电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 14 Modeling and Simulation in Epitaxial Growth

UQSTC 的 956 Modeling and Simulation in Epitaxial Growth
Modeling and Simulation in Epitaxial Growth
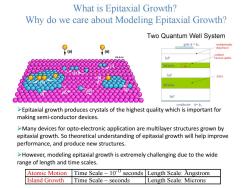
What is Epitaxial Growth? Why do we care about Modeling Epitaxial Growth? Two Quantum Well System gateφ=φo modulationally doped layer (a (a) confined 70-00444 InP Electron(qubit) InGaAs InP 2DEG InGaAs InP conductor=φ1 >Epitaxial growth produces crystals of the highest quality which is important for making semi-conductor devices. >Many devices for opto-electronic application are multilayer structures grown by epitaxial growth.So theoretical understanding of epitaxial growth will help improve performance,and produce new structures. >However,modeling epitaxial growth is extremely challenging due to the wide range of length and time scales. Atomic Motion Time Scale~103 seconds Length Scale:Angstrom Island Growth Time Scale seconds Length Scale:Microns
9750-00-444 (a) (a) (h) (f) (e) (b) (c) (i) (g) (d) What is Epitaxial Growth? Why do we care about Modeling Epitaxial Growth? Atomic Motion Time Scale ~ 10-13 seconds Length Scale: Angstrom Island Growth Time Scale ~ seconds Length Scale: Microns o ➢Epitaxial growth produces crystals of the highest quality which is important for making semi-conductor devices. ➢Many devices for opto-electronic application are multilayer structures grown by epitaxial growth. So theoretical understanding of epitaxial growth will help improve performance, and produce new structures. ➢However, modeling epitaxial growth is extremely challenging due to the wide range of length and time scales

Modeling of Thin Film Growth >Mean-field Rate Equations: Easy to formulate and easy to solve. Contain no spatial information.Do not readily yield information on surface morphology. >Continuum Models:Completely deterministic method. Appropriate mainly at large time and length scales. Lack detail. >KMC simulations:Completely stochastic method. Very useful for identifying relevant microscopic processes. The time and size limitations make them unfeasible for studying epitaxial growth Detailed KMC simulations are extremely slow and expensive
Modeling of Thin Film Growth ➢Mean-field Rate Equations: ✓Easy to formulate and easy to solve. ❖Contain no spatial information. Do not readily yield information on surface morphology. ➢ Continuum Models: Completely deterministic method. ✓Appropriate mainly at large time and length scales. ❖Lack detail. ➢KMC simulations: Completely stochastic method. ✓Very useful for identifying relevant microscopic processes. ❖The time and size limitations make them unfeasible for studying epitaxial growth ❖Detailed KMC simulations are extremely slow and expensive

Smallest Metallic Nanorods Using Physical Vapor Deposition
Smallest Metallic Nanorods Using Physical Vapor Deposition
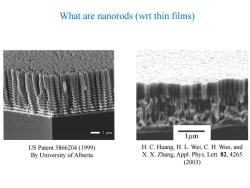
What are nanorods (wrt thin films) 1μm 1μm US Patent5866204(1999) H.C.Huang,H.L.Wei,C.H.Woo,and By University of Alberta X.X.Zhang,Appl.Phys.Lett.82,4265 (2003)
What are nanorods (wrt thin films) US Patent 5866204 (1999) By University of Alberta H. C. Huang, H. L. Wei, C. H. Woo, and X. X. Zhang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 4265 (2003)

Synthesis methods Atmosphere Multi-Agent Solution Substrate Vacuum Source COMPLEX
Synthesis methods COMPLEX

PVD and GLAD Physical Vapor Deposition Glancing Angle Deposition Substrate Electron Beam Electron Beam Magnetic Field 0 o ao o Magnetic Field H20 H20 H,O H20 Earth Earth Ground Ground 1959 Metallic Nanorods realized from PVD Diffusion distance of metals at room temperature microns Even GLAD should form dense films Nanorod growth is not understood
Physical Vapor Deposition PVD and GLAD Glancing Angle Deposition 1959 Metallic Nanorods realized from PVD Diffusion distance of metals at room temperature = microns Even GLAD should form dense films Nanorod growth is not understood

Three modes of epitaxial crystal growth Monolayer steps with Multi-layer steps with 3D ES conventional 2D ES barrier barrier result in nanorods result in islands with lateral diameter of~100 nm,or even dimension over 1000 nm smaller ~10 nm. H.C.Huang,JOM64,1253(2012)
Three modes of epitaxial crystal growth H. C. Huang, JOM 64, 1253 (2012) Monolayer steps with conventional 2D ES barrier result in islands with lateral dimension over 1000 nm Multi-layer steps with 3D ES barrier result in nanorods diameter of ~100 nm, or even smaller ~10 nm

Three dimensional ES barrier Atom moving Terrace on terrace 3a88 Terrace 0.0 白◆ Kink Step 0.1 -0.2 ...Monolayer (16 images) -0.3 -Monolayer (8 images) Atom moving ×-Two-layer (8 images) -0.4 acmoss Three-layer (8 images) a 3-D ES barrier -0.5 -Four-layer (8 images) ● Atom moving across a 1-D ES barer -0.6 Atom moving across (island corner barrer 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 a 2-D ES barrier Reaction Coordinate Contrast:0.06 ev,0.16 ev,0.40 ev. M.G.Lagally and Z.Y.Zhang,Nature,417,907(2002) S.K.Xiang and H.C.Huang,Appl.Phys.Lett.92,101923(2008)
Contrast: 0.06 eV, 0.16 eV, & 0.40 eV. Three dimensional ES barrier M. G. Lagally and Z. Y. Zhang, Nature, 417, 907 (2002) S. K. Xiang and H. C. Huang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 101923 (2008)

Three dimensional ES barrier E3D-0.16eV 20000000-¥ 000000-¥4 0000000000000000-¥k+2 0000000000000000000000000000000 R.L.Schwoebel and E.J.Shipsey,J. Appl.Phys.37,3682(1966) 20 45 90X ◆E2p-0.26eV das 15 -E2n0.16eV 一 E2-0.06eV 35 E3D-0.40 eV 10 30 25 20 15 0. 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 E3(ev)
Three dimensional ES barrier E3D=0.16 eV R. L. Schwoebel and E. J. Shipsey, J. Appl. Phys. 37, 3682 (1966) E3D=0.40 eV
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 13 Monte Carlo.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 12 An introduction of Monte Carlo method.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 11 Modeling, Computation, Simulation, Designing and Screening of New Materials.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 07 Surface calculations(1/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 06 Bulk calculations(2/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 05 Bulk calculations(1/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 04 DFT(3/3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 03 DFT(2/3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 02 DFT(1/3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 01 Introduction(张妍宁).pdf
- 《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(参考书籍)DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY - A Practical Introduction(DAVID S. SHOLL、JANICE A. STECKEL).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 热分析 Thermal analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 色谱法 chromatography.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 核磁共振谱 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy,NMR.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 拉曼光谱 Raman spectroscopy.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 红外光谱 Infrared Spectroscopy.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 分子荧光光谱 Molecular fluorescence spectroscopy.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 紫外——可见光谱 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy UV—Vis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 波谱分析.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 绪论(刘钰).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 15 Examples of MCMC:Reaction-Diffusion(R-D)model.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 16 MD in Materials Studio Key Modules.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 08 Surface calculations(2/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 09 Materials design.pdf
- 《金陵科技学院学报》:PZT压电材料参数在ANSYS中的定义方法.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(参考资料,打印版)塑料、纤维、橡胶的英文缩写语.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)高分子材料配方实例.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验三十一 一种隔热涂料的制备及其性能测试实验.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验三十 高分子材料3D打印实验.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验二十九 硬脂酸相变储能石膏板的制备与性能研究.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十六 扫描电子显微镜法观察聚合物聚态结构.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十五 差热分析.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十四 红外光谱分析.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十三 氧指数的测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十二 塑料的热老化实验.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十一 马丁耐热性测试.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十 维卡软化点测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验九 塑化性能转矩流变仪的测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验八 塑料熔体流动速率的测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验七 冲击强度测定.pdf
