电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Estimation of Specific Parameters

Chapter 11 Estimation of Specific Parameters UESTC 1
1 UESTC Chapter 11 Estimation of Specific Parameters

11.1 Chapter highlights Parameter estimation in WGN Amplitude estimation in the coherent case Amplitude estimation in the noncoherent case Phase estimation in WGN Time-delay estimation in WGN Frequency estimation in WGN UESTC 2
2 UESTC 11.1 Chapter highlights • Parameter estimation in WGN • Amplitude estimation in the coherent case • Amplitude estimation in the noncoherent case • Phase estimation in WGN • Time-delay estimation in WGN • Frequency estimation in WGN

11.2 Parameter estimation in WGN Assume k samples of the measured signal are y;=s;(a)+n,i=1,...,k where the noise is zero-mean,white Gaussian noise with variance o2.Therefore, 心e7齐-ej MAP.p可mx→p(ik)+小&np(a)-0 UESTC 是立(g-aa@+npa=0
11.2 Parameter estimation in WGN Assume k samples of the measured signal are where the noise is zero-mean, white Gaussian noise with variance . Therefore, MAP: 3 UESTC ( ) , 1, , i i i y n = + = s i k α 2 ( ) ( ) ( ( )) 2 / 2 2 2 1 1 1 exp 2 2 k k i i i p y y s = = − − ln ln 0 p y p ( ) ( ) + = p y ( ) max ( ( )) ( ) ( ) 2 1 1 ln 0 k i i i i s y s p = − + =
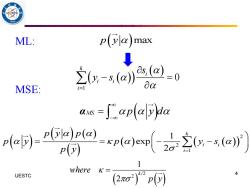
ML: p(a max 20x-sj)22-0 MSE: na as-aplaya e同-4 d 1 where K= UESTC 2o2p可 4
ML: MSE: 4 UESTC p y( )max ( ( )) ( ) 1 0 k i i i i s y s = − = MS p y d ( ) − = α ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ( ))2 2 1 1 exp 2 k i i i p y p p y p y s p y = = = − − ( ) ( ) / 2 2 1 2 where k p y =

5 For a ML estimate that is unbiased,the CRB provides the minimum variance that can be got. npa)-n2ar-2a立(ysai i1 品mp啡a之yag I- ↓ 品5网-空控n@- UESTC
For a ML estimate that is unbiased, the CRB provides the minimum variance that can be got. 5 UESTC ( ) ( ( )) 2 2 2 1 1 ln ln 2 2 2 k i i i k p y y s = = − − − ( ) ( ( )) ( ) 2 1 1 ln k i i i i s p y y s = = − ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 4 2 1 1 1 1 1 ln k k k i i j i j i j i s s s E p y E = = = = = n n
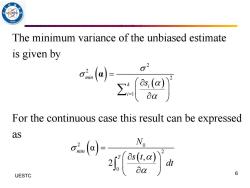
/9 The minimum variance of the unbiased estimate is given by For the continuous case this result can be expressed as N dt UESTC 6
The minimum variance of the unbiased estimate is given by For the continuous case this result can be expressed as 6 UESTC ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 1 min k i i s = = α ( ) ( ) 2 0 2 0 α , 2 min T N s t dt =
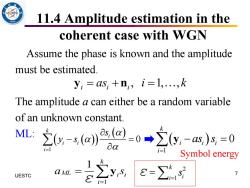
11.4 Amplitude estimation in the coherent case with WGN Assume the phase is known and the amplitude must be estimated. y;=aS+n,i=1,.,k The amplitude a can either be a random variable of an unknown constant. ML: -a四-0+2(0ag0 i=l Symbol energy UESTC ∑y e=∑s 7 i=l
11.4 Amplitude estimation in the coherent case with WGN Assume the phase is known and the amplitude must be estimated. The amplitude a can either be a random variable of an unknown constant. ML: 7 UESTC , 1, , i i i y n = + = as i k ( ( )) ( ) 1 0 k i i i i s y s = − = ( ) 1 0 k i i i i as s = y − = 1 1 k ML i i i a s = = y ε 2 1 k i i s = ε= Symbol energy
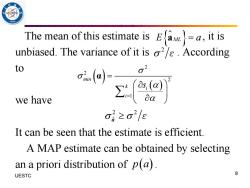
The mean of this estimate is Ea=a,it is unbiased.The variance of it is .According to we have o≥o2/e It can be seen that the estimate is efficient. A MAP estimate can be obtained by selecting an a priori distribution of p(a). UESTC 8
The mean of this estimate is , it is unbiased. The variance of it is . According to we have It can be seen that the estimate is efficient. A MAP estimate can be obtained by selecting an a priori distribution of . 8 UESTC E a aML = 2 ε ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 1 min k i i s = = α 2 2 aˆ ε p a( )

Example 11.2 Let a be a zero-mean Gaussian random variable with varianceo.According to y:=aS,+n,i=1,…,k and 空to但ana-0 aa we have 合0w+}-0 Therefore ∑y aMAP 2 UESTC E+ 9 2
Example 11.2 Let a be a zero-mean Gaussian random variable with variance . According to and we have Therefore 9 UESTC 2 a , 1, , i i i y n = + = as i k ( ( )) ( ) ( ) 2 1 1 ln 0 k i i i i s y s p = − + = ( ) 2 2 2 1 1 0 2 k i i i i a a y as s = a − + − = 1 2 2 k i i i MAP a s = = + y a ε

Since p(a)is Gaussian in this example,the posteriori pdf p(is 点m最-ar+刘 Letting 2 K We have UESTC 10
Since is Gaussian in this example, the posteriori pdf is Letting We have 10 UESTC p a( ) p a y ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 exp exp 2 2 2 2 k i i i i a i a a p a y y as y a s = = − − − + 2 2 0 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 exp 2 2 2 k MAP i i a a a y = = − + + ε ( ) ( ) 2 0 2 2 1 1 exp 2 MAP a p a y a a = − + − ε
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Estimation Theory.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Nonparametric detection.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 Multiple pulse detection with random parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 Detection of signals with random parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Multiple Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)chapter 04 Single Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Introduction、Chapter 01 Preparations.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(教学大纲,何子述).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第二节 电子聚合物基电阻式湿度传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第三节 电子聚合物基电容式湿度传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第一节 电子聚合物基湿度传感器概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第二节 柔性传感器 Flexible Sensors.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第三节 电子皮肤 E-skin.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第一节 柔性电子学 Flexible Electronics.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(质量敏感型有毒有害气体传感器研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第二节 无机半导体气体传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(有机薄膜晶体管气体传感器的制备及特性研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(聚苯胺复合薄膜电阻型气体传感器的制备及特性研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第一节 新型气体传感器概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器 第3节 非致冷红外传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一讲 CMOS工艺(游飞).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三讲 单级放大器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二讲 CMOS器件.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四讲 噪声 Noise.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七讲 混合器 Mixers.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九讲 Power Amplifiers.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五讲 Transceiver Architecture.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八讲 Passive devices.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六讲 Low-Noise Amplifier.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(教学大纲)RF Circuit Design - Theory and Application(主讲:游长江).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第0章 绪论(主讲:游长江).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 射频通信系统理论.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 射频通信系统中电路理论(2/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 射频通信传播和天线基础理论.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 射频通信系统中电路理论(1/2).pdf
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(实验大纲,2022,王勇).doc
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,电子教案).ppt
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)基本仪器使用简介.pptx
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)模拟与数字电路实验(上).ppt
- 复旦大学:《模拟与数字电路实验 Analog and Digital Circuit Experiments》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)电子教案.ppt
