《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 12 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT(HRM)

Chapter 12 HUMAN ROB B I N S COULTER RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM) ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-1
Chapter 12 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM) © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: Explain the strategic importance of human resource management (HRM) -Describe the HRM process Differentiate between job descriptions and job specifications Contrast recruitment and derecruitment options Describe the selection devices that work best with various kinds of jobs ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-2
Learning Objectives You should learn to: – Explain the strategic importance of human resource management (HRM) – Describe the HRM process – Differentiate between job descriptions and job specifications – Contrast recruitment and derecruitment options – Describe the selection devices that work best with various kinds of jobs © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-2

Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: Identify the various training categories Explain the various approaches to performance appraisal -Describe what an organization's compensation system should include -Discuss the current issues affecting HRM ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Identify the various training categories – Explain the various approaches to performance appraisal – Describe what an organization’s compensation system should include – Discuss the current issues affecting HRM © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-3

Why HRM Is Important All Managers Must Engage in Some HRM Activities -interview job candidates orient new employees evaluate work performance HRM Policies and Practices Have a Positive Impact on Performance -high performance work practices commit to improving knowledge and skills ·increase motivation retain quality employees encourage nonperformers to leave ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-4
Why HRM Is Important All Managers Must Engage in Some HRM Activities – interview job candidates – orient new employees – evaluate work performance HRM Policies and Practices Have a Positive Impact on Performance – high performance work practices • commit to improving knowledge and skills • increase motivation • retain quality employees • encourage nonperformers to leave © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-4

Examples of High-Performance Work Practices Self-directed work teams Implementation of employee suggestions 。Job rotation oingent pay basedn performance High levels of skills training Coaching and mentoring Problem-solving groups Sinificant amounts of information sharing Total quality management procedures and Use of employee attitude surveys processes Cross-functional integration Encouragement of innovative and creative behavior Comprehensive employee ritmntand Extensive employe involvement and training selection procedures Se:Basedn M.Huselid.The Impact of Human Resoue Management Practicesn Tumover,Prodctivity. and Corporate Financial Performance.Academyf Managemental,ne 995.p.635;and B.Becker and B.Gerhart,The mpact of Human Resource Managemetranizational Performance:Progress and Prospects,"Academy of Managementof ural.Auqust 1996.p.785 ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-5
Examples of High-Performance Work Practices © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-5

The HRM Process HRM Process 一 necessary for staffing the organization and sustaining high employee performance identify and select competent employees provide up-to-date knowledge and skills retain competent,high performing employees influenced by the external environment labor ion-represents workers and protects their interests through collective bargaining HRM decisions regulated by the terms of collective agreements ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-6
The HRM Process HRM Process – necessary for staffing the organization and sustaining high employee performance • identify and select competent employees • provide up-to-date knowledge and skills • retain competent, high performing employees – influenced by the external environment – labor union - represents workers and protects their interests through collective bargaining • HRM decisions regulated by the terms of collective agreements © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-6
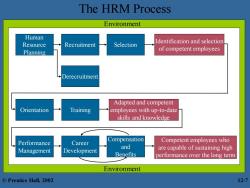
The HRM Process Environment Human Resource Identification and selection Recruitment Selection Planning of competent employees Derecruitment Adapted and competent Orientation Training employees with up-to-date skills and knowledge Performance Career Compensation Competent employees who and Management Development are capable of sustaining high Benefits performance over the long term Environment ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-7
The HRM Process Compensation and Benefits Career Development Performance Management Human Resource Planning Recruitment Derecruitment Selection Identification and selection of competent employees Orientation Training Adapted and competent employees with up-to-date skills and knowledge Competent employees who are capable of sustaining high performance over the long term Environment Environment © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-7

The HRM Process (cont. HRM Process (cont.) expanding influence of federal regulations to assure equal employment opportunities gtirmaive action-ensures that decisions and practices enhance the employment,upgrading, and retention of members from protected groups organization: -refrains from discrimination actively seeks to enhance the status of members of protected groups ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-8
The HRM Process (cont.) HRM Process (cont.) – expanding influence of federal regulations to assure equal employment opportunities – affirmative action - ensures that decisions and practices enhance the employment, upgrading, and retention of members from protected groups • organization: –refrains from discrimination –actively seeks to enhance the status of members of protected groups © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-8

Major U.S.Federal Laws and Regulations Related to HRM Year Law or Regulation Description 1963 Equal Pay Act Prohibits pay differences based on sex for equal work 1964 Civil Rights Act,Title Vll Prohibits discrimination based on race,color,religion. (amended in 1972) national origin,or sex 1967 Age Discrimination in Prohibits age discrimination against employees between Employment Act 40 and 65 years of age 1973 Vocational Rehabilitation Act Prohibits discrimination on the basis of physical or mental disabilities 1974 Privacy Act Gives employees the legal right to examine personnel files and letters of reference concerning them 1978 Mandatory Retirement Act Prohibits the forced retirement of most employees before the age of 70:upper limit on age was removed in 1986 1986 Immigration Reform and Prohibits unlawful employment of aliens and unfair Control Act immigration-related employment practices 1988 Polygraph Protection Act Limits an employer's ability to use lie detectors 1988 Worker Adjustment and Requires employers with 100 or more employees to provide Retraining Notification Act 60 days'notice before a facility closing or mass layoff 1990 Americans with Disabilities Act Prohibits employers from discriminating against individuals with physical or mental disabilities or the chronically ill;also requires organizations to reasonably accommodate these individuals 1991 Civil Rights Act of 1991 Reaffirms and tightens prohibition of discrimination: permits individuals to sue for punitive damages in cases of international discrimination 1993 Family and Medical Leave Act Permit employees in organizations with 50 or more of1993 workers to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave each year for family or medical reasons ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-9
Major U.S. Federal Laws and Regulations Related to HRM © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-9

Human Resource Planning Ensures: that organization has the right number and kind of people in the right places and at the right time employees are capable of effectively and efficiently performing their assigned tasks Current Assessment -human resource inventory-review of organization's human resource status sophisticated databases contain background information on each employee ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-10
Human Resource Planning Ensures: – that organization has the right number and kind of people in the right places and at the right time – employees are capable of effectively and efficiently performing their assigned tasks Current Assessment – human resource inventory - review of organization’s human resource status • sophisticated databases contain background information on each employee © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 11 MANAGERIAL COMMUNICATION AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 10 ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE AND DESIGN.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 09 PLANNING TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 08 STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 07 FOUNDATIONS OF PLANNING.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 06 DECISION MAKING:THE ESSENCE OF THE MANAGER’S JOB.ppt
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Stephen P.Robbins(9)Chapter 2 Management Yesterday and Today.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Stephen P.Robbins(9)Chapter 1 Introduction to Management and Organizations.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(教师手册)Stephen P.Robbins(9)CHAPTER TWO Management Yesterday.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(教师手册)Stephen P.Robbins(9)CHAPTER ONE Introduction to Management.pdf
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十二章 人力资源管理 Human Resource Management.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十章 组织结构与设计 Organizational Structure and Design.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十五章 理解群体与团队 Understanding Groups and Teams.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十九章 运营及价值链管理 Operations and Value Chain Management.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第三章 组织文化与环境——约束力量 Organizational Culture and Environment - The Constraints.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第二章 管理的昨天和今天 Management Yesterday and Today.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第五章 社会责任与道德管理 Social Responsibility and Managerial Ethics.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第四章 全球环境中的管理 Managing in a Global Environment.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第六章 制定决策——管理者工作的实质 Decision-Making - The Essence of the Manager’s Job.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第八章 战略管理 Strategic Management.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 13 MANAGING CHANGE AND INNOVATION.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 14 FOUNDATIONS OF BEHAVIOR.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 15 UNDERSTANDING GROUPS AND TEAMS.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 16 MOTIVATING EMPLOYEES.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 18 FOUNDATIONS OF CONTROL.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 19 OPERATIONS AND VALUE CHAIN MANAGEMENT.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 20 CONTROLLING FOR ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE.ppt
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)企业竞争模拟攻略篇.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第1章 管理活动与管理理论.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第3章 全球化与管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第6章 计划与计划工作.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第十章 组织变革与组织文化.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第16章 管理的创新职能.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第1章 管理活动与管理理论.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第3章 全球化与管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第4章 信息与信息化管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第5章 决策与决策方法.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第6章 计划与计划工作.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第7章 战略性计划与战略实施.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第8章 组织设计.doc
