清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十九章 核小体(Nucleosomes)

Chapter 19 Nucleosomes 清革大当
Chapter 19 Nucleosomes

19.1 Introduction 19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin 19.3 DNA is coiled in arrays of nucleosomes 19.4 Nucleosomes have a common structure 19.5 DNA structure varies on the nucleosomal surface 19.6 Supercoiling and the periodicity of DNA 19.7 The path of nucleosomes in the chromatin fiber 19.8 Organization of the histone octamer 19.9 Histones are modified 19.10 Reproduction of chromatin requires assembly of nucleosomes 19.11 Do nucleosomes lie at specific positions? 19.12 Are transcribed genes organized in nucleosomes? 19.13 Histone octamers are displaced by transcription 19.14 DNAase hypersensitive sites change chromatin structure 19.15 Domains define regions that contain active genes 19.16 Heterochromatin propagates from a nucleation event 19.17 Heterochromatin depends on interactions with histones 19.18 X chromosomes undergo global changes 19.19 Chromosome condensation is caused by condensins 19.20 Methylation is perpetuated by a maintenance methylase 19.21 Methylation is responsible for imprinting 19.22 Epigenetic effects can be inherited 19.23 Yeast prions show unusual inheritance 19.24 Prions cause diseases in mammals 情莘大当
19.1 Introduction 19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin 19.3 DNA is coiled in arrays of nucleosomes 19.4 Nucleosomes have a common structure 19.5 DNA structure varies on the nucleosomal surface 19.6 Supercoiling and the periodicity of DNA 19.7 The path of nucleosomes in the chromatin fiber 19.8 Organization of the histone octamer 19.9 Histones are modified 19.10 Reproduction of chromatin requires assembly of nucleosomes 19.11 Do nucleosomes lie at specific positions? 19.12 Are transcribed genes organized in nucleosomes? 19.13 Histone octamers are displaced by transcription 19.14 DNAase hypersensitive sites change chromatin structure 19.15 Domains define regions that contain active genes 19.16 Heterochromatin propagates from a nucleation event 19.17 Heterochromatin depends on interactions with histones 19.18 X chromosomes undergo global changes 19.19 Chromosome condensation is caused by condensins 19.20 Methylation is perpetuated by a maintenance methylase 19.21 Methylation is responsible for imprinting 19.22 Epigenetic effects can be inherited 19.23 Yeast prions show unusual inheritance 19.24 Prions cause diseases in mammals

19.1 Introduction Histones are conserved DNA-binding proteins of eukaryotes that form the nucleosome,the basic subunit of chromatin. Nucleosome is the basic structural subunit of chromatin,consisting of~200 bp of DNA and an octamer of histone proteins. 清苇大当
Histones are conserved DNA-binding proteins of eukaryotes that form the nucleosome, the basic subunit of chromatin. Nucleosome is the basic structural subunit of chromatin, consisting of ~200 bp of DNA and an octamer of histone proteins. 19.1 Introduction

19.1 Introduction Centromere Figure 18.9 The sister chromatids of a mitotic pair each consist of a fiber(~30 nm in diameter)compactly folded into the chromosome.Photograph kindly provided by E.J.DuPraw. 情華大当
Figure 18.9 The sister chromatids of a mitotic pair each consist of a fiber (~30 nm in diameter) compactly folded into the chromosome. Photograph kindly provided by E. J. DuPraw. 19.1 Introduction

19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin Micrococcal nuclease is an endonuclease that cleaves DNA;in chromatin,DNA is cleaved preferentially between nucleosomes. 清苇大当
Micrococcal nuclease is an endonuclease that cleaves DNA; in chromatin, DNA is cleaved preferentially between nucleosomes. 19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin

19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin Figure 19.1 Chromatin spilling out of lysed nuclei consists of a compactly organized series of particles. The bar is 100 nm. Photograph kindly provided by Pierre Chambon. 情菜大学
Figure 19.1 Chromatin spilling out of lysed nuclei consists of a compactly organized series of particles. The bar is 100 nm. Photograph kindly provided by Pierre Chambon. 19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin

19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin Figure 19.2 Individual nucleosomes are released by digestion of chromatin with micrococcal nuclease.The bar is 100 nm.Photograph kindly provided by Pierre Chambon. 清苇大当
Figure 19.2 Individual nucleosomes are released by digestion of chromatin with micrococcal nuclease. The bar is 100 nm. Photograph kindly provided by Pierre Chambon. 19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin

19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin ●OH2A×2=28k0 ●0H2B×2=28k0 Figure 19.3 The N OOH3×2=30k0 nucleosome consists of O●H4×2=22k0 200 bp DNA=130 KD Total protein 108 kD approximately equal Length 67 nm masses of DNA and histones (including H1) The predicted mass of the H1=24 KD nucleosome is 262 kD. 6 nm 11nm 情華大当
Figure 19.3 The nucleosome consists of approximately equal masses of DNA and histones (including H1). The predicted mass of the nucleosome is 262 kD. 19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin

19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin Figure 19.4 The DNA "leaves nucleosome may be a cylinder with DNA organized into two turns DNA "enters" around the surface. 清菜大兰
Figure 19.4 The nucleosome may be a cylinder with DNA organized into two turns around the surface. 19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin
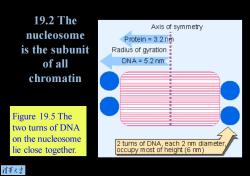
19.2 The Axis of symmetry nucleosome Protein 3.2 nm is the subunit Radius of gyration of all DNA=5.2 nm chromatin Figure 19.5 The two turns of DNA on the nucleosome 2 turns of DNA,each 2 nm diameter lie close together. occupy most of height (6 nm) 情莘大学
Figure 19.5 The two turns of DNA on the nucleosome lie close together. 19.2 The nucleosome is the subunit of all chromatin
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十八章 染色体(Chromosomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十七章 DNA的重新排列(Rearrangement of DNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十六章 逆转录病毒和逆转座子(Retroviruses and retroposons).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十五章 转座子(Transposons).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十四章 重组和修复(Recombination and repair).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十三章 DNA复制(DNA replication).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十二章 复制子(The replicon).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十一章 噬菌体的战略(Phage strategies).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十章 操纵子(The operon).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第九章 转录(Transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第八章 蛋白质定位(Protein localization).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第七章 遗传密码的利用(Using the genetic code).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第六章 蛋白质合成(Protein synthesis).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第五章 信使RNA(Messenger RNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第四章 簇和重复(Clusters and repeats).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第三章 有多少基因(How many genes are there).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二章 从基因到基因组(From Genes to Genomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第一章 基因是DNA(Genes are DNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)绪论 Molecular Biology(主讲:王钊).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 免疫多样性产生的机制.ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十章 转录的起始(Initiation of transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十一章 转录的调控(Regulation of Transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十二章 核的剪切(Nuclear splicing).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十三章 催化RNA(Catalytic RNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十四章 免疫多样性(Immune diversity).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十五章 蛋白质间的开放交通(Protein trafficking).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十六章 信号的传输(Signal transduction).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十七章 细胞循环和生长调控(Cell cycle and growth regulation).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十八章 致癌基因和癌症(Oncogenes and cancer).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十九章 梯度、级联和发信号的途径(Gradients, cascades, and signaling pathways).ppt
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 植物的细胞和组织.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 植物体的形态结构和发育.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 植物的无机营养.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 光合作用.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 植物的繁殖.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 植物的生长发育及其调控.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第七章 生物多样性和植物的分类及命名.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第八章 藻类植物.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第九章 苔藓植物.pdf
- 四川大学:《植物生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十章 蕨类植物.pdf
