厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 01 Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics

兼院究研满勰南臣王季大門厦。 Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics Professor Yongmiao Hong Cornell University May23,2019
Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics Professor Yongmiao Hong Cornell University May 23, 2019

CONTENTS 1.1 General methodology of modern economic research 1.2 Roles of Econometrics 1.3 lllustrative Examples 1.4 Roles of Probability and Statistics Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 2
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 2 1.1 General methodology of modern economic research 1.2 Roles of Econometrics 1.3 Illustrative Examples 1.4 Roles of Probability and Statistics CONTENTS
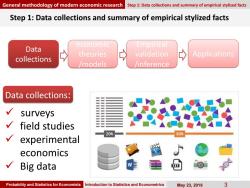
General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts economic Empirica Data theories validation Applications collections models inference Data collections: surveys field studies 20% 80% experimental economics Big data Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 3
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 3 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Data collections: surveys field studies experimental economics Big data General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Data collections economic theories /models Empirical validation /inference Applications

General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts The so-called stylized facts are often summarized from observed economic data. Example 1:Engel curve in microeconomics The share of a consumer's expenditure on a commodity out of her or his total income will vary as his/her income changes; Engel Curves Income (per month) 30 Inferior Engel curves slope 20 backward bending for inferior goods. Normal 10 Food(units 8 12 16 per month) Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 4
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 4 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts The so-called stylized facts are often summarized from observed economic data. General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 1:Engel curve in microeconomics The share of a consumer’s expenditure on a commodity out of her or his total income will vary as his/her income changes;
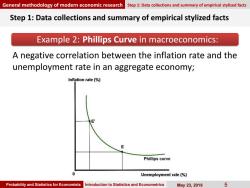
General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 2:Phillips Curve in macroeconomics: A negative correlation between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate in an aggregate economy; Inflation rate (% 不 E Phillips curve 0 Unemployment rate(%) Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 5
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 5 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 2: Phillips Curve in macroeconomics: A negative correlation between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate in an aggregate economy; General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts
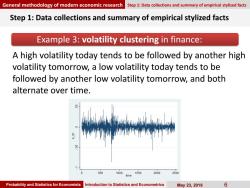
General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 3:volatility clustering in finance: A high volatility today tends to be followed by another high volatility tomorrow,a low volatility today tends to be followed by another low volatility tomorrow,and both alternate over time. 4产中 500 10001500 2000 2500 time Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 6
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 6 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 3: volatility clustering in finance: A high volatility today tends to be followed by another high volatility tomorrow, a low volatility today tends to be followed by another low volatility tomorrow, and both alternate over time. General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts

General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts a starting point the empirical serve as for economic stylized facts research Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 7
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 7 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts the empirical stylized facts a starting point for economic research serve as
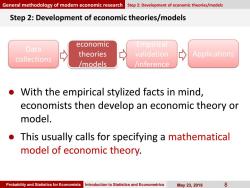
General methodology of modern economic research Step 2:Development of economic theories/models Step 2:Development of economic theories/models economic Empirical Data theories validation Applications collections /models inference With the empirical stylized facts in mind, economists then develop an economic theory or model. This usually calls for specifying a mathematical model of economic theory. Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 8
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 8 Step 2: Development of economic theories/models ● With the empirical stylized facts in mind, economists then develop an economic theory or model. ● This usually calls for specifying a mathematical model of economic theory. General methodology of modern economic research Step 2: Development of economic theories/models Data collections economic theories /models Empirical validation /inference Applications

General methodology of modern economic research Step 2:Development of economic theories/models Step 2:Development of economic theories/models An example is the Euler equation for rational expectations in macroeconomics. The objective of economic modeling is not merely to explain the stylized facts,but also to understand the economic mechanism. Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 9
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 9 Step 2: Development of economic theories/models • An example is the Euler equation for rational expectations in macroeconomics. • The objective of economic modeling is not merely to explain the stylized facts, but also to understand the economic mechanism. General methodology of modern economic research Step 2: Development of economic theories/models
General methodology of modern economic research Step 3:Empirical validation/inference of economic models Step 3:Empirical validation/inference of economic models economic Empirical Data theories validation Applications collections models /inference A key is to transform an economic model into a testable empirical econometric model. One often has to assume some functional form, up to some unknown model parameters,or to choose suitable instrumental variables to form a set of moment conditions. Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May23,2019 10
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 23, 2019 10 Step 3: Empirical validation/inference of economic models General methodology of modern economic research Step 3: Empirical validation/inference of economic models • A key is to transform an economic model into a testable empirical econometric model. • One often has to assume some functional form, up to some unknown model parameters, or to choose suitable instrumental variables to form a set of moment conditions. Data collections economic theories /models Empirical validation /inference Applications
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 09 Hypothesis Testing.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 08 Parameter Estimation and Evaluation.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 07 Convergences and Limit Theorems.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 06 Multivariate Probability Distributions.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 05 Multivariate Probability Distributions.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 10 Big Data, Machine Learning and Statistics.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 03 Random Variables and Univariate Probability Distributions.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 02 Foundation of Probability Theory.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学资源(教学大纲,主讲:洪永淼).pdf
- 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 Professor Yongmiao Hong.pdf
- 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 Classical Linear Regression Model.pdf
- 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 General Regression Analysis.pdf
- 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 Introduction to Econometrics.pdf
- 厦门大学:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics.pdf
- 厦门大学:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)A Course on Advanced Econometrics(主讲:洪永淼).pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版,负责人:李吉续).pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第五章 国际经济的基本知识.pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第四章 失业与通货膨胀.pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第三章 凯恩斯的宏观经济政策主张.pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第二章 凯恩斯的均衡国民收入理论.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 04 Important Probability Distributions.pdf
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)导论(主讲:洪永淼).pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 资本主义经济发展规律.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 附录——商品生产基本概念.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)马克思恩格斯社会主义思想的理论来源(主讲:侯金光).pdf
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)三十年代苏联党内斗争和大镇压(主讲:侯金光).pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)彼得堡大学的经济学家们.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第八章 西方学者关于社会主义的论争.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第九章 新民主主义经济与社会主义改造(主讲:张兴祥).pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十一章 从有计划的商品经济到市场经济.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十章 中国计划经济模式.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十三章 中国模式特征与发展趋势.pptx
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)目录(经济科学出版社,主编:姜旭朝、胡金焱,副主编:孔丹凤).doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第一章 货币基本理论.doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第三章 信用与信用制度.doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第二章 货币制度的形成与演化.doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第四章 利息与利率.doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第五章 金融市场.doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第六章 金融机构体系.doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第七章 商业银行——业务与管理.doc
