电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Multiple Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses

The Signal Detection in Gaussian Noise Chapter 5 Multiple Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses UESTC 1
1 UESTC The Signal Detection in Gaussian Noise Chapter 5 Multiple Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses
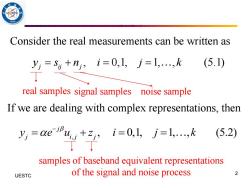
Consider the real measurements can be written as yi=Si+nj,i=0,1,j=1,...,k (5.1) real samples signal samples noise sample If we are dealing with complex representations,then y=e4*9i-01j-lk (5.2) samples of baseband equivalent representations UESTC of the signal and noise process 2
2 UESTC Consider the real measurements can be written as If we are dealing with complex representations, then , 0,1, 1, , (5.1) j ij j y s n i j k = + = = real samples signal samples noise sample , , 0,1, 1, , (5.2) j j i j j y e u z i j k − = + = = samples of baseband equivalent representations of the signal and noise process
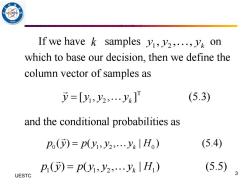
If we have k samples y,y2,...,y on which to base our decision,then we define the column vector of samples as =[1,y2,…y] (5.3) and the conditional probabilities as P()=p1,y2,…yk|Ho) (5.4) P()=p(y1,Jy2,…ykH1) (5.5) UESTC
3 UESTC If we have samples on which to base our decision, then we define the column vector of samples as and the conditional probabilities as k 1 2 , , , k y y y 1 2 [ , , ] (5.3) k y y y y = 0 1 2 0 ( ) ( , , | ) (5.4) k p y p y y y H = 1 1 2 1 ( ) ( , , | ) (5.5) k p y p y y y H =

5.5 The optimum digital detector in additive gaussian noise Assume there are two hypothesis,Ho and Hi,each one corresponds to a set of k complex values 42,j)i=0,1, j=1,.,k (5.31) Under hypothesis H,we obtain k complex measurements,each of which contain an additive complex Gaussian noise variable yy=4,y+2) (5.32) UESTC 4
4 UESTC 5.5 The optimum digital detector in additive Gaussian noise Assume there are two hypothesis, H0 and H1 , each one corresponds to a set of k complex values , , 0,1, 1, , (5.31) i j u i j k = = Under hypothesis Hi , we obtain k complex measurements, each of which contain an additive complex Gaussian noise variable , (5.32) j i j j y u z = +
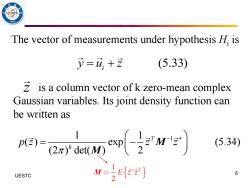
5 The vector of measurements under hypothesis H is 少=4,+2 (5.33) is a column vector of k zero-mean complex Gaussian variables.Its joint density function can be written as 1 p(2)= 2rd3而ns (5.34) UESTC M-E) 5
5 UESTC The vector of measurements under hypothesis Hi is (5.33) i y u z = + is a column vector of k zero-mean complex Gaussian variables. Its joint density function can be written as z 1 1 1 ( ) exp (5.34) (2 ) det( ) 2 T k p z z z − = − M M
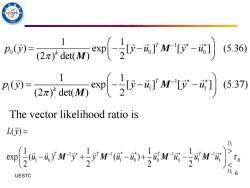
p)= xF530 p( ardw-酊M1r-g到s3n The vector likelihood ratio is L()= D -eyw了与r-0wg宁w Do UESTC 6
6 UESTC 1 0 0 0 1 1 ( ) exp [ ] [ ] (5.36) (2 ) det( ) 2 T k p y y u y u − = − − − M M 1 1 1 1 1 1 ( ) exp [ ] [ ] (5.37) (2 ) det( ) 2 T k p y y u y u − = − − − M M The vector likelihood ratio is 1 0 1 1 * * 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 ( ) 1 1 1 1 exp ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 2 D T T T T B D L y u u y y u u u u u u − − − − = − + − + − M M M M
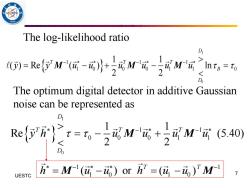
The log-likelihood ratio 0)=Re付M'-+方M-买MG之n,= D The optimum digital detector in additive Gaussian noise can be represented as D e它万}:-对M元+方M元540) Do UESTC 万=M(-)or方=(d-,)TM1 7
7 UESTC 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 ( ) Re ( ) ln 2 2 D T T T B D y y u u u u u u − − − = − + − = M M M The optimum digital detector in additive Gaussian noise can be represented as 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 Re (5.40) 2 2 D T T T D y h u u u u − − = − + M M The log-likelihood ratio 1 1 1 0 1 0 ( ) or ( ) T T h u u h u u − − = − = − M M
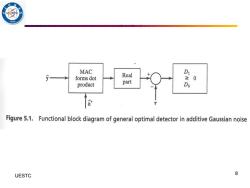
/936 MAC forms dot Real 0 product part Figure 5.1.Functional block diagram of general optimal detector in additive Gaussian noise UESTC 8
8 UESTC
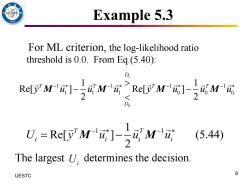
Example 5.3 For ML criterion,the log-likelihood ratio threshold is 0.0.From Eq.(5.40): D RelM RelMM Do U.=ReM元]-)M'或 (5.44) The largest U,determines the decision. UESTC 9
9 UESTC Example 5.3 For ML criterion, the log-likelihood ratio threshold is 0.0. From Eq.(5.40): 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 Re[ ] Re[ ] 2 2 D T T T T D y u u u y u u u − − − − − − M M M M 1 1 1 Re[ ] (5.44) 2 T T U y u u u i i i i − − = − M M The largest determines the decision. Ui
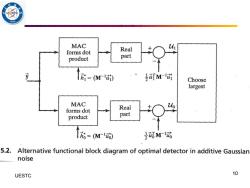
36 MAC forms dot Real product part 宿=M动 号M-1 Choose largest MAC forms dot Real product part 福= (M16) 是裙M-1话 5.2.Alternative functional block diagram of optimal detector in additive Gaussian noise UESTC 10
10 UESTC
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)chapter 04 Single Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Introduction、Chapter 01 Preparations.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(教学大纲,何子述).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第二节 电子聚合物基电阻式湿度传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第三节 电子聚合物基电容式湿度传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第一节 电子聚合物基湿度传感器概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第二节 柔性传感器 Flexible Sensors.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第三节 电子皮肤 E-skin.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第一节 柔性电子学 Flexible Electronics.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(质量敏感型有毒有害气体传感器研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第二节 无机半导体气体传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(有机薄膜晶体管气体传感器的制备及特性研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(聚苯胺复合薄膜电阻型气体传感器的制备及特性研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第一节 新型气体传感器概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器 第3节 非致冷红外传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器 第2节 红外传感器分类及性能参数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器 第1节 红外辐射的基本知识.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 有机敏感材料.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 半导体材料.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 Detection of signals with random parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 Multiple pulse detection with random parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Nonparametric detection.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Estimation Theory.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Estimation of Specific Parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一讲 CMOS工艺(游飞).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三讲 单级放大器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二讲 CMOS器件.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四讲 噪声 Noise.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七讲 混合器 Mixers.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九讲 Power Amplifiers.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五讲 Transceiver Architecture.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八讲 Passive devices.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六讲 Low-Noise Amplifier.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(教学大纲)RF Circuit Design - Theory and Application(主讲:游长江).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第0章 绪论(主讲:游长江).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 射频通信系统理论.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 射频通信系统中电路理论(2/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 射频通信传播和天线基础理论.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 射频通信系统中电路理论(1/2).pdf
