上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Catalytic Strategies

Berg·Tymoczko·Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition Chapter 9: Catalytic Strategies Copyright 2007 by W.H.Freeman and Company
Biochemistry Sixth Edition Chapter 9: Catalytic Strategies Copyright © 2007 by W. H. Freeman and Company Berg • Tymoczko • Stryer

Chess and enzymes have in common the use of strategy, consciously thought out in the game of chess and selected by evolution for the action of an enzyme. 酶和下棋有异曲同工之处: 下棋要精细考虑;酶作用的选择性进化。 Chapter 9Opener Biochemistry,Sixth Edition 2007 W.H.Freeman and Company The three amino acid residues at the right constitute a catalytic triad.催化三联体加入象棋中的皇后,不能有损
Chess and enzymes have in common the use of strategy, consciously thought out in the game of chess and selected by evolution for the action of an enzyme. 酶和下棋有异曲同工之处: 下棋要精细考虑;酶作用的选择性进化 The three amino acid residues at the right constitute a catalytic triad. 催化三联体加入象棋中的皇后,不能有损

Sources of the catalytic power and specificity of enzymes? 酶催化能力及特异性从何而来? The catalytic strategies used by four classes of enzymes: 1.serine proteases:丝氨酸蛋白酶 2.carbonic anhydrases碳酸脱水酶 3.restriction endonucleases限制性核酸内切酶 4.Nucleotide Monophosphate Kinases:核苷单磷酸激酶 water to a substrate The mechanism of each enzyme was revealed through the use of incisive experimental probes机制清楚,实验可证明 protein structure determination (Chapter 3) site-directed mutagenesis (Chapter 5)
The catalytic strategies used by four classes of enzymes: 1. serine proteases丝氨酸蛋白酶 2. carbonic anhydrases碳酸脱水酶 3. restriction endonucleases限制性核酸内切酶 4. Nucleotide Monophosphate Kinases核苷单磷酸激酶 Sources of the catalytic power and specificity of enzymes? 酶催化能力及特异性从何而来? The mechanism of each enzyme was revealed through the use of incisive experimental probes 机制清楚,实验可证明 - protein structure determination (Chapter 3) - site-directed mutagenesis (Chapter 5). water to a substrate

Strategies to solve a different problem解决催化反应面临的挑战 每类酶的催化机制能解决各种化学反应所面临的问题。 -Serine proteases丝氨酸蛋白酶:to promote a reaction that is almost immeasurably slow at neutral pH in the absence of a catalyst.pH 7.0 几乎不发生的反应(蛋白质水解)进行下去 -Carbonic anhydrasesi碳酸脱水酶:to achieve a high absolute rate of reaction,suitable for integration with other rapid physiological processes. 加速,以与其他快速生理过程融合 -Restriction endonucleases限制性核酸内切酶,to attain a high degree of specificity.实现酶切反应的高度特异性 -NMP kinases核苷单磷酸激酶:to transfer a phosphoryl group from AT P to a nucleotide and not to water.磷酸基团从ATP转移给另一个核苷酸(而 不会转移到水分子) Structural and mechanistic comparisons of enzyme action are thus the sources of insight into the evolutionary history of enzymes.In addition,our knowledge of catalytic strategies has been used to develop practical applications,including potent drugs
-Serine proteases丝氨酸蛋白酶: to promote a reaction that is almost immeasurably slow at neutral pH in the absence of a catalyst. 将pH 7.0 几乎不发生的反应(蛋白质水解)进行下去 -Carbonic anhydrases碳酸脱水酶: to achieve a high absolute rate of reaction, suitable for integration with other rapid physiological processes. 加速, 以与其他快速生理过程融合 -Restriction endonucleases限制性核酸内切酶, to attain a high degree of specificity.实现酶切反应的高度特异性 - NMP kinases核苷单磷酸激酶: to transfer a phosphoryl group from AT P to a nucleotide and not to water.磷酸基团从ATP转移给另一个核苷酸(而 不会转移到水分子) Strategies to solve a different problem 解决催化反应面临的挑战 Structural and mechanistic comparisons of enzyme action are thus the sources of insight into the evolutionary history of enzymes. In addition, our knowledge of catalytic strategies has been used to develop practical applications, including potent drugs. 每类酶的催化机制能解决各种化学反应所面临的问题

A few basic catalytic principles基本催化原理 Enzymatic catalysis begins with substrate binding. The binding energy结合能:a large number of weak interactions between the enzyme and the substrate.弱相互作用 The binding energy as serving two purposes: establishes substrate specificity Only the correct substrate can participate in the interactions increases catalytic efficiency the full complement of such interactions is formed only when the combination of enzyme and substrate is in the transition state. The binding energy can also promote structural changes in both the enzyme and the substrate that facilitate catalysis,a process referred to as induced fit
The binding energy结合能: a large number of weak interactions between the enzyme and the substrate. 弱相互作用 The binding energy as serving two purposes: - establishes substrate specificity Only the correct substrate can participate in the interactions - increases catalytic efficiency the full complement of such interactions is formed only when the combination of enzyme and substrate is in the transition state. A few basic catalytic principles 基本催化原理 The binding energy can also promote structural changes in both the enzyme and the substrate that facilitate catalysis, a process referred to as induced fit. Enzymatic catalysis begins with substrate binding

Enzymes commonly employ one or more of the following strategies to catalyze specific reactions: 1.Covalent Catalysis共价催化:the active site contains a reactive group,usually a powerful nucleophile,that becomes temporarily covalently attached to a part of the substrate in the course of catalysis.The proteolytic enzyme provides an excellent example of this strategy 共价催化的活性位点有活泼基团,通常是很强的亲核基团。 在酶促过程中亲核基团能暂时性共价连接底物。 2.General Acid-Base Catalysis酸碱催化.In general acid- base catalysis,a molecule other than water plays the role of a proton donor or acceptor. 酸碱催化中,水分子之外的物质提供质子或接受质子
1. Covalent Catalysis共价催化: the active site contains a reactive group, usually a powerful nucleophile, that becomes temporarily covalently attached to a part of the substrate in the course of catalysis. The proteolytic enzyme provides an excellent example of this strategy . 共价催化的活性位点有活泼基团,通常是很强的亲核基团。 在酶促过程中亲核基团能暂时性共价连接底物。 2. General Acid–Base Catalysis酸碱催化. In general acid– base catalysis, a molecule other than water plays the role of a proton donor or acceptor. 酸碱催化中,水分子之外的物质提供质子或接受质子 Enzymes commonly employ one or more of the following strategies to catalyze specific reactions:

3.( Catalysis by Approximation邻近催化.Many reactions include two distinct substrates.The reaction rate may be considerably enhanced by bringing the two substrates together along a single binding surface on an enzyme. 很多酶有两个不同的底物。将两种底物置于一个酶分 子的同一结合面能显著增加反应速度 4.Metal lon Catalysist金属离子催化.Metal ions can function catalytically in several ways,ie. Nucleophiles and an electrophile 金属离子起催化作用的方式有几种。配位作用、亲电 作用或亲核作用等
3. Catalysis by Approximation邻近催化. Many reactions include two distinct substrates. The reaction rate may be considerably enhanced by bringing the two substrates together along a single binding surface on an enzyme. 很多酶有两个不同的底物。将两种底物置于一个酶分 子的同一结合面能显著增加反应速度 4. Metal Ion Catalysis金属离子催化. Metal ions can function catalytically in several ways, ie. Nucleophiles and an electrophile 金属离子起催化作用的方式有几种。配位作用、亲电 作用或亲核作用等

Cases -Serine proteases:to promote a reaction that is almost immeasurably slow at neutral pH in the absence of a catalyst.将pH7.0几乎不发生 的反应(蛋白质水解)进行下去 -Carbonic anhydrases:to achieve a high absolute rate of reaction,suitable for integration with other rapid physiological processes.加速以与其他快速生理过程融合 -Restriction endonucleases,to attain a high degree of specificity. 酶切反应的高度特异性 NMP kinases:to transfer a phosphoryl group from AT P to a nucleotide and not to water.磷酸基团从ATP转移给另一个核苷酸(而不 会转移到水分子)
-Serine proteases : to promote a reaction that is almost immeasurably slow at neutral pH in the absence of a catalyst. 将pH 7.0几乎不发生 的反应(蛋白质水解)进行下去 -Carbonic anhydrases: to achieve a high absolute rate of reaction,suitable for integration with other rapid physiological processes. 加速以与其他快速生理过程融合 -Restriction endonucleases, to attain a high degree of specificity.实现 酶切反应的高度特异性 - NMP kinases: to transfer a phosphoryl group from AT P to a nucleotide and not to water.磷酸基团从ATP转移给另一个核苷酸(而不 会转移到水分子) Cases

Proteases Facilitate a Fundamentally Difficult Reaction Protein turnover is an important process in living systems (Chapter 23).Proteins degradation into their constituent amino acids can be recycled for the synthesis of new proteins.蛋白质降解产物可以为新蛋白合成所利用。 Proteins ingested in the diet must be broken down for absorption in the gut.膳食中的蛋白在肠道中完全降解 Proteolytic reactions are important in regulating the activity of certain enzymes and other proteins(Chapter10)蛋白降 解反应对于某些酶及蛋白质的活性的调节作用 Proteases cleave proteins by a hydrolysis reaction- the addition of a molecule of water to a peptide bond. R ,+R2一NH Unnumbered figure pg 243a Biochemistry,Sixth Edition 2007 W.H.Freeman and Company
Proteases Facilitate a Fundamentally Difficult Reaction Protein turnover is an important process in living systems (Chapter 23). Proteins degradation into their constituent amino acids can be recycled for the synthesis of new proteins. 蛋白质降解产物可以为新蛋白合成所利用。 - Proteins ingested in the diet must be broken down for absorption in the gut. 膳食中的蛋白在肠道中完全降解 - Proteolytic reactions are important in regulating the activity of certain enzymes and other proteins(Chapter 10)蛋白降 解反应对于某些酶及蛋白质的活性的调节作用 . Proteases cleave proteins by a hydrolysis reaction – the addition of a molecule of water to a peptide bond
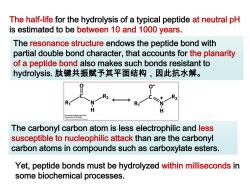
The half-life for the hydrolysis of a typical peptide at neutral pH is estimated to be between 10 and 1000 years. The resonance structure endows the peptide bond with partial double bond character,that accounts for the planarity of a peptide bond also makes such bonds resistant to hydrolysis.肽键共振赋予其平面结构,因此抗水解。 R H duP924h The carbonyl carbon atom is less electrophilic and less susceptible to nucleophilic attack than are the carbonyl carbon atoms in compounds such as carboxylate esters. Yet,peptide bonds must be hydrolyzed within milliseconds in some biochemical processes
The half-life for the hydrolysis of a typical peptide at neutral pH is estimated to be between 10 and 1000 years. The resonance structure endows the peptide bond with partial double bond character, that accounts for the planarity of a peptide bond also makes such bonds resistant to hydrolysis. 肽键共振赋予其平面结构,因此抗水解。 The carbonyl carbon atom is less electrophilic and less susceptible to nucleophilic attack than are the carbonyl carbon atoms in compounds such as carboxylate esters. Yet, peptide bonds must be hydrolyzed within milliseconds in some biochemical processes
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学(8.4-8.5).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学(8.1-8.2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 13 Membrane Channels and Pumps 膜通道和泵.pdf
- 厦门理工学院:《环境工程微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(傅海燕).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(习题)转基因技术自测题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)生物常用设备及耗材.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(课件)绪论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)酶的“奥妙”——蛋白质的分析检测(SDS-PAGE电泳).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)酶的“奥妙”——蛋白质的盐析沉淀.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)生物柴油的制备.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)耐药性话题讨论.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)抗生素的抑菌作用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第2章 基因工程.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第1章 现代生物技术总论(主讲:赵静雅).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《现代遗传学》课程教学资源(各章练习题及解答).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《极端环境中的微生物生命 Microbial Life in Extreme Environments》课程教学资源_Thermophiles.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《极端环境中的微生物生命 Microbial Life in Extreme Environments》课程教学资源_Thermophiles notes.doc
- 上海交通大学:《极端环境中的微生物生命 Microbial Life in Extreme Environments》课程教学资源_Piezophiles.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《极端环境中的微生物生命 Microbial Life in Extreme Environments》课程教学资源_Piezophile notes.doc
- 上海交通大学:《微生物的世界 Microbial World》通识教育课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 公共健康与生物恐怖主义 Public Health and Bioterrorism.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Regulatory Strategies 调控策略.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Carbohydrates 糖类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 12 Lipids and Cell Membranes 脂质和细胞膜.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 Exploring Proteins and Proteomes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 DNA, RNA, and Genetic Information.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Exploring Genes and Genomes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 酶:基本概念及动力学 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics(8.1-8.4).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Biochemistry:An Evolving Science.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Protein Composition and Structure.pdf
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)【美】Jeremy Berg, John Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer《Biochemistry(Seventh Edition)》.pdf
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第01章 生物化学——不断发展的科学(生物化学属于进化科学).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第10章 调节机制.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第11章 糖.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第12章 脂质与细胞膜.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第13章 膜通道和泵.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第14章 信号传导途径.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第02章 生化进化.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第02章 蛋白质的组成和结构(第六版).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第03章 蛋白质和蛋白质组学研究技术.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第04章 核酸与遗传信息流(DNA、RNA、和遗传信息流).doc
