电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一讲 CMOS工艺(游飞)

第一讲 CMOS工艺 游飞博导,副教授 电子科学与工程学院,feiyou@uestc.edu.cn
第一讲 CMOS工艺 游飞 博导,副教授 电子科学与工程学院, feiyou@uestc.edu.cn
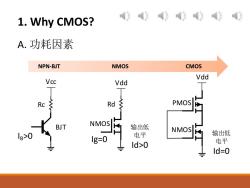
1.Why CMOS? 作传作传作 A.功耗因素 NPN-BJT NMOS CMOS Vdd Vcc Vdd Rc Rd PMOS BJT NMOS 输出低 NMOS 8>0 Ig=0 电平 输出低 Id>0 电平 Id=0
1. Why CMOS? BJT NMOS Rc Vcc Rd Vdd I B >0 Ig=0 输出低 电平 Id>0 NMOS Vdd 输出低 电平 Id=0 PMOS A. 功耗因素 NPN-BJT NMOS CMOS
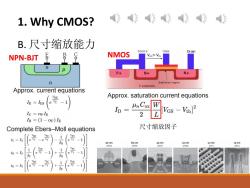
1.Why CMOS? 作作作作作 B.尺寸缩放能力 Source Gate Drain NPN-BJT NMOS VGs<VTH P+ N+ N+ n depletion region P substrate Approx.current equations VBE Approx.saturation current equations Ie=Ies ID= Hn Cox Ic OF IE 2 H[Vas -Vi]2 IB =(1-aF)IE Complete Ebers-Moll equations 尺寸缩放因子 VBE C ic Is -e VT 1 R 90 nm 65 nm 45 nm 32 nm 22nm 14nm 2003 2005 2007 2009 2011 2014 1 VBE 1 VBC iB=Is e vr -1 十 e vr 厥 分 1 -e vr SiGe VT SiGe
1. Why CMOS? B. 尺寸缩放能力 NPN-BJT Complete Ebers–Moll equations Approx. current equations NMOS Approx. saturation current equations 尺寸缩放因子
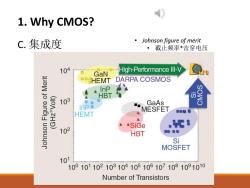
1.Why CMOS? C.集成度 Johnson figure of merit 。截止频率*击穿电压 104 High-Performance Ill-V GaN OSHEMT DARPA COSMOS InP HBT (OAZH5) 103 InP GaAs MESFET HEMT ASiGe 102 HBT 日0a Si MOSFET 10 1001011021031041051061071081091010 Number of Transistors
1. Why CMOS? C. 集成度 • Johnson figure of merit • 截止频率*击穿电压
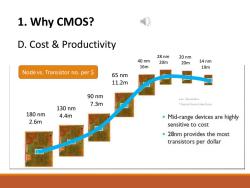
1.Why CMOS? 传 D.Cost Productivity 28 nm 20nm 40nm 20m 20m 14 nm 16m 19m Node vs.Transistor no.per S 65 nm 11.2m 90 nm .nm -Nanometres 7.3m .Forecast Source Linley Group 130nm 180nm 4.4m Mid-range devices are highly 2.6m sensitive to cost 28nm provides the most transistors per dollar
1. Why CMOS? D. Cost & Productivity 180 nm 2.6m 130 nm 4.4m 90 nm 7.3m 65 nm 11.2m 40 nm 16m 28 nm 20m 20 nm 20m 14 nm 19m Node vs. Transistor no. per $
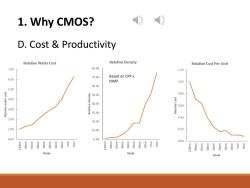
1.Why CMOS? 作 D.Cost Productivity Relative Wafer Cost Relative Density Relative Cost Per Unit 7.00 80.00 1.20 70.00 Based on CPP x 6.00 MMP 1.00 60.00 5.00 0.80 4.00 40.00 0.60 3.00 30.00 2.00 0.40 20.00 1.00 10.00 020 0.00 0.00 0.00 Node Node Node
1. Why CMOS? D. Cost & Productivity
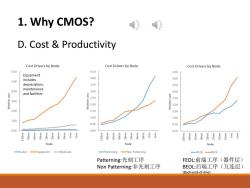
1.Why CMOS? D.Cost Productivity Cost Drivers by Node Cost Drivers by Node Cost Drivers by Node 6.00 4.50 4.50 Equipment includes 4.00 4.00 5.00 depreciation, 3.50 3.50 maintenance 4.00 3.00 3.00 and facilities 2.50 3.00 2.00 annelay 2.00 2.00 1.50 1.50 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.50 0.50 0.00 0.00 0.00 Node Node Node Equipment Materials -Patterning -Non Patterning Patterning:光刻工序 FEOL:前端工序(器件层) Non Patterning:非光刻工序 BEOL:后端工序(互连层) (Back-end-of-line)
1. Why CMOS? D. Cost & Productivity Patterning:光刻工序 Non Patterning:非光刻工序 FEOL:前端工序(器件层) BEOL:后端工序(互连层) (Back-end-of-line)
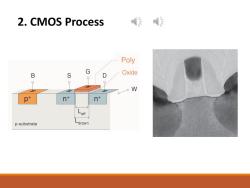
2.CMOS Process 传 Poly G B S D Oxide p W p+ n+ nt Leff p-substrate -drawn
2. CMOS Process
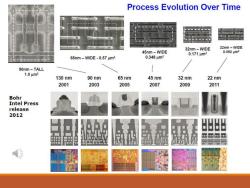
Process Evolution Over Time 32nm-WIDE 22nm-WIDE 45nm-WIDE 0.171m2 0.0924m2 65nm-WIDE-0.57 um2 0.346μm2 90nm-TALL 1.0μm2 130nm 90 nm 65 nm 45 nm 32 nm 22 nm 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 2011 Bohr Intel Press release 2012
2. CMOS Process
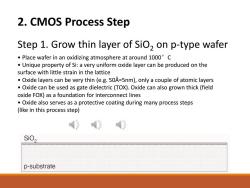
2.CMOS Process Step Step 1.Grow thin layer of SiO,on p-type wafer Place wafer in an oxidizing atmosphere at around 1000C Unique property of Si:a very uniform oxide layer can be produced on the surface with little strain in the lattice Oxide layers can be very thin (e.g.50A=5nm),only a couple of atomic layers Oxide can be used as gate dielectric(TOX).Oxide can also grown thick(field oxide FOX)as a foundation for interconnect lines Oxide also serves as a protective coating during many process steps (like in this process step) SiO, p-substrate
2. CMOS Process Step Step 1. Grow thin layer of SiO2 on p-type wafer • Place wafer in an oxidizing atmosphere at around 1000°C • Unique property of Si: a very uniform oxide layer can be produced on the surface with little strain in the lattice • Oxide layers can be very thin (e.g. 50Å=5nm), only a couple of atomic layers • Oxide can be used as gate dielectric (TOX). Oxide can also grown thick (field oxide FOX) as a foundation for interconnect lines • Oxide also serves as a protective coating during many process steps (like in this process step)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Estimation of Specific Parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Estimation Theory.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Nonparametric detection.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 Multiple pulse detection with random parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 Detection of signals with random parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Multiple Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)chapter 04 Single Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Introduction、Chapter 01 Preparations.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(教学大纲,何子述).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第二节 电子聚合物基电阻式湿度传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第三节 电子聚合物基电容式湿度传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第一节 电子聚合物基湿度传感器概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第二节 柔性传感器 Flexible Sensors.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第三节 电子皮肤 E-skin.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第一节 柔性电子学 Flexible Electronics.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(质量敏感型有毒有害气体传感器研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第二节 无机半导体气体传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(有机薄膜晶体管气体传感器的制备及特性研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(聚苯胺复合薄膜电阻型气体传感器的制备及特性研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第一节 新型气体传感器概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三讲 单级放大器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二讲 CMOS器件.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四讲 噪声 Noise.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七讲 混合器 Mixers.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九讲 Power Amplifiers.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五讲 Transceiver Architecture.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八讲 Passive devices.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六讲 Low-Noise Amplifier.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(教学大纲)RF Circuit Design - Theory and Application(主讲:游长江).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第0章 绪论(主讲:游长江).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 射频通信系统理论.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 射频通信系统中电路理论(2/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 射频通信传播和天线基础理论.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 射频通信系统中电路理论(1/2).pdf
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(实验大纲,2022,王勇).doc
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,电子教案).ppt
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)基本仪器使用简介.pptx
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)模拟与数字电路实验(上).ppt
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)电子教案.ppt
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)模拟与数字电路实验(下).ppt
