电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Introduction、Chapter 01 Preparations

呀 Signal Detection and Estimation 2020 edition UESTC 1
UESTC 何子述等 Signal Detection and Estimation 2020 edition 1

Introduction 1 The fundamental structure of signal transmission v(t Information I(t) s(@ s() x() extract I(t)or s(t) Or modulation signal channel receiver Message 下s(①) signal source Usually,the received signal: x(t)=so(t)+v(t入 additive UESTC noise 2
UESTC 何子述等 2 1、The fundamental structure of signal transmission Usually, the received signal: ( ) ( ) ( ) o x t s t v t = + additive noise 0 s (t) signal channel receiver Information Or Message modulation signal source 1 I(t) s (t) s (t) o v(t) x(t) 1 extract I(t) or s (t) + Introduction

In addition.some other noise types Multiplicative Noise Amplitude has changed during signal transmission process. S,(t)=a(t)s,(t) a(t)changes randomly (such as fading channel in mobile communication); Convolution Noise s.()=s(t)*B()(such as multi-path effect impulse response B(t)is a random process UESTC 3
UESTC 何子述等 3 Multiplicative Noise :Amplitude has changed during signal transmission process. changes randomly (such as fading channel in mobile communication); Convolution Noise : 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) o s t t s t = 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) o s t s t t = (such as multi-path effect ) impulse response ( )t is a random process ( )t In addition , some other noise types :

0 This course mainly discuss the signal detection and estimation of additive noise. By taking logarithm,the multiplicative noise can be transformed to additive noise. By taking FFT,the convolution noise can be transformed to multiplicative noise ,and t then to additive noise by taking logarithm. So all kinds of noise can transform to additive noise to discuss. UESTC何子述等 4
UESTC 何子述等 4 • This course mainly discuss the signal detection and estimation of additive noise. • By taking logarithm, the multiplicative noise can be transformed to additive noise. • By taking FFT, the convolution noise can be transformed to multiplicative noise ,and then to additive noise by taking logarithm. So all kinds of noise can transform to additive noise to discuss

2 The signal types with additive noise (1)deterministic signal x(t)=s(t)+v() For example:PAM signal (Pulse Amplitude Modulation st0=A0cosa40=0 within the period T PFM signal (Pulse Frequency Modulation s(t)=Acos()0 J0,1 within the period T Synchronous digital communication (without random phase) UESTC 5
UESTC 何子述等 5 2、The signal types with additive noise For example:PAM signal (Pulse Amplitude Modulation ) PFM signal (Pulse Frequency Modulation ) x t s t v t ( ) ( ) ( ) = + 1 ( ) ( )cos( ), ( ) 0 o s t A t t A t = = within the period T 1 i i 2 , 1 ( ) cos( ), , 0 s t A t = = within the period T Synchronous digital communication (without random phase) (1) deterministic signal

(2)signals with random parameters With random parameters x(t)=s(t)+v(t) ·PAM:s(t)=A(t)Cos(o,t十p) PFM: Random phases -8e】 4cos(@+) Asynchronous digital communication often encounter! UESTC 6
UESTC 何子述等 6 (2) signals with random parameters x t s t v t ( ) ( ) ( ) = + • PAM: ( ) ( )cos( ) o s t A t t = + • PFM: 1 1 2 2 cos( ) ( ) cos( ) A t s t A t + = + Asynchronous digital communication often encounter ! With random parameters Random phases
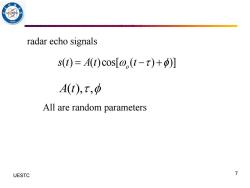
radar echo signals s(1)=A(t)cos[@(t-t)+) A(t),t,o All are random parameters UESTC 7
UESTC 何子述等 7 ( ) ( )cos[ ( ) )] o s t A t t = − + radar echo signals All are random parameters A t( ), ,

(3)stochastic signals or random signals stochastic signal x(t)=s(t)+v(t) (random process) electronic reconnaissance receiving signal; seismic signal monitoring; astronomical observing signal; passive radar signal; sonar signal and so on. UESTC 8
UESTC 何子述等 8 (3) stochastic signals or random signals x t s t v t ( ) ( ) ( ) = + electronic reconnaissance receiving signal; seismic signal monitoring; astronomical observing signal; passive radar signal; sonar signal and so on. stochastic signal (random process)

3 The concept of signal detection S1() s(t) x(t) signal observation(input) signal source channel space x(t)has some sampling values:,N N sampling values can be combined to observation vector,and the spanned space called observation space The distribution of noise might be known.s(t)has M states, S1,S2,...,SM;which is called M hypotheses H1,H2,...,HM UESTC 9
UESTC 何子述等 9 3、The concept of signal detection signal source signal channel observation (input) space s1(t) + s(t) v(t) x(t) x(t) has some sampling values: 1 2 N x x x , , , N sampling values can be combined to observation vector, and the spanned space called observation space ; The distribution of noise might be known. s(t) has M states, S1 ,S2 ,…,SM; which is called M hypotheses H1 ,H2 ,…,HM

Generally,the probability of P(H) is also known and ∑P(H,)=1 i=l Question:According to observing vector,determine which hypothesis in M hypotheses is true on an optimum criterion.This process is called signal detection x(t) decision criterion H true,denoted by Di detection=make a decision UESTC 10
UESTC 何子述等 10 Question: According to observing vector, determine which hypothesis in M hypotheses is true on an optimum criterion. This process is called signal detection decision criterion x(t) Hi true, denoted by Di detection=make a decision Generally, the probability of is also known and 1 ( ) 1 M i i P H = = ( ) P Hi
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(教学大纲,何子述).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第二节 电子聚合物基电阻式湿度传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第三节 电子聚合物基电容式湿度传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 电子聚合物基湿度传感器 第一节 电子聚合物基湿度传感器概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第二节 柔性传感器 Flexible Sensors.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第三节 电子皮肤 E-skin.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 专题讲座 第一节 柔性电子学 Flexible Electronics.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(质量敏感型有毒有害气体传感器研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第二节 无机半导体气体传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(有机薄膜晶体管气体传感器的制备及特性研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第三节 电子聚合物薄膜气体传感器(聚苯胺复合薄膜电阻型气体传感器的制备及特性研究).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 新型气体传感器 第一节 新型气体传感器概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器 第3节 非致冷红外传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器 第2节 红外传感器分类及性能参数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器 第1节 红外辐射的基本知识.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 新型红外传感器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 有机敏感材料.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 半导体材料.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 陶瓷敏感材料.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《敏感材料与传感器 Sensitive Materials and Sensors》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 金属敏感材料 第4节 超导敏感材料.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)chapter 04 Single Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Multiple Sample Detection of Binary Hypotheses.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 Detection of signals with random parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 Multiple pulse detection with random parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Nonparametric detection.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Estimation Theory.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《信号检测与估计 Signal Detection and Estimation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Estimation of Specific Parameters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一讲 CMOS工艺(游飞).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三讲 单级放大器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二讲 CMOS器件.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四讲 噪声 Noise.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七讲 混合器 Mixers.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九讲 Power Amplifiers.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五讲 Transceiver Architecture.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八讲 Passive devices.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频集成电路 RF Integrated Circuits》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六讲 Low-Noise Amplifier.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(教学大纲)RF Circuit Design - Theory and Application(主讲:游长江).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第0章 绪论(主讲:游长江).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 射频通信系统理论.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《射频电路理论与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 射频通信系统中电路理论(2/2).pdf
