《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 13 MANAGING CHANGE AND INNOVATION

Chapter 13 MANAGING DROB BI NS ACOULTER CHANGE AND INNOVATION ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-1
Chapter 13 MANAGING CHANGE AND INNOVATION © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: -Contrast the calm waters and white-water rapids metaphors of change Describe what managers can change in organizations Explain why people are likely to resist change -List techniques for reducing resistance to change Describe the situational factors that facilitate cultural change ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-2
Learning Objectives You should learn to: – Contrast the calm waters and white-water rapids metaphors of change – Describe what managers can change in organizations – Explain why people are likely to resist change – List techniques for reducing resistance to change – Describe the situational factors that facilitate cultural change © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-2

Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: Explain how process reengineering is related to change Describe techniques for reducing employee stress Differentiate between creativity and innovation Explain how organizations can stimulate and nurture innovation ©Prentice Hall,.2002 13-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Explain how process reengineering is related to change – Describe techniques for reducing employee stress – Differentiate between creativity and innovation – Explain how organizations can stimulate and nurture innovation © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-3

What Is Change? Change -alterations in people,structure,or technology change is an organizational reality managing change is an integral part of every manager's job complicates the jobs of managers ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-4
What Is Change? Change – alterations in people, structure, or technology – change is an organizational reality – managing change is an integral part of every manager’s job • complicates the jobs of managers © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-4

Forces For Change External Forces markeiollace-adapt to changing consumer desires governmental laws and regulations-frequent impetus for change -teclanollogy-source of change in almost all industries labor markeis HRM activities must change to attract and retain skilled employees in the areas of greatest need ecomomie-uncertainties about interest rates, budget deficits,and currency exchange rates ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-5
Forces For Change External Forces – marketplace - adapt to changing consumer desires – governmental laws and regulations - frequent impetus for change – technology - source of change in almost all industries – labor markets - HRM activities must change to attract and retain skilled employees in the areas of greatest need – economic - uncertainties about interest rates, budget deficits, and currency exchange rates © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-5

Forces For Change (cont. Internal Forces -originate from the operations of the organization forces may include strategy,workforce,new equipment. or employee attitudes Manager as Change Agent -change agenis-act as catalysts and assume responsibility for change manager may serve as change agent -may be more thoughtful,overcautious outside consultant-used for systemwide changes -produce more drastic changes than insiders ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-6
Forces For Change (cont.) Internal Forces – originate from the operations of the organization – forces may include strategy, workforce, new equipment, or employee attitudes Manager as Change Agent – change agents - act as catalysts and assume responsibility for change • manager may serve as change agent –may be more thoughtful, overcautious • outside consultant - used for systemwide changes – produce more drastic changes than insiders © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-6

Two Views Of The Change Process The Calm Waters Metaphor Lewin's three-step model odfreezing-preparing for the needed change by -increasing the driving orces that direct behavior away from the status quo decreasing the restrining forces that push behavior towards the status quo >stains quto-conceived to be an equilibrium changing-move to another equilibrium level orefeezing -make change permanent -objective is to stabilize the new situation change is a break in the organization's equilibrium state ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-7
Two Views Of The Change Process The Calm Waters Metaphor – Lewin’s three-step model • unfreezing - preparing for the needed change by: – increasing the driving forces that direct behavior away from the status quo – decreasing the restraining forces that push behavior towards the status quo »status quo - conceived to be an equilibrium • changing - move to another equilibrium level • refreezing - make change permanent – objective is to stabilize the new situation – change is a break in the organization’s equilibrium state © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-7
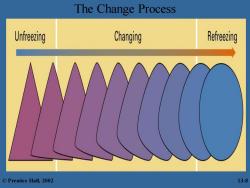
The Change Process Unfreezing Changing Refreezing ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-8
The Change Process © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-8

Two Views Of The Change Process (cont. White-Water Rapids Metaphor consistent with uncertain and dynamic environments consistent with a world increasingly dominated by information,ideas,and knowledge managers must continually maneuver in uninterrupted rapids managers face constant change today,managers must be ready to efficiently and effectively manage the changes facing their organizations or their work areas ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-9
Two Views Of The Change Process (cont.) White-Water Rapids Metaphor – consistent with uncertain and dynamic environments – consistent with a world increasingly dominated by information, ideas, and knowledge – managers must continually maneuver in uninterrupted rapids • managers face constant change – today, managers must be ready to efficiently and effectively manage the changes facing their organizations or their work areas © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-9
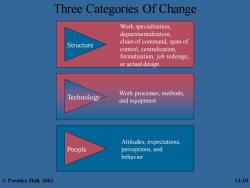
Three Categories Of Change Work specialization, departmentalization. Structure chain of command,span of control,centralization, formalization,job redesign, or actual design Technology Work processes,methods, and equipment Attitudes,expectations, People perceptions,and behavior ©Prentice Hall,2002 13-10
Three Categories Of Change Work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, span of control, centralization, formalization, job redesign, or actual design Structure Attitudes, expectations, perceptions, and behavior People Work processes, methods, and equipment Technology © Prentice Hall, 2002 13-10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 12 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT(HRM).ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 11 MANAGERIAL COMMUNICATION AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 10 ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE AND DESIGN.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 09 PLANNING TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 08 STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 07 FOUNDATIONS OF PLANNING.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 06 DECISION MAKING:THE ESSENCE OF THE MANAGER’S JOB.ppt
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Stephen P.Robbins(9)Chapter 2 Management Yesterday and Today.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Stephen P.Robbins(9)Chapter 1 Introduction to Management and Organizations.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(教师手册)Stephen P.Robbins(9)CHAPTER TWO Management Yesterday.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(教师手册)Stephen P.Robbins(9)CHAPTER ONE Introduction to Management.pdf
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十二章 人力资源管理 Human Resource Management.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十章 组织结构与设计 Organizational Structure and Design.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十五章 理解群体与团队 Understanding Groups and Teams.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第十九章 运营及价值链管理 Operations and Value Chain Management.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第三章 组织文化与环境——约束力量 Organizational Culture and Environment - The Constraints.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第二章 管理的昨天和今天 Management Yesterday and Today.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第五章 社会责任与道德管理 Social Responsibility and Managerial Ethics.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第四章 全球环境中的管理 Managing in a Global Environment.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management)Stephen P.Robbins(9)第六章 制定决策——管理者工作的实质 Decision-Making - The Essence of the Manager’s Job.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 14 FOUNDATIONS OF BEHAVIOR.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 15 UNDERSTANDING GROUPS AND TEAMS.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 16 MOTIVATING EMPLOYEES.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 18 FOUNDATIONS OF CONTROL.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 19 OPERATIONS AND VALUE CHAIN MANAGEMENT.ppt
- 《管理学》课程PPT教学课件(Management, 7th Edition)Chapter 20 CONTROLLING FOR ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE.ppt
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)企业竞争模拟攻略篇.pdf
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第1章 管理活动与管理理论.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第3章 全球化与管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第6章 计划与计划工作.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第十章 组织变革与组织文化.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第16章 管理的创新职能.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第1章 管理活动与管理理论.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第3章 全球化与管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第4章 信息与信息化管理.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第5章 决策与决策方法.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第6章 计划与计划工作.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第7章 战略性计划与战略实施.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第8章 组织设计.doc
- 《管理学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)第9章 人力资源管理.doc
