清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十章 转录的起始(Initiation of transcription)

Chapter 20 Initiation of transcription 清苇大当
Chapter 20 Initiation of transcription

20.1 Introduction 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting 20.4 RNA polymerase I has a bipartite promoter 20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters 20.6 The startpoint for RNA polymerase II 20.7 TBP is a universal factor 20.8 TBP binds DNA in an unusual way 20.9 The basal apparatus assembles at the promoter 20.10 Initiation is followed by promoter clearance 20.11 A connection between transcription and repair 20.12 Promoters for RNA polymerase II have short sequence elements 20.13 Some promoter-binding proteins are repressors 20.14 Enhancers contain bidirectional elements that assist initiation 20.15 Independent domains bind DNA and activate transcription 20.16 The two hybrid assay detects protein-protein interactions 20.17 Interaction of upstream factors with the basal apparatus 清苇大兰
20.1 Introduction 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting 20.4 RNA polymerase I has a bipartite promoter 20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters 20.6 The startpoint for RNA polymerase II 20.7 TBP is a universal factor 20.8 TBP binds DNA in an unusual way 20.9 The basal apparatus assembles at the promoter 20.10 Initiation is followed by promoter clearance 20.11 A connection between transcription and repair 20.12 Promoters for RNA polymerase II have short sequence elements 20.13 Some promoter-binding proteins are repressors 20.14 Enhancers contain bidirectional elements that assist initiation 20.15 Independent domains bind DNA and activate transcription 20.16 The two hybrid assay detects protein-protein interactions 20.17 Interaction of upstream factors with the basal apparatus

20.1 Introduction Enhancer element is a cis-acting sequence that increases the utilization of (some)eukaryotic promoters,and can function in either orientation and in any location (upstream or downstream) relative to the promoter. 情莘大当
Enhancer element is a cis-acting sequence that increases the utilization of (some) eukaryotic promoters, and can function in either orientation and in any location (upstream or downstream) relative to the promoter. 20.1 Introduction

20.1 Introduction Enhancer Prom oter Gene ~100bp ~200 bp upstream of startpoint Contains several Separation of Contains dispersed sequence elem ents dosely arranged enhancer from that bind transcription factors. sequence promoter m ay elements that bind be several kb Only the elem ents in the imm ediate transcription vicnity (200 bp.An enhancer containing a more closely packed array of elements that also bind transcription factors may be located several kb distant.(DNA may be coiled or otherwise rearranged so that transcription factors at the promoter 清菜大当 and at the enhancer interact to form a large protein complex.)
Figure 20.1 A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated. The promoter contains several short (200 bp. An enhancer containing a more closely packed array of elements that also bind transcription factors may be located several kb distant. (DNA may be coiled or otherwise rearranged so that transcription factors at the promoter and at the enhancer interact to form a large protein complex.) 20.1 Introduction

20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits Amanitin (more fully a-amanitin)is a bicyclic octapeptide derived from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides;it inhibits transcription by certain eukaryotic RNA polymerases, especially RNA polymerase II. 情華大当
Amanitin (more fully a-amanitin)is a bicyclic octapeptide derived from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides; it inhibits transcription by certain eukaryotic RNA polymerases, especially RNA polymerase II. 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits
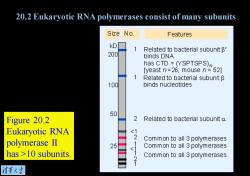
20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits Size No. Features kD 1 Related to bacterial subunit B' 200 binds DNA has CTD =(YSPTSPS) [yeast n=26;mouse n =52] 1 Related to bacterial subunit B 100 binds nucleotides 50 Figure 20.2 2 Related to bacterial subunito Eukaryotic RNA 10 subunits. 2 Common to all 3 polymerases 清苇大当
Figure 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerase II has >10 subunits. 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits

20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting Cotransfection is the simultaneous transfection of two markers. 清菜大当
Cotransfection is the simultaneous transfection of two markers. 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting

Upstream Promoter Transcribed region 20.3 Promoter 八入入八八NN elements are defined N八八八八N by mutations and Delete and reconnect footprinting NN八N入NNN Figure 20.3 Promoter boundaries Transcription can be determined by making RNA still made: deletions that progressively deletion does not enter promoter remove more material from one N入八八入入八八 side.When one deletion fails to Delete and reconnect prevent RNA synthesis but the next stops transcription,the NiN八入NN boundary of the promoter must lie between them. No RNA made:deletion has entered promoter 清第大当 Upstream boundary of promoter lies between ends of deletions
Figure 20.3 Promoter boundaries can be determined by making deletions that progressively remove more material from one side. When one deletion fails to prevent RNA synthesis but the next stops transcription, the boundary of the promoter must lie between them. 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting

P ol I prom oters have two sequence components 20.4 RNA CTCCGAGTCGNNNNNNTGGGC Startpoint polymerase I has a Upstream control element Core prom oter -170160-150-140.130120.110 -605040-30-2010+10+20 bipartite promoter 入NM八NNN八N八八八八八 The initiation complex assembles in three stages Figure 20.4 Transcription units UBFI UBFI binds to G-C-rich sequence for RNA polymerase I have a core promoter separated by ~70 bp from the upstream control 八八代NN八八八入心 element.UBF1 binds to both SL1 SL1 binds cooperatively with UBF1 regions,after which SLI can bind.RNA polymerase I then binds to the core promoter.The N入NN入八入 nature of the interaction between the factors bound at the Poll upstream control element and those at the core promoter is not N八NNN入NNN known 情華大当
Figure 20.4 Transcription units for RNA polymerase I have a core promoter separated by ~70 bp from the upstream control element. UBF1 binds to both regions, after which SL1 can bind. RNA polymerase I then binds to the core promoter. The nature of the interaction between the factors bound at the upstream control element and those at the core promoter is not known. 20.4 RNA polymerase I has a bipartite promoter

20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters Preinitiation complex in eukaryotic transcription describes the assembly of transcription factors at the promoter before RNA polymerase binds. 清菜大当
Preinitiation complex in eukaryotic transcription describes the assembly of transcription factors at the promoter before RNA polymerase binds. 20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十九章 核小体(Nucleosomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十八章 染色体(Chromosomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十七章 DNA的重新排列(Rearrangement of DNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十六章 逆转录病毒和逆转座子(Retroviruses and retroposons).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十五章 转座子(Transposons).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十四章 重组和修复(Recombination and repair).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十三章 DNA复制(DNA replication).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十二章 复制子(The replicon).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十一章 噬菌体的战略(Phage strategies).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十章 操纵子(The operon).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第九章 转录(Transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第八章 蛋白质定位(Protein localization).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第七章 遗传密码的利用(Using the genetic code).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第六章 蛋白质合成(Protein synthesis).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第五章 信使RNA(Messenger RNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第四章 簇和重复(Clusters and repeats).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第三章 有多少基因(How many genes are there).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二章 从基因到基因组(From Genes to Genomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第一章 基因是DNA(Genes are DNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)绪论 Molecular Biology(主讲:王钊).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十一章 转录的调控(Regulation of Transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十二章 核的剪切(Nuclear splicing).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十三章 催化RNA(Catalytic RNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十四章 免疫多样性(Immune diversity).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十五章 蛋白质间的开放交通(Protein trafficking).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十六章 信号的传输(Signal transduction).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十七章 细胞循环和生长调控(Cell cycle and growth regulation).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十八章 致癌基因和癌症(Oncogenes and cancer).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十九章 梯度、级联和发信号的途径(Gradients, cascades, and signaling pathways).ppt
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 植物的细胞和组织.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 植物体的形态结构和发育.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 植物的无机营养.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 光合作用.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 植物的繁殖.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 植物的生长发育及其调控.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第七章 生物多样性和植物的分类及命名.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第八章 藻类植物.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第九章 苔藓植物.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十章 蕨类植物.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十一章 裸子植物.pdf
