香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 05

CSCI 3160 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Tutorial 5 Chengyu Lin
CSCI 3160 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Tutorial 5 Chengyu Lin

Outline 。Dynamic programming -Chain Matrix Multiplication Longest increasing subsequence (LIS) Goal:help understand the lecture materials further
Outline • Dynamic programming – Chain Matrix Multiplication – Longest increasing subsequence (LIS) • Goal: help understand the lecture materials further
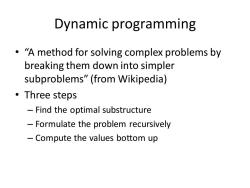
Dynamic programming "A method for solving complex problems by breaking them down into simpler subproblems"(from Wikipedia) ·Three steps Find the optimal substructure Formulate the problem recursively Compute the values bottom up
Dynamic programming • “A method for solving complex problems by breaking them down into simpler subproblems” (from Wikipedia) • Three steps – Find the optimal substructure – Formulate the problem recursively – Compute the values bottom up

Chain Matrix Multiplication You want to multiply N matrices A1,...,A Suppose the cost of multiplying an m-by-n matrix with an n-by-/matrix is mn/. The product is an m-by-/matrix What is the minimum total cost to get the product of the N matrices P=A1...AN?
Chain Matrix Multiplication • You want to multiply N matrices A1 , …, AN • Suppose the cost of multiplying an m-by-n matrix with an n-by-l matrix is mnl. – The product is an m-by-l matrix • What is the minimum total cost to get the product of the N matrices P = A1…AN ?
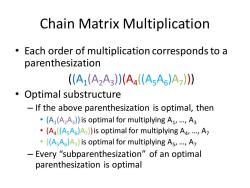
Chain Matrix Multiplication Each order of multiplication corresponds to a parenthesization (A1(A2A3(A4(AsA6)A7) Optimal substructure If the above parenthesization is optimal,then .(A(A2A3))is optimal for multiplying A1,...A3 .(A((AsA )A))is optimal for multiplying Aa,...,A .((AsA)A)is optimal for multiplying As,...,A -Every“"subparenthesization”of an optimal parenthesization is optimal
Chain Matrix Multiplication • Each order of multiplication corresponds to a parenthesization ((A1 (A2A3 ))(A4 ((A5A6 )A7 ))) • Optimal substructure – If the above parenthesization is optimal, then • (A1 (A2A3 )) is optimal for multiplying A1 , …, A3 • (A4 ((A5A6 )A7 )) is optimal for multiplying A4 , …, A7 • ((A5A6 )A7 )is optimal for multiplying A5 , …, A7 – Every “subparenthesization” of an optimal parenthesization is optimal
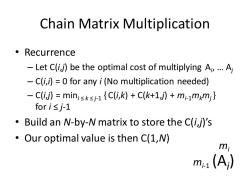
Chain Matrix Multiplication ·Recurrence -Let C(i,j)be the optimal cost of multiplying Ai,...A -C(i,i)=0 for any i(No multiplication needed) -C(i,j)minisksj-1 {C(i,k)+C(k+1,j)+mi-1mkmj} fori≤j-1 Build an N-by-N matrix to store the C(i,j)'s Our optimal value is then C(1,N) mi m1(A)
Chain Matrix Multiplication • Recurrence – Let C(i,j) be the optimal cost of multiplying Ai , … Aj – C(i,i) = 0 for any i (No multiplication needed) – C(i,j) = mini ≤ k ≤ j-1 { C(i,k) + C(k+1,j) + mi-1mkmj } for i ≤ j-1 • Build an N-by-N matrix to store the C(i,j)’s • Our optimal value is then C(1,N) (Ai ) mi mi-1
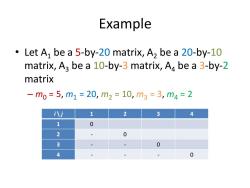
Example Let A1 be a 5-by-20 matrix,A,be a 20-by-10 matrix,Aa be a 10-by-3 matrix,Aa be a 3-by-2 matrix -m0=5,m1=20,m2=10,m3=3,m4=2 i八j 1 2 3 4 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0
Example • Let A1 be a 5-by-20 matrix, A2 be a 20-by-10 matrix, A3 be a 10-by-3 matrix, A4 be a 3-by-2 matrix – m0 = 5, m1 = 20, m2 = 10, m3 = 3, m4 = 2 i \ j 1 2 3 4 1 0 2 - 0 3 - - 0 4 - - - 0
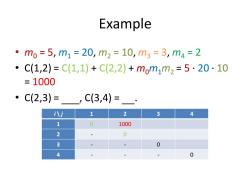
Example 。m0=5,m1=20,m2=10,m3=3,m4=2 ● C(1,2)=C(1,1)+C(2,2)+mom1m2=5·20·10 =1000 C(2,3)=,C(3,4)=· i八j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 2 0 3 0 4 0
Example • m0 = 5, m1 = 20, m2 = 10, m3 = 3, m4 = 2 • C(1,2) = C(1,1) + C(2,2) + m0m1m2 = 5 · 20 · 10 = 1000 • C(2,3) = , C(3,4) = . i \ j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 2 - 0 3 - - 0 4 - - - 0
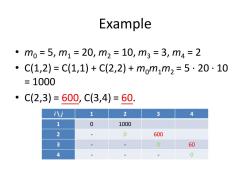
Example 。m0=5,m1=20,m2=10,m3=3,m4=2 0 C(1,2)=C(1,1)+C(2,2)+mom1m2=5·20·10 =1000 C(2,3)=600,C(3,4)=60. i八j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 2 0 600 3 0 60 4 0
Example • m0 = 5, m1 = 20, m2 = 10, m3 = 3, m4 = 2 • C(1,2) = C(1,1) + C(2,2) + m0m1m2 = 5 · 20 · 10 = 1000 • C(2,3) = 600, C(3,4) = 60. i \ j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 2 - 0 600 3 - - 0 60 4 - - - 0
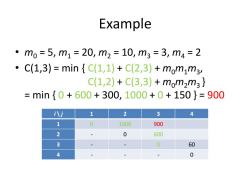
Example 。m0=5,m1=20,m2=10,m3=3,m4=2 ·C(1,3)=min{C(1,1)+C(2,3)+mom1m3 C(1,2)+C(3,3)+mom2m3} =min{0+600+300,1000+0+150}=900 i八j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 900 2 0 600 3 0 60 4 0
Example • m0 = 5, m1 = 20, m2 = 10, m3 = 3, m4 = 2 • C(1,3) = min { C(1,1) + C(2,3) + m0m1m3 , C(1,2) + C(3,3) + m0m2m3 } = min { 0 + 600 + 300, 1000 + 0 + 150 } = 900 i \ j 1 2 3 4 1 0 1000 900 2 - 0 600 3 - - 0 60 4 - - - 0
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 04.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 03.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 02.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 12.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 11.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 10.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 01.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 10 Stable Matching and Secretary Problem.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 8 Maximum Network Flow.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 7 Divide and Conquer.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 6 Linear Programming.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 12 Online Algorithms.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 11 Approximation Algorithms.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 10 NP-completeness.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 5 Dynamic Programming.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 4 Randomized Algorithms.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 3 Greedy Algorithms.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 2 Single Source Shortest Paths.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 1 Introduction to the course.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 12 Quantum information theory 4.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 06.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 08.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 09.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 1 Samples of possibility and impossibility results in algorithm designing.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 2 More samples.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 3 Communication complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 4 Multiparty Communication Complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 5 Formula complexity I.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 6 Formula complexity II.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 7 Decision Tree Complexity and Fourier analysis.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 9 Circuit Complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 10 Circuit Complexity 2.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 11 Information theoretical argument.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 12 A glimpse of computational complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 08 An introduction to expander graphs(EXPANDER GRAPHS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS).pdf
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 01 A Secure Overlay Cloud Storage System with Access Control and Assured Deletion.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 02 Game theory in computer science.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 03 Controlling Salinity in a Potable Water Supply System Using a Constraint Programming Approach.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 04 CRYPTOGRAPHY.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 05 Fault-Tolerant Computing.ppt
