清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第七章 遗传密码的利用(Using the genetic code)

Chapter 7 Using the genetic code 清革大当
Chapter 7 Using the genetic code

7.1 Introduction 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling 7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties 7.4 (There are sporadic alterations of the universal code) 7.5 tRNAs are charged with amino acids by synthetases 7.6 Accuracy depends on proofreading 7.7 Suppressor tRNAs have mutated anticodons that read new codons 7.8 The accuracy of translation 7.9 tRNA may influence the reading frame 情莘大当
7.1 Introduction 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling 7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties 7.4 (There are sporadic alterations of the universal code) 7.5 tRNAs are charged with amino acids by synthetases 7.6 Accuracy depends on proofreading 7.7 Suppressor tRNAs have mutated anticodons that read new codons 7.8 The accuracy of translation 7.9 tRNA may influence the reading frame

7.1 Introduction Stop codons are the three triplets (UAA,UAG. UGA)which terminate protein synthesis. 清苇大当
Stop codons are the three triplets (UAA, UAG, UGA) which terminate protein synthesis. 7.1 Introduction

900h啊 7.1 Introduction U 0 UUU Phe UCU UAU UUC UAC Tyr UGU UGC Cys UUA Ser UAA UUG Leu UAG STOPUGA STOP UGG Trp Figure 7.1 All the CUU triplet codons have cuc Leu CAU CAC His CGU cGc CUA CCA CAA CGA Arg CUG cce GIn meaning:61 CAG cGG represent amino Asn AGU AGCI Ser acids,and 3 cause AA Met Lys AGA AGG Arg termination (STOP) 勇 GAU GGU Val Ala GAC GGc GUG Glu GGA Gly CGG 情華大当
Figure 7.1 All the triplet codons have meaning: 61 represent amino acids, and 3 cause termination (STOP). 7.1 Introduction

7.1 Introduction Per cent of residues in protein 10 Le墙 8 Ala Gu● Gly Ser◆ Figure 7.2 The ●Val 6 ●Thr number of codons Pro Arge for each amino acid 4 does not correlate Mete closely with its T frequency of use in 2 3 4 5 6 proteins. Number of codons 清苇大当
Figure 7.2 The number of codons for each amino acid does not correlate closely with its frequency of use in proteins. 7.1 Introduction

7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling Wobble hypothesis accounts for the ability of a tRNA to recognize more than one codon by unusual (non-G C non-A T)pairing with the third base of a codon. 情莘大当
Wobble hypothesis accounts for the ability of a tRNA to recognize more than one codon by unusual (non-G C, non-A T) pairing with the third base of a codon. 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling
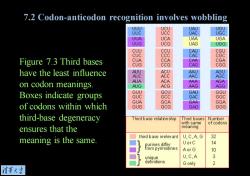
7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling UUU UCU UAU UGU UUC ucc UAC UGC UUA UCA UAA UGA UUG UCG UAG UGG CUU CCU CAU CGU cuC ccc CAC CGC Figure 7.3 Third bases CUA CCA CAA CGA CUG cCG CAG CGG have the least influence AUU ACU AAU AGU AUC ACC AAC AGC on codon meanings AUA ACA AAA AGA AUG ACG AAG AGG Boxes indicate groups GUU GCU GAU GGU GUC Gcc GAC GGC GUA GCA GAA GGA of codons within which GUG GCG GAG GGG third-base degeneracy Third base relation ship Third bases Number with same of codons ensures that the meaning third base irrelev ant U,C,A,G 32 meaning is the same. purines differ UorC 14 from pyrimidines AorG 10 unique U,C,A 3 definitions G only 2 清苇大兰
Figure 7.3 Third bases have the least influence on codon meanings. Boxes indicate groups of codons within which third-base degeneracy ensures that the meaning is the same. 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling

Standard base pairs occur at all positions 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling Cytosine Guanine ugar Figure 7.4 Wobble in base pairing allows G-U Uracil pairs to form between Adenine Sugar the third base of the G-U wobble pairing occurs only at third codon position codon andand the first base of the anticodon. Uracil N Guanine suar 情莘大当
Figure 7.4 Wobble in base pairing allows G-U pairs to form between the third base of the codon and and the first base of the anticodon. 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling

7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling Base in First Base(s)Recognized Position of in Third Position of Anticodon Codon U AorG G only U only G C or U Figure 7.5 Codon-anticodon pairing involves wobbling at the third position. 清苇大当
Figure 7.5 Codon-anticodon pairing involves wobbling at the third position. 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling

7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties Modification of DNA or RNA includes all changes made to the nucleotides after their initial incorporation into the polynucleotide chain. 情莘大当
Modification of DNA or RNA includes all changes made to the nucleotides after their initial incorporation into the polynucleotide chain. 7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第六章 蛋白质合成(Protein synthesis).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第五章 信使RNA(Messenger RNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第四章 簇和重复(Clusters and repeats).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第三章 有多少基因(How many genes are there).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二章 从基因到基因组(From Genes to Genomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第一章 基因是DNA(Genes are DNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)绪论 Molecular Biology(主讲:王钊).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 免疫多样性产生的机制.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 病毒的分子生物学.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 遗传重组.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 真核生物基因表达调控.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 原核生物基因表达调控.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 蛋白质翻译(Protein Translation).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 RNA转录(RNA transcription).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 DNA损伤、修复和突变.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 DNA复制(DNA Replication).ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 有机体、染色体和基因.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 DNA的结构.ppt
- 河北农业大学:《分子生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(参考资料)微生物基本术语(英汉对照词汇).pdf
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第八章 蛋白质定位(Protein localization).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第九章 转录(Transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十章 操纵子(The operon).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十一章 噬菌体的战略(Phage strategies).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十二章 复制子(The replicon).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十三章 DNA复制(DNA replication).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十四章 重组和修复(Recombination and repair).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十五章 转座子(Transposons).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十六章 逆转录病毒和逆转座子(Retroviruses and retroposons).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十七章 DNA的重新排列(Rearrangement of DNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十八章 染色体(Chromosomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第十九章 核小体(Nucleosomes).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十章 转录的起始(Initiation of transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十一章 转录的调控(Regulation of Transcription).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十二章 核的剪切(Nuclear splicing).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十三章 催化RNA(Catalytic RNA).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十四章 免疫多样性(Immune diversity).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十五章 蛋白质间的开放交通(Protein trafficking).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十六章 信号的传输(Signal transduction).ppt
- 清华大学:《分子生物学》课程PPT教学课件(基因ene)第二十七章 细胞循环和生长调控(Cell cycle and growth regulation).ppt
