同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch12-1 Consumption and Investment

0 Ch12-1 Consumption and Investment Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Ch12-1 Consumption and Investment

1907 14-2 3树 Topics to be Discussed The Consumption Theory ·Investment Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-2 Topics to be Discussed • The Consumption Theory • Investment

14-3 0 12.1 The Consumption Theory This chapter surveys the most prominent work on consumption: John Maynard Keynes:consumption and current income Irving Fisher and Intertemporal Choice Franco Modigliani:the Life-Cycle Hypothesis Milton Friedman:the Permanent Income Hypothesis Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-3 12.1 The Consumption Theory This chapter surveys the most prominent work on consumption: John Maynard Keynes: consumption and current income Irving Fisher and Intertemporal Choice Franco Modigliani: the Life-Cycle Hypothesis Milton Friedman: the Permanent Income Hypothesis

190 14-4 12.1.1 Keynes's Conjectures 1.0<MPC<1 2.APC falls as income rises where APC average propensity to consume C/Y 3.Income is the main determinant of consumption. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-4 12.1.1 Keynes’s Conjectures 1. 0 < MPC < 1 2. APC falls as income rises where APC = average propensity to consume = C/Y 3. Income is the main determinant of consumption

14-5 Problems for the Keynesian Consumption Function Based on the Keynesian consumption function, economists predicted that c would grow more slowly than r over time. This prediction did not come true: As incomes grew,the APC did not fall, and C grew just as fast. Simon Kuznets showed that C/Y was very stable in long time series data. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-5 Problems for the Keynesian Consumption Function Based on the Keynesian consumption function, economists predicted that C would grow more slowly than Y over time. This prediction did not come true: As incomes grew, the APC did not fall, and C grew just as fast. Simon Kuznets showed that C/Y was very stable in long time series data
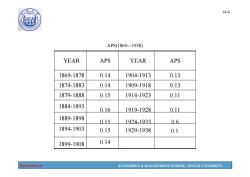
1907 14-6 APS(1869-1938) YEAR APS YEAR APS 1869-1878 0.14 1904-1913 0.13 1874-1883 0.14 1909-1918 0.13 1879-1888 0.15 1914-1923 0.11 1884-1893 016 1919-1928 011 1889-1898 015 1924-1933 06 1894-1903 0.15 1929-1938 0.1 1899-1908 0.14 Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-6 APS(1869---1938) 0.14 1899-1908 0.15 1929-1938 0.1 1894-1903 0.15 1924-1933 0.6 1889-1898 0.16 1919-1928 0.11 1884-1893 1879-1888 0.15 1914-1923 0.11 1874-1883 0.14 1909-1918 0.13 1869-1878 0.14 1904-1913 0.13 YEAR APS YEAR APS
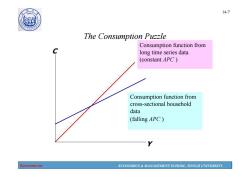
14-7 A90 砂 The Consumption Puzzle Consumption function from C long time series data (constant APC) Consumption function from cross-sectional household data (falling APC) Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-7 The Consumption Puzzle C Y Consumption function from long time series data (constant APC ) Consumption function from cross-sectional household data (falling APC )

14-8 10 © 12.1.2 Irving Fisher and Intertemporal Choice Assumes consumer is forward-looking and chooses consumption for the present and future to maximize lifetime satisfaction. Consumer's choices are subject to an intertemporal budget constraint,a measure of the total resources available for present and future consumption Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-8 12.1.2 Irving Fisher and Intertemporal Choice • Assumes consumer is forward-looking and chooses consumption for the present and future to maximize lifetime satisfaction. • Consumer’s choices are subject to an intertemporal budget constraint,a measure of the total resources available for present and future consumption

14-9 The basic two-period model 。Period 1:the present ·Period2:the future Notation Y is income in period 1 Y2 is income in period 2 C is consumption in period 1 C2 is consumption in period 2 S=Y-Ci is saving in period 1 (S<0 if the consumer borrows in period 1) Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-9 The basic two-period model • Period 1: the present • Period 2: the future • Notation Y1 is income in period 1 Y2 is income in period 2 C1 is consumption in period 1 C2 is consumption in period 2 S = Y1 C1 is saving in period 1 (S < 0 if the consumer borrows in period 1)
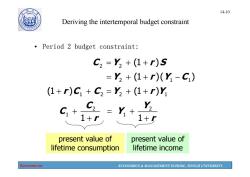
190 14-10 Deriving the intertemporal budget constraint Period 2 budget constraint: C2=Y2+(1+r)S =Y2+(1+r)(Y-C) (1+r)C+C2=Y3+(1+r)Y C,+ C2 1+r =Y+ Y2 1+5 present value of present value of lifetime consumption lifetime income Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 14-10 Deriving the intertemporal budget constraint • Period 2 budget constraint: 2 2 C Y rS (1 ) 2 11 Y (1 )( ) rY C 1 22 1 (1 ) (1 ) rC C Y rY 2 2 1 1 1 1 C Y C Y r r present value of lifetime consumption present value of lifetime income
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch11 National Income Accounting.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch09 Externalities and Public Goods.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch10 Overview of Macroeconomics.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch08 Market For Factors of Production.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch07 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch06-2 Imperfect Competition.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch06-1 Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch05 Analysis of Cost.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch04 Producer Behavior.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch03 Demand and Consumer Behavior.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch02-2 Applications of Supply and Demand.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch02-1 Supply and Demand.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch01 The Fundamentals of Economics(负责人:李永).pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(B卷)答案.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(B卷)试题.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(A卷)答案.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(A卷)试题.pdf
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 ERP应用概述.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 会计信息系统审计.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 会计信息系统的建设与管理.ppt
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch12-2 The Determination of Equilibrium Output.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch13 Money Market Equilibrium.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch14 Outputs and Money Market - IS-LM Model.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch15 Aggregate Demand And Supply.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch16 Economic Growth.pdf
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 中央银行制度的形成和发展.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 中央银行的其他业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 中央银行业务活动的法规原则与资产负债表.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 中央银行货币政策的目标与工具.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 中央银行在现代经济体系中的地位与作用.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 中央银行的资产业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 中央银行货币政策概述.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 中央银行的支付清算业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 中央银行的金融监管.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 中央银行与外汇管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 货币政策的作用机制.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 中央银行的负债业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)中央银行学课程总结与辅导(共十二章,负责人:齐艺莹).ppt
- 吉林大学:《宏观经济学》课程j电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 宏观经济学导论(负责人:赵静杰).ppt
- 吉林大学:《宏观经济学》课程j电子教案(PPT课件)古典宏观经济模型.ppt
