香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 05 Fault-Tolerant Computing

CMSC 5719 MSc Seminar Fault-Tolerant Computing X,Qiang(Johnny)徐強 [Partly adapted from Koren Krishna,and B.Parhami Slides] Part.1.1 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .1 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 CMSC 5719 MSc Seminar Fault-Tolerant Computing XU, Qiang (Johnny) 徐強 [Partly adapted from Koren & Krishna, and B. Parhami Slides]

Why Learn This Stuff? 空出= 滨治 Part.1.2 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .2 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Why Learn This Stuff?

Outline ◆Motivation Fault classification ◆Redundancy Metrics for Reliability ◆Case studies Part.1.3 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .3 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Outline Motivation Fault classification Redundancy Metrics for Reliability Case studies

Fault-Tolerance Basic definition Fault-tolerant systems ideally systems capable of executing their tasks correctly regardless of either hardware failures or software errors +In practice we can never guarantee the flawless execution of tasks under any circumstances Limit ourselves to types of failures and errors which are more likely to occur Part.1.4 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .4 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Fault-Tolerance - Basic definition Fault-tolerant systems - ideally systems capable of executing their tasks correctly regardless of either hardware failures or software errors In practice - we can never guarantee the flawless execution of tasks under any circumstances Limit ourselves to types of failures and errors which are more likely to occur

Need For Fault-Tolerance ◆ Critical applications require extreme fault tolerance (e.g.,aircrafts,nuclear reactors, medical equipment,and financial applications) A malfunction of a computer in such applications can lead to catastrophe Their probability of failure must be extremely low, possibly one in a billion per hour of operation System operating in a harsh environment with high failure possibilities electromagnetic disturbances particle hits and alike Complex systems consisting of millions of devices Part.1.5 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .5 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Need For Fault-Tolerance Critical applications require extreme fault tolerance (e.g., aircrafts, nuclear reactors, medical equipment, and financial applications) A malfunction of a computer in such applications can lead to catastrophe Their probability of failure must be extremely low, possibly one in a billion per hour of operation System operating in a harsh environment with high failure possibilities electromagnetic disturbances particle hits and alike Complex systems consisting of millions of devices
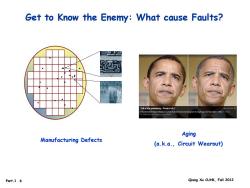
Get to Know the Enemy:What cause Faults? Toll of the presidency-Photo 6 of 6 HEco地0aBO Presidert-elect a photo ustration how he might age over four years Pp地com-PHoto by Kovn D动 Aging Manufacturing Defects (a.k.a.,Circuit Wearout) Part.1.6 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .6 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Get to Know the Enemy: What cause Faults? Manufacturing Defects Aging (a.k.a., Circuit Wearout)

Get to Know the Enemy:What cause Faults? WEATHERPIX STOCK IMAGES Power Supply Noise AV=IR+L Al/At Internal Electronic Noise Electromagnetic Interference Part.1.7 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .7 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Get to Know the Enemy: What cause Faults? Internal Electronic Noise Electromagnetic Interference

Get to Know the Enemy:What cause Faults? ZDNet UK Home News Blogs Reviews Videos Jobs Resources Community Hardware Software Communications I Intemet Security IT Management Emerging Tech Lead lnte°Parallel Studio ZDNet UK Create parallel applications for the desktop Click here to find out mo and compete in a multiccre industry You are here:ZDNet.co.uk>News Software LOGIN ENTERPRISE APPLICATIONS TOOLKIT Email address US software 'blew up Russian gas pipeline' Pentium FDIV Error Password Matt Lon◆Y ZDNet.co.uk Published:.01 Mar 2004 15:10 GMT □Remember mo 色Em家Tre4e:品c饰Lht目Print Post a comme Subreit Help JOIN Faulty US software was to blame for one of the biggest non- ZDNET.CO.UK nuclear explosions the world has ever seen,which took place in a Become part of the Siberian natural gas pipeline,according to a new book published ZDNet community. on Monday. Bugs… Malicious attack (beyond the scope) Part.1.8 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .8 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Get to Know the Enemy: What cause Faults? Bugs … Malicious attack (beyond the scope)

Fault Classification according to Duration Permanent Faults never go away,component has to be repaired or replaced Transient Faults disappear after a relatively short time Example a memory cell whose contents are changed due to some electromagnetic interference Overwriting the memory cell with the right content will make the fault go away Intermittent Faults cycle between active and benign states Example a loose connection An increasing threat largely due to temeprature and voltage fluctuations Part.1.9 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .9 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Fault Classification according to Duration Permanent Faults - never go away, component has to be repaired or replaced Transient Faults - disappear after a relatively short time Example - a memory cell whose contents are changed due to some electromagnetic interference Overwriting the memory cell with the right content will make the fault go away Intermittent Faults - cycle between active and benign states Example - a loose connection An increasing threat largely due to temeprature and voltage fluctuations
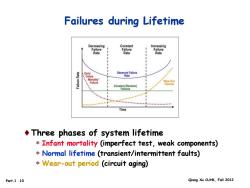
Failures during Lifetime Decreasing Constant Increasing Failure Failure Failure Rate Rate Rate Observed Failure Rate Mortality" Failure Wear Out Fallures Constant(Random) Failures Time Three phases of system lifetime Infant mortality (imperfect test,weak components) Normal lifetime (transient/intermittent faults) Wear-out period (circuit aging) Part.1.10 Qiang Xu CUHK,Fall 2012
Part.1 .10 Qiang Xu CUHK, Fall 2012 Failures during Lifetime Three phases of system lifetime Infant mortality (imperfect test, weak components) Normal lifetime (transient/intermittent faults) Wear-out period (circuit aging)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 04 CRYPTOGRAPHY.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 03 Controlling Salinity in a Potable Water Supply System Using a Constraint Programming Approach.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 02 Game theory in computer science.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 01 A Secure Overlay Cloud Storage System with Access Control and Assured Deletion.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 08 An introduction to expander graphs(EXPANDER GRAPHS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS).pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 12 A glimpse of computational complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 11 Information theoretical argument.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 10 Circuit Complexity 2.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 9 Circuit Complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 7 Decision Tree Complexity and Fourier analysis.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 6 Formula complexity II.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 5 Formula complexity I.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 4 Multiparty Communication Complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 3 Communication complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 2 More samples.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Theory of Computational Complexity》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 1 Samples of possibility and impossibility results in algorithm designing.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 09.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 08.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 06.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(辅导课件)tutorial 05.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 06 3D computer vision techniques.ppt
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 07-1 Research and Applications of Virtual Medicine Part I Introduction to Medical Visualization.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 07-2 Research and Applications of Virtual Medicine Part II Virtual Reality Based Surgical Simulations.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 11 Design of Microfluidics-Based Biochips.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 10 An Introduction to Bioinformatics and its application in Protein-DNA/Protein Interactions Research and Drug Discovery.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《CMSC5719 Seminar》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 12 Introduction to Computational Photography.ppt
- Minimal Cover-Automata for Finite Languages.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 7 Stable matching.Gale-Shapley algorithm.pptx
- 《农业信息技术概论》课程教学资源(教学大纲).pdf
- 《仿真与虚拟农业》课程教学资源(实验指导).pdf
- 天津农学院:《微机原理与汇编语言程序设计》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 《3S技术导论》课程教学资源(实验指导).pdf
- 《3S技术导论》课程教学资源(讲义).pdf
- 《仿真与虚拟农业》课程教学资源(教学大纲).pdf
- 软件设计师考试同步辅导(第4版)第2章 程序设计语言基础.pdf
- 安徽理工大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithm Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第1章 导引与基本数据结构论(任课老师:郭娟、方欢).ppt
- 安徽理工大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithm Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第2章 递归算法设计与分析.ppt
- 安徽理工大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithm Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第3章 分治法——“分”而治之.ppt
- 安徽理工大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithm Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第4章 贪心方法.ppt
- 安徽理工大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithm Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第5章 动态规划.ppt
