上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Biochemistry:An Evolving Science

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 教材: 编者: ●JEREMY M.BERG -Ph.D.in chemistry from Harvard Biochemistry -Professor of Johns Hopkins University,School of Medicine -Director of the Department of Biophysics and Biophysical Chemistry ●JOHN L.TYMOCZKO -Towsley Professor of Biology at Jeremy M.Berg Carleton College John L.Tymoczko Lubert Stryer (第六版) ●LUBERT STRYER -Winzer Professor of Cell Biology, School of Medicine And Professor of Neurobiology at Stanford University
教材: 编者: • JEREMY M. BERG -Ph.D. in chemistry from Harvard -Professor of Johns Hopkins University, School of Medicine -Director of the Department of Biophysics and Biophysical Chemistry • JOHN L. TYMOCZKO -Towsley Professor of Biology at Carleton College • LUBERT STRYER -Winzer Professor of Cell Biology, School of Medicine And Professor of Neurobiology at Stanford University (第六版)

上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 1: Biochemistry:An Evolving Science Berg·Tymoczko·Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition
Berg • Tymoczko • Stryer Biochemistry Sixth Edition Chapter 1: Biochemistry: An Evolving Science
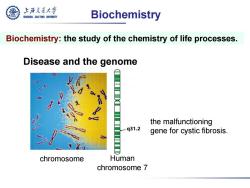
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Biochemistry Biochemistry:the study of the chemistry of life processes. Disease and the genome the malfunctioning q31.2 gene for cystic fibrosis. chromosome Human chromosome 7
Disease and the genome the malfunctioning gene for cystic fibrosis. chromosome Human chromosome 7 Biochemistry: the study of the chemistry of life processes. Biochemistry

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1828,the discovery that biological molecules such as urea (could be synthesized from nonliving components, scientists have explored the chemistry of life. Many of the most fundamental mysteries of how living things function have now been solved.However,much remains to be investigated.(很多未知) the application of our tremendous knowledge of biochemistry to problems in medicine,agriculture, environmental sciences...(已知与应用的联系) One of the most startling discoveries of the past century:the great unity of all living things at the biochemical level所有生物在生化水平上的统一性
1828, the discovery that biological molecules such as urea (尿素)could be synthesized from nonliving components, scientists have explored the chemistry of life. Many of the most fundamental mysteries of how living things function have now been solved. However, much remains to be investigated. (很多未知) the application of our tremendous knowledge of biochemistry to problems in medicine, agriculture, environmental sciences…….(已知与应用的联系) One of the most startling discoveries of the past century: the great unity of all living things at the biochemical level 所有生物在生化水平上的统一性

上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY OUTLINES 1.Biochemical Unity Underlies Biological Diversity 2.DNA Illustrates the Interplay between Form and Function 3.Concepts from Chemistry Explain the Properties of Biological Molecules 4.The Genomic Revolution Is Transforming Biochemistry and Medicine
1. Biochemical Unity Underlies Biological Diversity 2. DNA Illustrates the Interplay between Form and Function 3. Concepts from Chemistry Explain the Properties of Biological Molecules 4.The Genomic Revolution Is Transforming Biochemistry and Medicine OUTLINES

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY OUTLINES 1.Biochemical Unity Underlies Biological Diversity 2.DNA Illustrates the Interplay between Form and Function 3.Concepts from Chemistry Explain the Properties of Biological Molecules 4.The Genomic Revolution Is Transforming Biochemistry and Medicine
1. Biochemical Unity Underlies Biological Diversity 2. DNA Illustrates the Interplay between Form and Function 3. Concepts from Chemistry Explain the Properties of Biological Molecules 4.The Genomic Revolution Is Transforming Biochemistry and Medicine OUTLINES
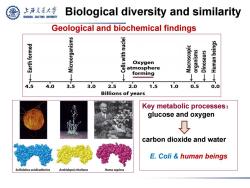
上游充通大学 Biological diversity and similarity SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Geological and biochemical findings Oxygen atmosphere sunesou! ↓ ↓ ↓ forming ↓ ↓ 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 Billions of years Key metabolic processes: glucose and oxygen carbon dioxide and water E.Coli human beings Sulfolobus acidicaldarius Arabidopsis thaliana Homo sapiens
Biological diversity and similarity Key metabolic processes: glucose and oxygen carbon dioxide and water E. Coli & human beings Geological and biochemical findings
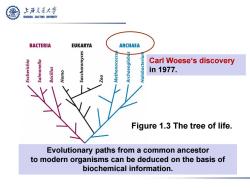
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY BACTERIA EUKARYA ARCHAEA Carl Woese's discovery in1977. Figure 1.3 The tree of life. Evolutionary paths from a common ancestor to modern organisms can be deduced on the basis of biochemical information
Figure 1.3 The tree of life. Carl Woese‘s discovery in 1977. Evolutionary paths from a common ancestor to modern organisms can be deduced on the basis of biochemical information

上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Comparing and contrasting details of particular biochemical pathways in different organisms how biological challenges are solved at the biochemical level. In most cases,these challenges are addressed by the adaptation of existing macromolecules 物大分子适应性to new roles rather than by the evolution of entirely new ones. Structure Function
Comparing and contrasting details of particular biochemical pathways in different organisms • how biological challenges are solved at the biochemical level. • In most cases, these challenges are addressed by the adaptation of existing macromolecules 生 物大分子适应性 to new roles rather than by the evolution of entirely new ones. Structure & Function

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY OUTLINES 1.Biochemical Unity Underlies Biological Diversity 2.DNA Illustrates the Interplay between Form and Function 3.Concepts from Chemistry Explain the Properties of Biological Molecules 4.The Genomic Revolution Is Transforming Biochemistry and Medicine
1. Biochemical Unity Underlies Biological Diversity 2. DNA Illustrates the Interplay between Form and Function 3. Concepts from Chemistry Explain the Properties of Biological Molecules 4.The Genomic Revolution Is Transforming Biochemistry and Medicine OUTLINES
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 酶:基本概念及动力学 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics(8.1-8.4).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Exploring Genes and Genomes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 DNA, RNA, and Genetic Information.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 Exploring Proteins and Proteomes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 12 Lipids and Cell Membranes 脂质和细胞膜.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Carbohydrates 糖类.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Regulatory Strategies 调控策略.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Catalytic Strategies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学(8.4-8.5).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 Enzymes:Basic Concepts and Kinetics 酶:基本概念及动力学(8.1-8.2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 13 Membrane Channels and Pumps 膜通道和泵.pdf
- 厦门理工学院:《环境工程微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(傅海燕).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(习题)转基因技术自测题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)生物常用设备及耗材.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(课件)绪论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)酶的“奥妙”——蛋白质的分析检测(SDS-PAGE电泳).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)酶的“奥妙”——蛋白质的盐析沉淀.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)生物柴油的制备.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)耐药性话题讨论.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《在实验中探究生物技术》课程教学资源(实验)抗生素的抑菌作用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Protein Composition and Structure.pdf
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)【美】Jeremy Berg, John Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer《Biochemistry(Seventh Edition)》.pdf
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第01章 生物化学——不断发展的科学(生物化学属于进化科学).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第10章 调节机制.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第11章 糖.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第12章 脂质与细胞膜.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第13章 膜通道和泵.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第14章 信号传导途径.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第02章 生化进化.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第02章 蛋白质的组成和结构(第六版).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第03章 蛋白质和蛋白质组学研究技术.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第04章 核酸与遗传信息流(DNA、RNA、和遗传信息流).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第05章 基因和基因组的研究技术方法.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第06章 生物信息学和进化的研究方法.doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第07章 血红蛋白(蛋白质发挥作用的图景).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第08章 酶(基本概念与动力学).doc
- 《生物化学 Biochemistry》课程教学资源(课本材料)第09章 催化机制.doc
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(题库与答案)Chapter 10 Regulatory Strategies.doc
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(题库与答案)Chapter 11 Carbohydrates.doc
- 上海交通大学:《生物化学 Biochemistry(B类)》课程教学资源(题库与答案)Chapter 12 Lipids and Cell Membranes.doc
