《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 15 UNDERSTANDING GROUPS AND TEAMS

Chapter 15 UNDERSTANDING ROB B I N S COULTER GROUPS AND TEAMS ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-1
Chapter 15 UNDERSTANDING GROUPS AND TEAMS © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: Differentiate between formal and informal groups Describe the five stages of group development -Identify how roles and norms influence an employee's behavior -Describe the key components in the group behavior model Identify the advantages and disadvantages of group decision making ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-2
Learning Objectives You should learn to: – Differentiate between formal and informal groups – Describe the five stages of group development – Identify how roles and norms influence an employee’s behavior – Describe the key components in the group behavior model – Identify the advantages and disadvantages of group decision making © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-2

Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: -Explain the increased popularity of teams in organizations -Describe the four most common types of teams in organizations -List the characteristics of effective teams Identify how managers can build trust ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Explain the increased popularity of teams in organizations – Describe the four most common types of teams in organizations – List the characteristics of effective teams – Identify how managers can build trust © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-3

Understanding Group Behavior Group two or more interacting and interdependent individuals who come together to achieve particular goals foragroups-established by the organization -have designated work assignments and specific tasks different types exist informal groups-occur naturally in the workplace in response to the need for social contact ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-4
Understanding Group Behavior Group – two or more interacting and interdependent individuals who come together to achieve particular goals • formal groups - established by the organization –have designated work assignments and specific tasks –different types exist • informal groups- occur naturally in the workplace in response to the need for social contact © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-4

Examples of Formal Groups mmado These re the basic,rar groups determined byfomuthy reltiornshipsanddeoictedontheorgenizationalchat.Theytypicalyincludeamanagrandthose susprtttohimh. m These n tothrth dandsills fnis fromvaious wrkareas inmthirainoblm.fiatmas incudehmmbers have benndchos. S Theseare ssntially independnto that,inthir rain takemanagemniis snai and performance evaluaions. Task forces.These are tmporary goupracomplish aii task.One th task is mle,thisisan ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-5
Examples of Formal Groups © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-5

Understanding Group Behavior (cont. Stages of Group Development -oring-people join the group either because of a work assignment or for some other benefit begin to define the group's purpose,structure,and leadership stage marked by much uncertainty -soraing-acceptance of the group's existence conflict over who will control the group -ording-relationships and a sense of group identity develop group assimilates a common set of expectations of what defines correct member behavior ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-6
Understanding Group Behavior (cont.) Stages of Group Development – forming - people join the group either because of a work assignment or for some other benefit • begin to define the group’s purpose, structure, and leadership • stage marked by much uncertainty – storming - acceptance of the group’s existence • conflict over who will control the group – norming - relationships and a sense of group identity develop • group assimilates a common set of expectations of what defines correct member behavior © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-6

Understanding Group Behavior (cont. Stages of Group Development (cont.) -peroring-group structure is functional and accepted group energy has moved to task performance -adfouring-group prepares to disband attention devoted to wrapping up activities group does not necessarily become more effective as it moves through the first four stages group effectiveness is a complex issue that is affected by factors other than developmental stage ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-7
Understanding Group Behavior (cont.) Stages of Group Development (cont.) – performing - group structure is functional and accepted • group energy has moved to task performance – adjourning - group prepares to disband • attention devoted to wrapping up activities – group does not necessarily become more effective as it moves through the first four stages • group effectiveness is a complex issue that is affected by factors other than developmental stage © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-7
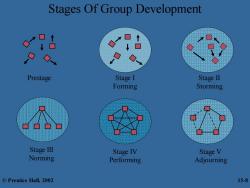
Stages Of Group Development Prestage Stage I StageⅡ Forming Storming StageⅢ Stage IV Stage V Norming Performing Adjourning ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-8
Stages Of Group Development Prestage Stage I Forming Stage II Storming Stage III Norming Stage V Adjourning Stage IV Performing © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-8

Understanding Group Behavior (cont.) Basic Group Concepts -Rolle-set of expected behavior patterns attributed to someone who occupies a given position in a social unit group members have particular roles -roles oriented towards task accomplishment or maintaining group member satisfaction individuals play multiple roles -rolle conlict-individual confronted by different role expectations ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-9
Understanding Group Behavior (cont.) Basic Group Concepts – Role - set of expected behavior patterns attributed to someone who occupies a given position in a social unit • group members have particular roles –roles oriented towards task accomplishment or maintaining group member satisfaction • individuals play multiple roles –role conflict - individual confronted by different role expectations © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-9

Understanding Group Behavior (cont. Basic Group Concepts (cont.) -Nors-acceptable standards or expectations that are shared by the group's members ·each group has. -its own unique set of norms common norms related to levels of effort and performance >exert powerful influence on performance Coormiiy-acceptance by group makes some members susceptible to conformity pressures group norms push members toward conformity results in alignment of opinions ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-10
Understanding Group Behavior (cont.) Basic Group Concepts (cont.) – Norms - acceptable standards or expectations that are shared by the group’s members • each group has: – its own unique set of norms – common norms related to levels of effort and performance »exert powerful influence on performance – Conformity - acceptance by group makes some members susceptible to conformity pressures • group norms push members toward conformity • results in alignment of opinions © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 14 FOUNDATIONS OF BEHAVIOR.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 13 MANAGING CHANGE AND INNOVATION.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 12 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT(HRM).ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 11 MANAGERIAL COMMUNICATION AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 10 ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE AND DESIGN.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 09 PLANNING TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 08 STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 07 FOUNDATIONS OF PLANNING.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 06 DECISION MAKING:THE ESSENCE OF THE MANAGER’S JOB.ppt
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Stephen P.Robbins(9)Chapter 2 Management Yesterday and Today.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Stephen P.Robbins(9)Chapter 1 Introduction to Management and Organizations.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(教师手册)Stephen P.Robbins(9)CHAPTER TWO Management Yesterday.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(教师手册)Stephen P.Robbins(9)CHAPTER ONE Introduction to Management.pdf
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十二章 人力资源管理 Human Resource Management.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十章 组织结构与设计 Organizational Structure and Design.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十五章 理解群体与团队 Understanding Groups and Teams.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十九章 运营及价值链管理 Operations and Value Chain Management.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第三章 组织文化与环境——约束力量 Organizational Culture and Environment - The Constraints.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第二章 管理的昨天和今天 Management Yesterday and Today.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第五章 社会责任与道德管理 Social Responsibility and Managerial Ethics.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 16 MOTIVATING EMPLOYEES.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 18 FOUNDATIONS OF CONTROL.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 19 OPERATIONS AND VALUE CHAIN MANAGEMENT.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 20 CONTROLLING FOR ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE.ppt
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)企业竞争模拟攻略篇.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第1章 管理活动与管理理论.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第3章 全球化与管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第6章 计划与计划工作.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第十章 组织变革与组织文化.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第16章 管理的创新职能.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第1章 管理活动与管理理论.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第3章 全球化与管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第4章 信息与信息化管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第5章 决策与决策方法.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第6章 计划与计划工作.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第7章 战略性计划与战略实施.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第8章 组织设计.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第9章 人力资源管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第10章 组织变革与组织文化.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第11章 领导概论.doc
