上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 酶:基本概念及动力学 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics(8.1-8.4)

上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 8: Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学 Berg·Tymoczko·Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition
Berg • Tymoczko • Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition Chapter 8: Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学

OUTLINES 1.Enzymes Are Powerful and Highly Specific Catalysts一概论 2.Free Energy Is a Useful Thermodynamic Function for Understanding Enzymes-热力学 3.Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State一化学 4.The Michaelis-Menten Model Accounts for the Kinetic Properties of Many Enzymes一动力学 5.Enzymes Can Be Inhibited by Specific Molecules一抑制作用
1. Enzymes Are Powerful and Highly Specific Catalysts - 概论 2. Free Energy Is a Useful Thermodynamic Function for Understanding Enzymes -热力学 3. Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State -化学 4. The Michaelis-Menten Model Accounts for the Kinetic Properties of Many Enzymes -动力学 5. Enzymes Can Be Inhibited by Specific Molecules -抑制作用 OUTLINES

The most striking characteristics of enzymes: 一 Catalytic power(催化高效性) Specificity(选择性) Chemical nature: 一Proteins蛋白质(Nearly all known enzymes are proteins,but proteins are not an absolute monopoly on catalysis);
The most striking characteristics of enzymes: - Catalytic power (催化高效性) - Specificity (选择性) Chemical nature: - Proteins 蛋白质 (Nearly all known enzymes are proteins, but proteins are not an absolute monopoly on catalysis);
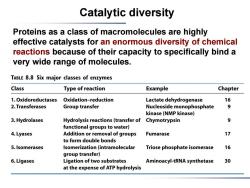
Catalytic diversity Proteins as a class of macromolecules are highly effective catalysts for an enormous diversity of chemical reactions because of their capacity to specifically bind a very wide range of molecules. TABLE 8.8 Six major classes of enzymes Class Type of reaction Example Chapter 1.Oxidoreductases Oxidation-reduction Lactate dehydrogenase 16 2.Transferases Group transfer Nucleoside monophosphate 9 kinase(NMP kinase) 3.Hydrolases Hydrolysis reactions(transfer of Chymotrypsin 9 functional groups to water) 4.Lyases Addition or removal of groups Fumarase 17 to form double bonds 5.Isomerases Isomerization(intramolecular Triose phosphate isomerase 16 group transfer) 6.Ligases Ligation of two substrates Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase 30 at the expense of ATP hydrolysis
Catalytic diversity Proteins as a class of macromolecules are highly effective catalysts for an enormous diversity of chemical reactions because of their capacity to specifically bind a very wide range of molecules

Active site活性中心 Active site活性中心:Catalysis takes place at a particular site on the enzyme. Substrate ES complex Enryme By untilizing the full repertoire of intermolecular forces 分子间作用力,enzymes bring substrates together in an optimal orientation定位,the prelude to making and breaking chemical bonds.They catalyze reactions by stabilizing transition states:过渡态,the highest-energy speciesi高能物质in reaction pathways
Active site 活性中心:Catalysis takes place at a particular site on the enzyme. By untilizing the full repertoire of intermolecular forces 分子间作用力, enzymes bring substrates together in an optimal orientation定位, the prelude to making and breaking chemical bonds. They catalyze reactions by stabilizing transition states过渡态, the highest-energy species高能物质 in reaction pathways. Active site 活性中心

OUTLINES 1.Enzymes Are Powerful and Highly Specific Catalysts 2.Free Energy Is a Useful Thermodynamic Function for Understanding Enzymes-热力学 3.Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State一化学 4.The Michaelis-Menten Model Accounts for the Kinetic Properties of Many Enzymes一动力学 5.Enzymes Can Be Inhibited by Specific Molecules一抑制作用
1. Enzymes Are Powerful and Highly Specific Catalysts 2. Free Energy Is a Useful Thermodynamic Function for Understanding Enzymes -热力学 3. Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State -化学 4. The Michaelis-Menten Model Accounts for the Kinetic Properties of Many Enzymes -动力学 5. Enzymes Can Be Inhibited by Specific Molecules -抑制作用 OUTLINES
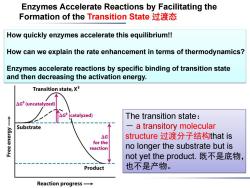
Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State过渡态 How quickly enzymes accelerate this equilibrium!! How can we explain the rate enhancement in terms of thermodynamics? Enzymes accelerate reactions by specific binding of transition state and then decreasing the activation energy. Transition state,X+ △Gt(uncatalyzed) The transition state: Substrate a transitory molecular △G structure过渡分子结构that is for the reaction no longer the substrate but is not yet the product.既不是底物, Product 也不是产物。 Reaction progress→
Enzymes Accelerate Reactions by Facilitating the Formation of the Transition State 过渡态 The transition state: - a transitory molecular structure 过渡分子结构that is no longer the substrate but is not yet the product. 既不是底物, 也不是产物。 How quickly enzymes accelerate this equilibrium!! How can we explain the rate enhancement in terms of thermodynamics? Enzymes accelerate reactions by specific binding of transition state and then decreasing the activation energy

Transition State(过渡态) A chemical reaction of substrate s to form product P goes through a transition state S*that has a higher free energy than does either S or F.(高能过渡分子) The star denotes a thermodynamic property of the transition state.The transition state is the most seldom occupied species 很难捕捉along the reaction pathway because it is the one with the highest free energy.(不稳定) .The difference in free energy between the transition state and the substrate is called the Gibbs free energy of activation or simply the activation energy,symbolized by AG*. △G*=Gs*-Gs
Transition State (过渡态) • A chemical reaction of substrate S to form product P goes through a transition state S* that has a higher free energy than does either S or P. (高能过渡分子) • The star * denotes a thermodynamic property of the transition state. The transition state is the most seldom occupied species 很难捕捉 along the reaction pathway because it is the one with the highest free energy. (不稳定) •The difference in free energy between the transition state and the substrate is called the Gibbs free energy of activation or simply the activation energy, symbolized by ΔG*
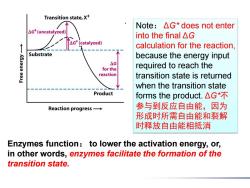
Transition state,X* Note:AG*does not enter △Gt(uncatalyzed) into the final△G △G(catalyzed) calculation for the reaction, Substrate K6Jeua because the energy input △G for the required to reach the reaction transition state is returned when the transition state Product forms the product.△G*不 Reaction progress→ 参与到反应自由能,因为 形成时所需自由能和裂解 时释放自由能相抵消 Enzymes function:to lower the activation energy,or, in other words,enzymes facilitate the formation of the transition state
Enzymes function: to lower the activation energy, or, in other words, enzymes facilitate the formation of the transition state. Note: ΔG* does not enter into the final ΔG calculation for the reaction, because the energy input required to reach the transition state is returned when the transition state forms the product. ΔG*不 参与到反应自由能,因为 形成时所需自由能和裂解 时释放自由能相抵消
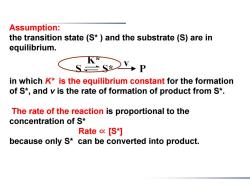
Assumption: the transition state (S*)and the substrate (S)are in equilibrium. in which K*is the equilibrium constant for the formation of S*,and v is the rate of formation of product from S*. The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of S* Rate [S*] because only S*can be converted into product
Assumption: the transition state (S* ) and the substrate (S) are in equilibrium. in which K* is the equilibrium constant for the formation of S*, and v is the rate of formation of product from S*. The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of S* Rate ∝ [S*] because only S* can be converted into product
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Exploring Genes and Genomes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 DNA, RNA, and Genetic Information.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 Exploring Proteins and Proteomes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 12 Lipids and Cell Membranes 脂质和细胞膜.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Carbohydrates 糖类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Regulatory Strategies 调控策略.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Catalytic Strategies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学(8.4-8.5).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学(8.1-8.2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 13 Membrane Channels and Pumps 膜通道和泵.pdf
- 厦门理工学院:《环境工程微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(傅海燕).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(习题)转基因技术自测题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)生物常用设备及耗材.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(课件)绪论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)酶的“奥妙”——蛋白质的分析检测(SDS-PAGE电泳).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)酶的“奥妙”——蛋白质的盐析沉淀.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)生物柴油的制备.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)耐药性话题讨论.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)抗生素的抑菌作用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第2章 基因工程.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Biochemistry:An Evolving Science.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Protein Composition and Structure.pdf
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)【美】Jeremy Berg, John Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer《Biochemistry(Seventh Edition)》.pdf
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第01章 生物化学——不断发展的科学(生物化学属于进化科学).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第10章 调节机制.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第11章 糖.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第12章 脂质与细胞膜.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第13章 膜通道和泵.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第14章 信号传导途径.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第02章 生化进化.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第02章 蛋白质的组成和结构(第六版).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第03章 蛋白质和蛋白质组学研究技术.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第04章 核酸与遗传信息流(DNA、RNA、和遗传信息流).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第05章 基因和基因组的研究技术方法.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第06章 生物信息学和进化的研究方法.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第07章 血红蛋白(蛋白质发挥作用的图景).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第08章 酶(基本概念与动力学).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第09章 催化机制.doc
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(题库与答案)Chapter 10 Regulatory Strategies.doc
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(题库与答案)Chapter 11 Carbohydrates.doc
