上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 12 Lipids and Cell Membranes 脂质和细胞膜

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 12: Lipids and Cell Membranes 脂质和细胞膜 Berg·ymoczko·Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition
Berg • Tymoczko • Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition Chapter 12: Lipids and Cell Membranes 脂质和细胞膜

上游充通大兽 Introduction SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent 剂)molecules.肥皂泡表面是一种去污剂分子形成的脂质双层膜。 The polar heads(red)pack together,leaving the hydrophobic groups (green)in contact with air on the inside and outside of the bubble
The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent (去垢 剂) molecules.肥皂泡表面是一种去污剂分子形成的脂质双层膜。 The polar heads (red) pack together, leaving the hydrophobic groups (green) in contact with air on the inside and outside of the bubble. Introduction
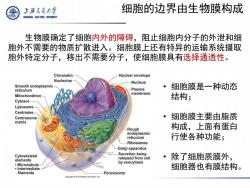
上游充通大兽 细胞的边界由生物膜构成 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 生物膜确定了细胞内外的障碍,阻止细胞内分子的外泄和细 胞外不需要的物质扩散进入。细胞膜上还有特异的运输系统摄取 胞外特定分子,移出不需要分子,使细胞膜具有选择通透性。 Chromatin Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Nucleus Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Plasma 细胞膜是一种动态 Mitochondrion membrane 结构; Cytosol- Lysosome Centrioles Centrosome 细胞膜主要由脂质 matrix Rough 构成,上面有蛋白 endoplasmic reticulum 行使各种功能; Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Cytoskeletal Secretion being released from cell ·除了细胞质膜外, elements ·Microtubule by exocytosis Intermediate 细胞器也有膜结构。 filaments Peroxisome Copyright 2010 Pearson Education,Inc
• 细胞膜是一种动态 结构; • 细胞膜主要由脂质 构成,上面有蛋白 行使各种功能; • 除了细胞质膜外, 细胞器也有膜结构。 细胞的边界由生物膜构成 生物膜确定了细胞内外的障碍,阻止细胞内分子的外泄和细 胞外不需要的物质扩散进入。细胞膜上还有特异的运输系统摄取 胞外特定分子,移出不需要分子,使细胞膜具有选择通透性

上游充通大兽 Many Common Features Underlie the Diversity SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY of Biological Membranes Membranes are as diverse in structure as they are in function.However, they do have in common a number of important attributes: 1.膜是层类结构,只有两个分子厚。Membranes are sheetlike structures, only two molecules thick,that form dosed boundaries between different compartments.The thickness of most membranes is between 60 A(6 nm) and 100 A(10 nm). 2.膜的主要组分是脂质和蛋白质。Membranes consist mainly of lipids and proteins.The mass ratio of lipids to proteins ranges from 1:4 to 4:1. Membranes also contain carbohydrates that are linked to lipids and proteins. 3.膜的脂质分子分为亲水和疏水两个部分。Membrane lipids are small molecules that have both hydrophilic(亲水的)and hydrophobic(疏水 的)moieties.这些脂质分子在水中能够自发形成封闭双层结构。These lipids spontaneously form closed bimolecular sheets in aqueous media. These lipid bilayers are barriers to the flow of polar molecules
Many Common Features Underlie the Diversity of Biological Membranes Membranes are as diverse in structure as they are in function. However, they do have in common a number of important attributes: 1.膜是层类结构,只有两个分子厚。Membranes are sheetlike structures, only two molecules thick, that form dosed boundaries between different compartments. The thickness of most membranes is between 60 Å (6 nm) and 100 Å (10 nm). 2.膜的主要组分是脂质和蛋白质。Membranes consist mainly of lipids and proteins. The mass ratio of lipids to proteins ranges from 1:4 to 4:1. Membranes also contain carbohydrates that are linked to lipids and proteins. 3.膜的脂质分子分为亲水和疏水两个部分。Membrane lipids are small molecules that have both hydrophilic (亲水的) and hydrophobic (疏水 的) moieties.这些脂质分子在水中能够自发形成封闭双层结构。These lipids spontaneously form closed bimolecular sheets in aqueous media. These lipid bilayers are barriers to the flow of polar molecules

上游充通大兽 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 4.通过特殊蛋白质介导,使生物膜有不同功能。Specific proteins mediate distinctive functions of membranes.Proteins serve as pumps ( channels(通道),receptors(受体),energy transducers(能量传感 器),and enzymes(酶).Membrane proteins are embedded in lipid bilayers which create suitable enviroments for their action. 5.Membranes are noncovalent assemblies.膜分子组装依依靠非共价相互 作用。The constituent protein and lipid molecules are held together by many noncovalent interactions,which act cooperatively. 6.Membranes are asymmetric.膜是非对称结构。The two faces of biological membranes always differ from each other
4.通过特殊蛋白质介导,使生物膜有不同功能。Specific proteins mediate distinctive functions of membranes. Proteins serve as pumps(泵), channels(通道), receptors(受体), energy transducers(能量传感 器), and enzymes(酶). Membrane proteins are embedded in lipid bilayers , which create suitable enviroments for their action. 5. Membranes are noncovalent assemblies. 膜分子组装依依靠非共价相互 作用。 The constituent protein and lipid molecules are held together by many noncovalent interactions, which act cooperatively. 6. Membranes are asymmetric. 膜是非对称结构。The two faces of biological membranes always differ from each other

上游充通大兽 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 7.Membranes are fluid structures.膜是流动性结构。Lipid molecules diffuse rapidly in the plane of the membrane,as do proteins,unless they are anchored by specific interactions.In contrast,lipid molecules and proteins do not readily rotate across the membrane.Membranes can be regarded as two-dimensional solutions of oriented proteins and lipids.生物膜可以看作是脂质和蛋白质之间有序排列的二维结构。 8.Most cell membranes are electrically polarized,大多数细胞膜两侧电 极化的,such that the inside is negative[typically-60 millivolts(mV)】 Membrane potential plays a key role in transport(运输),energy conversion(能量转换),and excitability(神经兴奋)
7. Membranes are fluid structures. 膜是流动性结构。Lipid molecules diffuse rapidly in the plane of the membrane, as do proteins, unless they are anchored by specific interactions. In contrast, lipid molecules and proteins do not readily rotate across the membrane. Membranes can be regarded as two-dimensional solutions of oriented proteins and lipids.生物膜可以看作是脂质和蛋白质之间有序排列的二维结构。 8. Most cell membranes are electrically polarized,大多数细胞膜两侧电 极化的,such that the inside is negative [typically - 60 millivolts (mV)]. Membrane potential plays a key role in transport(运输), energy conversion(能量转换), and excitability(神经兴奋)

上游充通大兽 OUTLINES SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.Fatty Acids Are Key Constituents of Lipids 脂肪酸是脂质的主要组成成分 2.There Are Three Common Types of Membrane Lipids 3.Phospholipids and Glycolipids Readily Form Bimolecular Sheets in Aqueous Media 4.Proteins Carry Out Most Membrane Processes 5.Lipids and Many Membrane Proteins Diffuse Rapidly in the plane of the Membrane 6.Eukaryotic Cells Contain Compartments Bounded by Internal Membranes
OUTLINES 1.Fatty Acids Are Key Constituents of Lipids 脂肪酸是脂质的主要组成成分 2.There Are Three Common Types of Membrane Lipids 3.Phospholipids and Glycolipids Readily Form Bimolecular Sheets in Aqueous Media 4.Proteins Carry Out Most Membrane Processes 5.Lipids and Many Membrane Proteins Diffuse Rapidly in the plane of the Membrane 6.Eukaryotic Cells Contain Compartments Bounded by Internal Membranes

上游文通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.Fatty Acids Are Key Constituents of Lipids The hydrophobic(疏水的)properties of lipids are essential to their ability to form membranes. 脂类的疏水特性是它们形成膜所必须的。 Most lipids owe their hydrophobic properties to one component,their fatty acids. 大多数脂类的疏水特性都是由于他们结构中的脂 肪酸部分带来的
The hydrophobic (疏水的) properties of lipids are essential to their ability to form membranes. 脂类的疏水特性是它们形成膜所必须的。 Most lipids owe their hydrophobic properties to one component, their fatty acids. 大多数脂类的疏水特性都是由于他们结构中的脂 肪酸部分带来的。 1.Fatty Acids Are Key Constituents of Lipids
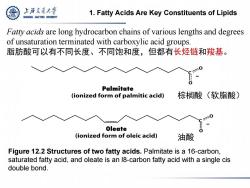
上游究更大学 1.Fatty Acids Are Key Constituents of Lipids SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Fatty acids are long hydrocarbon chains of various lengths and degrees of unsaturation terminated with carboxylic acid groups. 脂肪酸可以有不同长度、不同饱和度,但都有长烃链和羧基。 Palmitate (ionized form of palmitic acid) 棕榈酸(软脂酸) Oleate (ionized form of oleic acid) 油酸 Figure 12.2 Structures of two fatty acids.Palmitate is a 16-carbon, saturated fatty acid,and oleate is an 18-carbon fatty acid with a single cis double bond
1. Fatty Acids Are Key Constituents of Lipids Figure 12.2 Structures of two fatty acids. Palmitate is a 16-carbon, saturated fatty acid, and oleate is an l8-carbon fatty acid with a single cis double bond. 棕榈酸(软脂酸) 油酸 Fatty acids are long hydrocarbon chains of various lengths and degrees of unsaturation terminated with carboxylic acid groups. 脂肪酸可以有不同长度、不同饱和度,但都有长烃链和羧基

上游文通大学 Fatty Acid Names Are Based on Their SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Parent Hydrocarbons The systematic name for a fatty acid is derived from the name of its parent hydrocarbon by the substitution of oic for the final e. 脂肪酸的系统命名来自于它们的烷烃母体。 Octadecane(十八烷)Octadecanoic acid(十八烷酸) Hexadecane Palmitate Hexadecanoic acid (ionized form of palmitic acid) 棕榈酸(16:0) cis-△9.Octadecene Oleate (ionized form of oleic acid) cis-A9-Octadecenoic acid 油酸(18:1) The notation 18:0 denotes a Cis fatty acid with no double bonds,whereas 18:2 signifies that there are two double bonds
Fatty Acid Names Are Based on Their Parent Hydrocarbons The systematic name for a fatty acid is derived from the name of its parent hydrocarbon by the substitution of oic for the final e. 脂肪酸的系统命名来自于它们的烷烃母体。 Octadecane(十八烷) → Octadecanoic acid (十八烷酸) The notation 18:0 denotes a C18 fatty acid with no double bonds, whereas 18:2 signifies that there are two double bonds. 棕榈酸 (16:0) 油酸 (18:1) Hexadecane Hexadecanoic acid cis-D9 -Octadecene cis-D9 -Octadecenoic acid
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Carbohydrates 糖类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Regulatory Strategies 调控策略.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Catalytic Strategies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学(8.4-8.5).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学(8.1-8.2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 13 Membrane Channels and Pumps 膜通道和泵.pdf
- 厦门理工学院:《环境工程微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(傅海燕).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(习题)转基因技术自测题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)生物常用设备及耗材.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(课件)绪论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)酶的“奥妙”——蛋白质的分析检测(SDS-PAGE电泳).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)酶的“奥妙”——蛋白质的盐析沉淀.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)生物柴油的制备.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)耐药性话题讨论.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)抗生素的抑菌作用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第2章 基因工程.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物技术概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第1章 现代生物技术总论(主讲:赵静雅).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《现代遗传学》课程教学资源(各章练习题及解答).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《极端环境中的微生物生命 Microbial Life in Extreme Environments》课程教学资源_Thermophiles.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《极端环境中的微生物生命 Microbial Life in Extreme Environments》课程教学资源_Thermophiles notes.doc
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 Exploring Proteins and Proteomes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 DNA, RNA, and Genetic Information.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Exploring Genes and Genomes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 酶:基本概念及动力学 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics(8.1-8.4).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Biochemistry:An Evolving Science.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Protein Composition and Structure.pdf
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)【美】Jeremy Berg, John Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer《Biochemistry(Seventh Edition)》.pdf
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第01章 生物化学——不断发展的科学(生物化学属于进化科学).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第10章 调节机制.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第11章 糖.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第12章 脂质与细胞膜.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第13章 膜通道和泵.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第14章 信号传导途径.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第02章 生化进化.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第02章 蛋白质的组成和结构(第六版).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第03章 蛋白质和蛋白质组学研究技术.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第04章 核酸与遗传信息流(DNA、RNA、和遗传信息流).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第05章 基因和基因组的研究技术方法.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第06章 生物信息学和进化的研究方法.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第07章 血红蛋白(蛋白质发挥作用的图景).doc
