厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 06 Multivariate Probability Distributions

誉院宾所清怨南鱼王季大門厦黄 Multivariate Probability Distributions Professor Yongmiao Hong Cornell University April 16,2020
Multivariate Probability Distributions Professor Yongmiao Hong Cornell University April 16, 2020

CONTENTS 6.1 Population and Random Sample 6.2 Sampling Distribution of Sample Mean 6.3 Sampling Distribution of Sample Variance 6.4 Student's t-Distribution 6.5 Snedecor's F Distribution 6,6 Sufficient Statistics 6.7 Conclusion Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 2/167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 2/167 6.1 Population and Random Sample 6.2 Sampling Distribution of Sample Mean 6.3 Sampling Distribution of Sample Variance 6.4 Student’s t-Distribution 6.5 Snedecor's F Distribution 6.6 Sufficient Statistics 6.7 Conclusion CONTENTS

Introduction to Sampling Theory Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Statistical analysis is based on outcomes of a large number of repeated random experiments of same or similar kind. Suppose a random variable Xi denotes the outcome of the i-th experiment.We then obtain a sequence of out- comes,X1,...,Xn,if n experiments are implemented. .This sequence of outcomes then constitutes a so-called random sample from which one can make inference of the underlying probability law which has generated the observed data. Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 3/167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 3/167 Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample
Introduction to Sampling Theory Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Definition 1(6.1).[Random Sample] A random sample,denoted as X"=(X1,..,X),is a sequence of n random variables X1,...,Xn. A realization of the random sample X",denoted as x"= (1,,n),is called a data set generated from X"or a sample point of Xr. A random sample Xm can generate many different data sets. The collection of all possible sample points of X"constitutes the sample space of the random sample X". Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 4/167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 4/167 Definition 1 (6.1). [Random Sample] Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample

Introduction to Sampling Theory Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Example 1 (6.1).[Throwing n Coins] Let Xi denote the outcome of throwing the i-th coin,with Xi=1 if the head shows up,and Xi=0 if the tail shows up. Then X"=(X1,...,Xn)'constitutes a random sample. If we throw n coins,we will obtain a sequence of real numbers, such as xn=(1,1,0,0,1,0,·,1). This sequence is a data set of size n from the random sample Xn. Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 5/167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 5/167 Example 1 (6.1). [Throwing n Coins] Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample

Introduction to Sampling Theory Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Example 1 (6.1).[Throwing n Coins] Obviously,if we throw the n coins again,we will get a different sequence,such as x”=(1,0,0,1,1,1,,0). This is another data set from the random sample X". Apparently,the random sample X"can generate a total of 2m different data sets,each with size n. Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 6/167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 6/167 Example 1 (6.1). [Throwing n Coins] Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample
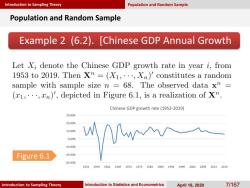
Introduction to Sampling Theory Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Example 2 (6.2).[Chinese GDP Annual Growth Let Xi denote the Chinese GDP growth rate in year i,from 1953 to 2019.Then X"=(X1,...,Xn)'constitutes a random sample with sample size n -68.The observed data x"= (1,,n)',depicted in Figure 6.1,is a realization of xn. Chinese GDP growth rate(1953-2019) 30.00% 20.00% 10.00% 0.00% -10.00% Figure 6.1 -20.00% -30.00% 19541959196419691974197919841989199419992004200920142019 Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 71167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 7/167 Example 2 (6.2). [Chinese GDP Annual Growth Rate] Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Figure 6.1 -30.00% -20.00% -10.00% 0.00% 10.00% 20.00% 30.00% 1954 1959 1964 1969 1974 1979 1984 1989 1994 1999 2004 2009 2014 2019 Chinese GDP growth rate (1953-2019)
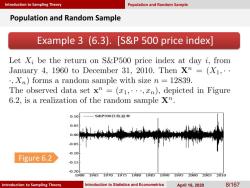
Introduction to Sampling Theory Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Example 3 (6.3).[S&P 500 price index] Let Xi be the return on S&P500 price index at day i,from January 4,1960 to December 31,2010.Then XT=(X1,.. .Xn)forms a random sample with size n 12839. The observed data set x"=(x1,..,xn),depicted in Figure 6.2,is a realization of the random sample X". 0.10 S&P500日收益率 0.05 0.00 0.05 -0.10 Figure 6.2 0.15 0.20f 19601965197019751980198519901995200020052010 Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 8/167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 8/167 Example 3 (6.3). [S&P 500 price index] Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Figure 6.2

Introduction to Sampling Theory Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Remarks: While in theory a random sample X"could generate many different data sets x",each with size n,one may only observe or obtain one data set x"in practice.This is the case with Examples 6.2 and 6.3 which are called time series data. For example,if we would like to obtain another data set for the Chinese GDP growth rate,we would have to let the Chinese economy repeat again back from 1953,and this is simply impossible due to the non-experimental nature of a real economy. Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 9/167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 9/167 Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample Remarks:
Introduction to Sampling Theory Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample In statistical analysis,we still assume that the only ob- served data in Example 6.2 or Example 6.3 is one of many possible realizations from the random sample X". For some random samples,the order of the random vari- ables X1,...,Xn in the sample,together with their real- izations,may not be altered freely. An example is the time series random sample of Ex- amples 6.2,where the random variables X1,...,Xn are not jointly independent,and the behavior of X;may de- pend on the previous outcomes {X-1,X:-2,..}.Such a dynamic structure could not be preserved if one altered the order of random variables and their realizations. Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16,2020 10/167
Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Sampling Theory Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics April 16, 2020 10/167 Population and Random Sample Population and Random Sample
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 05 Multivariate Probability Distributions.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 10 Big Data, Machine Learning and Statistics.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 03 Random Variables and Univariate Probability Distributions.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 02 Foundation of Probability Theory.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学资源(教学大纲,主讲:洪永淼).pdf
- 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 Professor Yongmiao Hong.pdf
- 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 Classical Linear Regression Model.pdf
- 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 General Regression Analysis.pdf
- 中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 Introduction to Econometrics.pdf
- 厦门大学:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics.pdf
- 厦门大学:《高级计量经济学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)A Course on Advanced Econometrics(主讲:洪永淼).pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版,负责人:李吉续).pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第五章 国际经济的基本知识.pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第四章 失业与通货膨胀.pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第三章 凯恩斯的宏观经济政策主张.pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第二章 凯恩斯的均衡国民收入理论.pdf
- 运城学院:《宏观经济学》课程教学资源(各章习题,含答案,打印版)第一章 福利经济学和微观经济政策.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《商业银行经营学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十四章 商业银行经营发展趋势.ppt
- 华东理工大学:《商业银行经营学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十三章 商业银行经营风险与内部控制.ppt
- 华东理工大学:《商业银行经营学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十二章 商业银行绩效评估.ppt
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 07 Convergences and Limit Theorems.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 08 Parameter Estimation and Evaluation.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 09 Hypothesis Testing.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 01 Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics.pdf
- 厦门大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics for Economists》课程教学课件(英文讲稿,2019)Chapter 04 Important Probability Distributions.pdf
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)导论(主讲:洪永淼).pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 资本主义经济发展规律.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 附录——商品生产基本概念.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)马克思恩格斯社会主义思想的理论来源(主讲:侯金光).pdf
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)三十年代苏联党内斗争和大镇压(主讲:侯金光).pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)彼得堡大学的经济学家们.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第八章 西方学者关于社会主义的论争.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第九章 新民主主义经济与社会主义改造(主讲:张兴祥).pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十一章 从有计划的商品经济到市场经济.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十章 中国计划经济模式.pptx
- 厦门大学:《社会主义政治经济学 Socialist Political Economics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第十三章 中国模式特征与发展趋势.pptx
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)目录(经济科学出版社,主编:姜旭朝、胡金焱,副主编:孔丹凤).doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第一章 货币基本理论.doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第三章 信用与信用制度.doc
- 国家十一五规划教材:《货币经济学》课程教学资源(讲义,货币银行学)第二章 货币制度的形成与演化.doc
