同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch12-2 The Determination of Equilibrium Output

1907 Ch12-2 The Determination of Equilibrium Output Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Ch12-2 The Determination of Equilibrium Output

15-2 0 Topics Chapter12 introduced the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply. ■Long run -prices flexible output determined by factors of production technology unemployment equals its natural rate ■Short run -prices fixed output determined by aggregate demand unemployment is negatively related to output We focus on the short run and assume the price level is fixed. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-2 Topics Chapter12 introduced the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Long run – prices flexible – output determined by factors of production & technology – unemployment equals its natural rate Short run – prices fixed – output determined by aggregate demand – unemployment is negatively related to output We focus on the short run and assume the price level is fixed

1907 15-3 12.1 Two Sector Economy ·YaY def:disposable income is total income minus total taxes:Y =Y-T Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-3 12.1 Two Sector Economy • Yd=Y • def: disposable income is total income minus total taxes: Yd =Y – T

15-4 0 12.1.1AE 。Notation: C=planned COMSUPTION I =planned investment AE C +I planned expenditure Y=real GDP=actual expenditure Difference between actual planned expenditure: unplanned inventory investment Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-4 12.1.1 AE • Notation: C = planned COMSUPTION I = planned investment AE = C + I = planned expenditure Y = real GDP = actual expenditure • Difference between actual & planned expenditure: unplanned inventory investment

490 15.5 © The Consumption Function C=C(Yd), C=a+b Yd APC=average propensity to consume =CYd MPC=△G/△Yb def:The marginal propensity to consume is the increase in C caused by a one-unit increase in disposable income. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-5 C=C(Yd ), C=a+b Yd APC = average propensity to consume = C/Y d MPC =△C/△Yd=b def: The marginal propensity to consume is the increase in C caused by a one-unit increase in disposable income. The Consumption Function

15-6 10 Keynes's Conjectures 1.0<MPC<1 2.APC falls as income rises 3.Income is the main determinant of consumption. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-6 Keynes’s Conjectures 1. 0 < MPC < 1 2. APC falls as income rises 3. Income is the main determinant of consumption
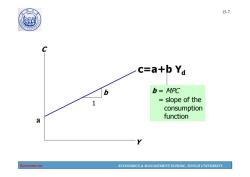
1907 15-7 c=a+b Ya 6 b=MPC = slope of the consumption function a Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-7 C Y 1 b b = MPC = slope of the consumption function c=a+b Yd a
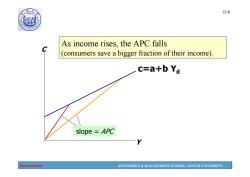
190 15-8 As income rises,the APC falls (consumers save a bigger fraction of their income) c=a+b Yd slope APC Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-8 C Y slope = APC As income rises, the APC falls (consumers save a bigger fraction of their income). c=a+b Yd
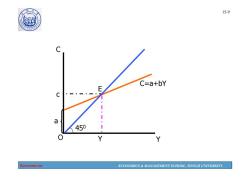
1907 15-9 C=a+bY 450 Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-9 C O Y C=a+bY c a Y E 450

190 15-10 Saving Function S=Y-C=Y-(a+bY)=-a+(1-b)Y APS=S/Y MPS=△S/△Y.=1-b APS+APC=1 MPS+MPC-1 Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 15-10 Saving Function s=Yd-c=Y-(a+bY)=-a+(1-b)Y APS=S/Yd MPS=△S/△Yd=1-b APS+APC=1 MPS+MPC=1
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch12-1 Consumption and Investment.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch11 National Income Accounting.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch09 Externalities and Public Goods.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch10 Overview of Macroeconomics.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch08 Market For Factors of Production.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch07 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch06-2 Imperfect Competition.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch06-1 Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch05 Analysis of Cost.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch04 Producer Behavior.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch03 Demand and Consumer Behavior.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch02-2 Applications of Supply and Demand.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch02-1 Supply and Demand.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch01 The Fundamentals of Economics(负责人:李永).pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(B卷)答案.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(B卷)试题.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(A卷)答案.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期终考试试卷(A卷)试题.pdf
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 ERP应用概述.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《会计信息系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 会计信息系统审计.ppt
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch13 Money Market Equilibrium.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch14 Outputs and Money Market - IS-LM Model.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch15 Aggregate Demand And Supply.pdf
- 同济大学:《经济学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Ch16 Economic Growth.pdf
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 中央银行制度的形成和发展.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 中央银行的其他业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 中央银行业务活动的法规原则与资产负债表.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 中央银行货币政策的目标与工具.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 中央银行在现代经济体系中的地位与作用.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 中央银行的资产业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 中央银行货币政策概述.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 中央银行的支付清算业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 中央银行的金融监管.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 中央银行与外汇管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 货币政策的作用机制.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 中央银行的负债业务.ppt
- 吉林大学:《中央银行业务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)中央银行学课程总结与辅导(共十二章,负责人:齐艺莹).ppt
- 吉林大学:《宏观经济学》课程j电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 宏观经济学导论(负责人:赵静杰).ppt
- 吉林大学:《宏观经济学》课程j电子教案(PPT课件)古典宏观经济模型.ppt
- 吉林大学:《宏观经济学》课程j电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 国民收入核算.ppt
