电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 16 MD in Materials Studio Key Modules

MD in materials studio Key Modules > Discover:Molecular mechanics computing engine in MS.Based on the carefully deduced force field,the lowest energy configuration,the structure and dynamic trajectory of the molecular system can be accurately calculated by using a variety of molecular mechanics and kinetics methods. > Forcite:Advanced molecular mechanics and dynamics tools.Can be used for fast energy calculation and reliable geometric optimization of molecules or periodic systems. Involved Modules Materials Visualizer:It provides all the tools needed to build structural models of molecules,crystals and polymers.It can operate,observe and analyze structural models,process data in the form of charts,tables or texts,and provide the basic environment and analysis tools for MS.It is the core module of MS. >Amorphous Cell:Constructing complex amorphous models and predicting key properties,usually used with Discovel,Forcite
MD in Materials Studio Key Modules Discover: Molecular mechanics computing engine in MS. Based on the carefully deduced force field, the lowest energy configuration, the structure and dynamic trajectory of the molecular system can be accurately calculated by using a variety of molecular mechanics and kinetics methods. Forcite: Advanced molecular mechanics and dynamics tools. Can be used for fast energy calculation and reliable geometric optimization of molecules or periodic systems. Involved Modules Materials Visualizer: It provides all the tools needed to build structural models of molecules, crystals and polymers. It can operate, observe and analyze structural models, process data in the form of charts, tables or texts, and provide the basic environment and analysis tools for MS. It is the core module of MS. Amorphous Cell: Constructing complex amorphous models and predicting key properties, usually used with Discovel, Forcite

Discover Discover is the molecular mechanics computing engine in MS.It provides a basic calculation method for Amorphous Cell, Forcite and other modules. > Calculate the lowest energy configuration > Give the dynamic trajectory of the system under different ensembles > Obtain all kinds of structural parameters Thermodynamic properties Mechanical properties Kinetic properties Vibration intensities
Discover is the molecular mechanics computing engine in MS. It provides a basic calculation method for Amorphous Cell, Forcite and other modules. Calculate the lowest energy configuration Give the dynamic trajectory of the system under different ensembles Obtain all kinds of structural parameters Thermodynamic properties Mechanical properties Kinetic properties Vibration intensities Discover
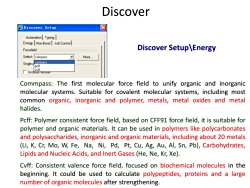
Discover □Discover Setup ☒ Automation Typing Energy Non-Bond Job Control Forcefield Discover Setup\Energy Select: compass Moe… Single compass pcff cvff Inclaue nessian Commpass:The first molecular force field to unify organic and inorganic molecular systems.Suitable for covalent molecular systems,including most common organic,inorganic and polymer,metals,metal oxides and metal halides. Pcff:Polymer consistent force field,based on CFF91 force field,it is suitable for polymer and organic materials.It can be used in polymers like polycarbonates and polysaccharides,inorganic and organic materials,including about 20 metals (Li,K,Cr,Mo,W,Fe,Na,Ni,Pd,Pt,Cu,Ag,Au,Al,Sn,Pb),Carbohydrates, Lipids and Nucleic Acids,and Inert Gases (He,Ne,Kr,Xe). Cvff:Consistent valence force field,focused on biochemical molecules in the beginning.It could be used to calculate polypeptides,proteins and a large number of organic molecules after strengthening
Discover Setup\Energy Commpass: The first molecular force field to unify organic and inorganic molecular systems. Suitable for covalent molecular systems, including most common organic, inorganic and polymer, metals, metal oxides and metal halides. Pcff: Polymer consistent force field, based on CFF91 force field, it is suitable for polymer and organic materials. It can be used in polymers like polycarbonates and polysaccharides, inorganic and organic materials, including about 20 metals (Li, K, Cr, Mo, W, Fe, Na, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Al, Sn, Pb), Carbohydrates, Lipids and Nucleic Acids, and Inert Gases (He, Ne, Kr, Xe). Cvff: Consistent valence force field, focused on biochemical molecules in the beginning. It could be used to calculate polypeptides, proteins and a large number of organic molecules after strengthening. Discover
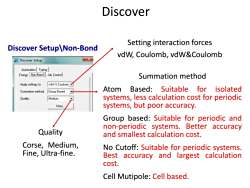
Discover Setting interaction forces Discover Setup\Non-Bond vdW,Coulomb,vdW&Coulomb Discover Setup Automation Typing Energy Non-Bond Job Control Summation method Apply settings to: vdw Coulomb Summation method: Group Based Atom Based:Suitable for isolated Quality: Medium systems,less calculation cost for periodic More.. systems,but poor accuracy. Group based:Suitable for periodic and non-periodic systems.Better accuracy Quality and smallest calculation cost. Corse,Medium, No Cutoff:Suitable for periodic systems. Fine,Ultra-fine. Best accuracy and largest calculation cost. Cell Mutipole:Cell based
Setting interaction forces vdW, Coulomb, vdW&Coulomb Summation method Atom Based: Suitable for isolated systems, less calculation cost for periodic systems, but poor accuracy. Group based: Suitable for periodic and non-periodic systems. Better accuracy and smallest calculation cost. No Cutoff: Suitable for periodic systems. Best accuracy and largest calculation cost. Cell Mutipole: Cell based. Quality Corse, Medium, Fine, Ultra-fine. Discover Discover Setup\Non-Bond
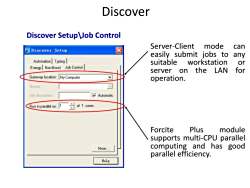
Discover Discover Setup Job Control Server-Client mode can Discover Setup easily submit jobs to any Automation Typing suitable workstation or Energy Non-Bond Job Control server on the LAN for Gateway location: My Computer operation. Queue: Job description: Automatic Run in parallel on: 1 of 1 cores Forcite Plus module supports multi-CPU parallel More… computing and has good parallel efficiency. Kelp
Discover Discover Setup\Job Control Server-Client mode can easily submit jobs to any suitable workstation or server on the LAN for operation. Forcite Plus module supports multi-CPU parallel computing and has good parallel efficiency

Discover Discover Minimization Convergence level:Convergence accuracy level. Discover Nininization ■ Maximum interactions:Maximum number of Method: Conjugate Gradient More... iterations. Convergence level: Medium Maximum iterations: 5000 Optimizer cell:Optimizing cell parameters and 厂Optimia2ecel atomic positions if chosen. Minimize Files..… Help Method (optimization method) Smart Minimizer:Synthetization of the following three methods Discover Iininization Steepest Descent:The calculation is simple and fast, Method: Smart Minimizer More... but the convergence near the minimum is not good Smart Minimizer Convergence level: enough,suitable for the initial stage of optimization Steepest Descent Conjugate Gradient Maximum iterations: Newton Conjugate gradient:Good convergence,but the Optimize cell requirement of initial structure is high.Often used Minimize Files... Help after the steepest descent method. Newton:High computational cost.Converge quickly when derivative is small.Often used in combination with the steepest descent method
Discover Minimization Method (optimization method) Smart Minimizer: Synthetization of the following three methods Steepest Descent: The calculation is simple and fast, but the convergence near the minimum is not good enough, suitable for the initial stage of optimization Conjugate gradient: Good convergence, but the requirement of initial structure is high. Often used after the steepest descent method. Newton: High computational cost. Converge quickly when derivative is small. Often used in combination with the steepest descent method. Convergence level: Convergence accuracy level. Maximum interactions: Maximum number of iterations. Optimizer cell: Optimizing cell parameters and atomic positions if chosen. Discover
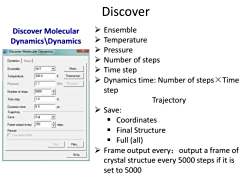
Discover Discover Molecular Ensemble Dynamics\Dynamics > Temperature Discover Molecular Dynamics Pressure Dynamics Stress >Number of steps Ensemble NVT More... > Time step Temperature: 300.0 K Thermostat... Pressure: 0.0 >Dynamics time:Number of steps XTime GPa Barostat.. Number of steps: 5000 step Time step: 1.0 fs Trajectory Dynamics time: 5.0 ps Trajectory Save: Save: Full Coordinates Frame output every: 250 日steps Restart ■Final Structure ■Use restart data ■Full(all Run Files... Frame output every:output a frame of Help crystal structue every 5000 steps if it is set to 5000
Discover Molecular Dynamics\Dynamics Ensemble Temperature Pressure Number of steps Time step Dynamics time: Number of steps×Time step Trajectory Save: Coordinates Final Structure Full (all) Frame output every:output a frame of crystal structue every 5000 steps if it is set to 5000 Discover
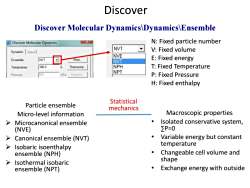
Discover Discover Molecular Dynamics\Dynamics\Ensemble Discover Molecular Dynamics N:Fixed particle number NVT Dynamics Stress V:Fixed volume NVE Ensemble: NVT More... NVT E:Fixed energy Temperature: 300.0 Thermostat... NPH T:Fixed Temperature NPT Pressure: 0.0 GPa Barostat... P:Fixed Pressure H:Fixed enthalpy Statistical Particle ensemble mechanics Micro-level information Macroscopic properties Microcanonical ensemble Isolated conservative system, (NVE) ∑P=0 > Canonical ensemble (NVT) Variable energy but constant > Isobaric isoenthalpy temperature ensemble (NPH) Changeable cell volume and Isothermal isobaric shape ensemble (NPT) Exchange energy with outside
N: Fixed particle number V: Fixed volume E: Fixed energy T: Fixed Temperature P: Fixed Pressure H: Fixed enthalpy Discover Discover Molecular Dynamics\Dynamics\Ensemble Particle ensemble Micro-level information Microcanonical ensemble (NVE) Canonical ensemble (NVT) Isobaric isoenthalpy ensemble (NPH) Isothermal isobaric ensemble (NPT) Macroscopic properties • Isolated conservative system, ∑P=0 • Variable energy but constant temperature • Changeable cell volume and shape • Exchange energy with outside Statistical mechanics
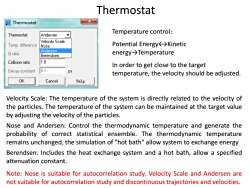
Thermostat Thermostat X Temperature control: Thermostat: Andersen Velocity Scale Temp.difference Nose Potential Energy←→Kinetic Andersen ratio Berendsen energy→Temperature Collision ratio 1.0 In order to get close to the target Decay constant 0.1 ps temperature,the velocity should be adjusted. OK Cancel Kelp Velocity Scale:The temperature of the system is directly related to the velocity of the particles.The temperature of the system can be maintained at the target value by adjusting the velocity of the particles. Nose and Andersen:Control the thermodynamic temperature and generate the probability of correct statistical ensemble.The thermodynamic temperature remains unchanged,the simulation of "hot bath"allow system to exchange energy Berendsen:Includes the heat exchange system and a hot bath,allow a specified attenuation constant. Note:Nose is suitable for autocorrelation study.Velocity Scale and Andersen are not suitable for autocorrelation study and discontinuous trajectories and velocities
Velocity Scale: The temperature of the system is directly related to the velocity of the particles. The temperature of the system can be maintained at the target value by adjusting the velocity of the particles. Nose and Andersen: Control the thermodynamic temperature and generate the probability of correct statistical ensemble. The thermodynamic temperature remains unchanged, the simulation of "hot bath" allow system to exchange energy Berendsen: Includes the heat exchange system and a hot bath, allow a specified attenuation constant. Note: Nose is suitable for autocorrelation study. Velocity Scale and Andersen are not suitable for autocorrelation study and discontinuous trajectories and velocities. Thermostat Temperature control: Potential Energy↔Kinetic energy→Temperature In order to get close to the target temperature, the velocity should be adjusted

Forcite Advanced molecular mechanics and dynamics simulation program. Supporting multiple molecular force fields >Applicabale to various systems >With the development of computer hardware and software,more and more attention has been paid to it in recent years Research field > Calculating Radial Distribution Function,orientation correlation function and scattering curve Measuring distribution of distance,angle and rotation radius Giving concentration curves of specific components Plotting temperature,pressure,volume,stress and cell parameters > Giving potential energy and its components,kinetic energy and total energy for MM and MD simulations >Studying mechanical properties of materials > Computing dipole correlation function Cohesive energy density and solubility parameters of molecular Systems >Estimating mean square displacement and velocity correlation function for self-diffusion > Simulating shear limit of lubricant and lubricating ability > Observing and plotting trajectory data in learning tables.Sorting by a specific
Advanced molecular mechanics and dynamics simulation program. Forcite Supporting multiple molecular force fields Applicabale to various systems With the development of computer hardware and software, more and more attention has been paid to it in recent years Research field Calculating Radial Distribution Function, orientation correlation function and scattering curve Measuring distribution of distance, angle and rotation radius Giving concentration curves of specific components Plotting temperature, pressure, volume, stress and cell parameters Giving potential energy and its components, kinetic energy and total energy for MM and MD simulations Studying mechanical properties of materials Computing dipole correlation function Cohesive energy density and solubility parameters of molecular Systems Estimating mean square displacement and velocity correlation function for self-diffusion Simulating shear limit of lubricant and lubricating ability Observing and plotting trajectory data in learning tables. Sorting by a specific property. If sorting by energy, find the lowest energy configration
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 15 Examples of MCMC:Reaction-Diffusion(R-D)model.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 14 Modeling and Simulation in Epitaxial Growth.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 13 Monte Carlo.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 12 An introduction of Monte Carlo method.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 11 Modeling, Computation, Simulation, Designing and Screening of New Materials.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 07 Surface calculations(1/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 06 Bulk calculations(2/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 05 Bulk calculations(1/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 04 DFT(3/3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 03 DFT(2/3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 02 DFT(1/3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 01 Introduction(张妍宁).pdf
- 《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(参考书籍)DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY - A Practical Introduction(DAVID S. SHOLL、JANICE A. STECKEL).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 热分析 Thermal analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 色谱法 chromatography.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 核磁共振谱 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy,NMR.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 拉曼光谱 Raman spectroscopy.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 红外光谱 Infrared Spectroscopy.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 分子荧光光谱 Molecular fluorescence spectroscopy.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料分子结构分析 Molecular Structure Analysis of Materials》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 紫外——可见光谱 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy UV—Vis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 08 Surface calculations(2/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《材料设计与计算 Materials Design and Computation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MDC 09 Materials design.pdf
- 《金陵科技学院学报》:PZT压电材料参数在ANSYS中的定义方法.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(参考资料,打印版)塑料、纤维、橡胶的英文缩写语.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)高分子材料配方实例.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验三十一 一种隔热涂料的制备及其性能测试实验.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验三十 高分子材料3D打印实验.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验二十九 硬脂酸相变储能石膏板的制备与性能研究.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十六 扫描电子显微镜法观察聚合物聚态结构.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十五 差热分析.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十四 红外光谱分析.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十三 氧指数的测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十二 塑料的热老化实验.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十一 马丁耐热性测试.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验十 维卡软化点测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验九 塑化性能转矩流变仪的测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验八 塑料熔体流动速率的测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验七 冲击强度测定.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验六 直角撕裂强度实验.pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《高分子材料加工实验》课程教学资源(实验,打印版)实验五 剪切强度实验.pdf
