RNA polymerase has two modes of termination 9.18 There are two types of terminator in E. coli. 9.19 How does rho factor work? 9.20 Antitermination is a regulatory event 9.21 Antitermination requires sites that are independent of the terminators 9.22 More subunits for RNA polymerase

9.1 Introduction Coding strand of DNA has the same sequence as mRNA. Downstream identifies sequences proceeding farther in the direction of expression;for example,the coding region is downstream of the initiation codon. Primary transcript is the original unmodified RNA product corresponding to a transcription unit. Promoter is a region of DNA involved in binding of RNA polymerase to initiate transcription. RNA polymerases are enzymes that synthesize RNA using a DNA template (formally described as DNA-dependent RNA polymerases). Terminator is a sequence of DNA,represented at the end of the transcript,that causes RNA polymerase to terminate transcription. Transeription unit is the distance between sites of initiation and termination by RNA polymerase;may include more than one gene. Upstream identifies sequences proceeding in the opposite direction from expression;for example,the bacterial promoter is upstream from the transcription unit,the initiation codon is upstream of the coding region. 清菜大兰
Coding strand of DNA has the same sequence as mRNA. Downstream identifies sequences proceeding farther in the direction of expression; for example, the coding region is downstream of the initiation codon. Primary transcript is the original unmodified RNA product corresponding to a transcription unit. Promoter is a region of DNA involved in binding of RNA polymerase to initiate transcription. RNA polymerases are enzymes that synthesize RNA using a DNA template (formally described as DNA-dependent RNA polymerases). Terminator is a sequence of DNA, represented at the end of the transcript, that causes RNA polymerase to terminate transcription. Transcription unit is the distance between sites of initiation and termination by RNA polymerase; may include more than one gene. Upstream identifies sequences proceeding in the opposite direction from expression; for example, the bacterial promoter is upstream from the transcription unit, the initiation codon is upstream of the coding region. 9.1 Introduction
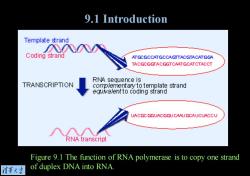
9.1 Introduction Template strand 入入0 Coding strand ATGCGCCATGCCAGTTACGTACATGGA TACGCGGTACGGTCAATGCATCTACCT RNA sequence is TRANSCRIPTION comp/emertary to template strand equva/entto coding strand LACGC GGUACGGUCAAUGCAUCUACCU RNA transcript Figure 9.1 The function of RNA polymerase is to copy one strand 情莱大当 of duplex DNA into RNA
Figure 9.1 The function of RNA polymerase is to copy one strand of duplex DNA into RNA. 9.1 Introduction

9.1 Introduction Figure 9.2 A transcription unit -20 -10 +1 +10+20+30+40 is a sequence of DNA transcribed into a single RNA, Startpoint starting at the Promoter proximal distal Teminator promoter and ending at the terminator. Downstream 清第大当
Figure 9.2 A transcription unit is a sequence of DNA transcribed into a single RNA, starting at the promoter and ending at the terminator. 9.1 Introduction

9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase Figure 9.3 Transcription takes place in a bubble,in which RNA is synthesized by base pairing with one strand of DNA in the transiently unwound region. As the bubble progresses, the DNA duplex reforms behind it,displacing the RNA in the form of a single polynucleotide chain. 清菜大当
Figure 9.3 Transcription takes place in a bubble, in which RNA is synthesized by base pairing with one strand of DNA in the transiently unwound region. As the bubble progresses, the DNA duplex reforms behind it, displacing the RNA in the form of a single polynucleotide chain. 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase

9.2 Transcription Enzym e movement is catalyzed by RNA polymerase DNA coding strand Rewind ing point Unwinding point Figure 9.4 During transcription,the bubble is maintained within bacterial RNA polymerase, which unwinds and rewinds DNA,maintains ONA template strand the conditions of the partner and template DNA strands,and synthesizes Catalytic site RNA. RNA bind ing site 清菜大当
Figure 9.4 During transcription, the bubble is maintained within bacterial RNA polymerase, which unwinds and rewinds DNA, maintains the conditions of the partner and template DNA strands, and synthesizes RNA. 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase
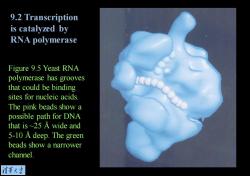
9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase Figure 9.5 Yeast RNA polymerase has grooves that could be binding sites for nucleic acids. The pink beads show a possible path for DNA that is ~25 A wide and 5-10 A deep.The green beads show a narrower channel. 清菜大当
Figure 9.5 Yeast RNA polymerase has grooves that could be binding sites for nucleic acids. The pink beads show a possible path for DNA that is ~25 Å wide and 5-10 Å deep. The green beads show a narrower channel. 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase

5 end of 5'nucleotide 9.2 Transcription triphosphate being added to chain is catalyzed by 0P,0 RNA polymerase Figure 9.6 Phosphodiester bond formation involves a hydrophilic attack by the 0=P0 3'-OH group of the last nucleotide of the chain on OH the 5'triphosphate of the Pyrophosphate is released incoming nucleotide,with release of pyrophosphate 清苇大兰
Figure 9.6 Phosphodiester bond formation involves a hydrophilic attack by the 3’-OH group of the last nucleotide of the chain on the 5’ triphosphate of the incoming nucleotide, with release of pyrophosphate. 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase

9.2 Transcription 工 is catalyzed by RNA polymerase Badk and ef enzyme 进进进进进进进 Figure 9.6 RNA polymerase moves like an inchworm during elongation, when it compresses from the back end and release from the front end 清菜大当
Figure 9.6 RNA polymerase moves like an inchworm during elongation, when it compresses from the back end and release from the front end. 9.2 Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第八章 蛋白质定位(Protein localization).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第七章 遗传密码的利用(Using the genetic code).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第六章 蛋白质合成(Protein synthesis).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第五章 信使RNA(Messenger RNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第四章 簇和重复(Clusters and repeats).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第三章 有多少基因(How many genes are there).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二章 从基因到基因组(From Genes to Genomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第一章 基因是DNA(Genes are DNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)绪论 Molecular Biology(主讲:王钊).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 免疫多样性产生的机制.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 病毒的分子生物学.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 遗传重组.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 真核生物基因表达调控.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 原核生物基因表达调控.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 蛋白质翻译(Protein Translation).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 RNA转录(RNA transcription).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 DNA损伤、修复和突变.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 DNA复制(DNA Replication).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 有机体、染色体和基因.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 DNA的结构.ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十章 操纵子(The operon).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十一章 噬菌体的战略(Phage strategies).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十二章 复制子(The replicon).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十三章 DNA复制(DNA replication).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十四章 重组和修复(Recombination and repair).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十五章 转座子(Transposons).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十六章 逆转录病毒和逆转座子(Retroviruses and retroposons).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十七章 DNA的重新排列(Rearrangement of DNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十八章 染色体(Chromosomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十九章 核小体(Nucleosomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十章 转录的起始(Initiation of transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十一章 转录的调控(Regulation of Transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十二章 核的剪切(Nuclear splicing).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十三章 催化RNA(Catalytic RNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十四章 免疫多样性(Immune diversity).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十五章 蛋白质间的开放交通(Protein trafficking).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十六章 信号的传输(Signal transduction).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十七章 细胞循环和生长调控(Cell cycle and growth regulation).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十八章 致癌基因和癌症(Oncogenes and cancer).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十九章 梯度、级联和发信号的途径(Gradients, cascades, and signaling pathways).ppt
