同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch06-1 Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets

1907 Ch06-1 Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Ch06-1 Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets

07-2 0 例 Topics to be Discussed Perfectly Competitive Markets ·Profit Maximization Marginal Revenue,Marginal Cost,and Profit Maximization Choosing Output in the Short-Run The Competitive Firm's Short-Run Supply Curve Short-Run Market Supply Choosing Output in the Long-Run The Industry's Long-Run Supply Curve Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-2 Topics to be Discussed • Perfectly Competitive Markets • Profit Maximization • Marginal Revenue, Marginal Cost, and Profit Maximization • Choosing Output in the Short-Run • The Competitive Firm’s Short-Run Supply Curve • Short-Run Market Supply • Choosing Output in the Long-Run • The Industry’s Long-Run Supply Curve

1907 07-3 树 6.1 Perfectly Competitive Markets Characteristics of Perfectly Competitive Markets 1)Price taking 2)Product homogeneity 3)Free entry and exit Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-3 6.1 Perfectly Competitive Markets • Characteristics of Perfectly Competitive Markets 1) Price taking 2) Product homogeneity 3) Free entry and exit

07-4 0 Perfectly Competitive Markets ·Price Taking -The individual firm sells a very small share of the total market output and,therefore,cannot influence market price. The individual consumer buys too small a share of industry output to have any impact on market price. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-4 Perfectly Competitive Markets • Price Taking – The individual firm sells a very small share of the total market output and, therefore, cannot influence market price. – The individual consumer buys too small a share of industry output to have any impact on market price

190 07-5 Perfectly Competitive Markets ·Product Homogeneity -The products of all firms are perfect substitutes. -Examples Agricultural products,oil,copper,iron,lumber Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-5 Perfectly Competitive Markets • Product Homogeneity – The products of all firms are perfect substitutes. – Examples • Agricultural products, oil, copper, iron, lumber

07-6 10 Perfectly Competitive Markets ·Free Entry and Exit -Buyers can easily switch from one supplier to another. -Suppliers can easily enter or exit a market. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-6 Perfectly Competitive Markets • Free Entry and Exit – Buyers can easily switch from one supplier to another. – Suppliers can easily enter or exit a market

1907 07-7 6.2 Profit Maximization Do firms maximize profits? -Possibility of other objectives Revenue maximization Dividend maximization Short-run profit maximization Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-7 6.2 Profit Maximization • Do firms maximize profits? – Possibility of other objectives • Revenue maximization • Dividend maximization • Short-run profit maximization

07-8 10 © Profit Maximization Do firms maximize profits? Long-run profit maximization is valid and does not exclude the possibility of altruistic behavior. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-8 Profit Maximization • Do firms maximize profits? – Long-run profit maximization is valid and does not exclude the possibility of altruistic behavior

1907 07-9 Marginal Revenue,Marginal Cost, and Profit Maximization Determining the profit maximizing level of output -Profit()=Total Revenue-Total Cost Total Revenue (TR)=Pg Total Cost (C) -Therefore: TR -TC Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-9 Marginal Revenue, Marginal Cost, and Profit Maximization • Determining the profit maximizing level of output – Profit ( ) = Total Revenue - Total Cost – Total Revenue (TR) = Pq – Total Cost (C) – Therefore: π = TR - TC
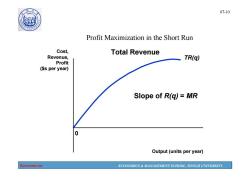
07-10 Profit Maximization in the Short Run Cost, Total Revenue Revenue, TR(q) Profit ($s per year) Slope of R(g)=MR Output(units per year) Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-10 Profit Maximization in the Short Run 0 Cost, Revenue, Profit ($s per year) Output (units per year) TR(q) Total Revenue Slope of R(q) = MR
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch05 Analysis of Cost.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch04 Producer Behavior.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch03 Demand and Consumer Behavior.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch02-2 Applications of Supply and Demand.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch02-1 Supply and Demand.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch01 The Fundamentals of Economics(负责人:李永).pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(B卷)答案.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(B卷)试题.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(A卷)答案.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(A卷)试题.pdf
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 ERP应用概述.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 会计信息系统审计.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 会计信息系统的建设与管理.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 其他业务核算子系统.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 报表子系统.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 账务处理子系统.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 会计信息系统概述(主讲教师:王伟).ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)综合理论练习题及答案.doc
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)复习思考题答案.doc
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)练习题8.doc
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch06-2 Imperfect Competition.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch07 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch08 Market For Factors of Production.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch10 Overview of Macroeconomics.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch09 Externalities and Public Goods.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch11 National Income Accounting.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch12-1 Consumption and Investment.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch12-2 The Determination of Equilibrium Output.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch13 Money Market Equilibrium.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch14 Outputs and Money Market - IS-LM Model.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch15 Aggregate Demand And Supply.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch16 Economic Growth.pdf
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 中央银行制度的形成和发展.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 中央银行的其他业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 中央银行业务活动的法规原则与资产负债表.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 中央银行货币政策的目标与工具.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 中央银行在现代经济体系中的地位与作用.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 中央银行的资产业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 中央银行货币政策概述.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 中央银行的支付清算业务.ppt
