南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)专题——RFID的识别与估算机制

“物联网技术导论”课程专题报告 专题1:RFID的识别与估算机制 谢磊教授 南京大学计算机科学与技术系
专题1:RFID的识别与估算机制 谢磊 教授 南京大学计算机科学与技术系 “物联网技术导论”课程专题报告

主要内容: 一、RFD的基本通信原理 二、基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制 三、RFID标签估算机制(Estimation) 四、开放性问题(Open Problem) 五、参考文献
二、基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制 主要内容: 五、参考文献 三、RFID标签估算机制(Estimation) 一、RFID的基本通信原理 四、开放性问题(Open Problem)
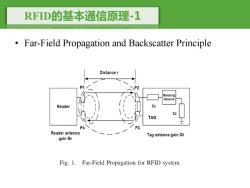
RFD的基本通信原理-1 Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle Distance r o" Matching Network Reader Za TAG P4 P3 Reader antenna Tag antenna gain Gt gain Gr Fig.1.Far-Field Propagation for RFID system
RFID的基本通信原理-1 • Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle

RFD的基本通信原理-2 Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle We denote the down-link communication from the reader to a tag as the forward channel,and denote the up-link communication from a tag to the reader as the reverse channel. forward channel Distance r P2 Matching Network Reader Za TAG Reader antenna Tag antenna gain Gt gain Gr reverse channel Fig.1.Far-Field Propagation for RFID system
RFID的基本通信原理-2 • Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle – We denote the down-link communication from the reader to a tag as the forward channel, and denote the up-link communication from a tag to the reader as the reverse channel. forward channel reverse channel
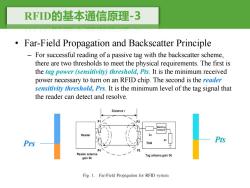
RFD的基本通信原理-3 Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle For successful reading of a passive tag with the backscatter scheme, there are two thresholds to meet the physical requirements.The first is the tag power (sensitivity)threshold,Pts.It is the minimum received power necessary to turn on an RFID chip.The second is the reader sensitivity threshold,Prs.It is the minimum level of the tag signal that the reader can detect and resolve. Distance r Matching Network Reader Za 9 Prs Pt灯 TAG P4 Reader antenna Tag antenna gain Gt gain Gr Fig.1.Far-Field Propagation for RFID system
RFID的基本通信原理-3 • Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle – For successful reading of a passive tag with the backscatter scheme, there are two thresholds to meet the physical requirements. The first is the tag power (sensitivity) threshold, Pts. It is the minimum received power necessary to turn on an RFID chip. The second is the reader sensitivity threshold, Prs. It is the minimum level of the tag signal that the reader can detect and resolve. Pts Prs
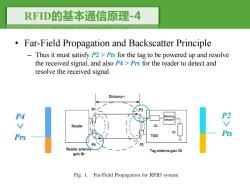
RFD的基本通信原理-4 Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle Thus it must satisfy P2>Pts for the tag to be powered up and resolve the received signal,and also P4 Prs for the reader to detect and resolve the received signal. Distance r P2 Matching Network Reader Za 四V胶 TAG Reader antenna Tag antenna gain Gt gain Gr Fig.1.Far-Field Propagation for RFID system
RFID的基本通信原理-4 • Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle – Thus it must satisfy P2 > Pts for the tag to be powered up and resolve the received signal, and also P4 > Prs for the reader to detect and resolve the received signal. Pts Prs P4 P2
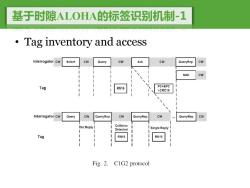
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-1 Tag inventory and access Interrogator cw Select CW Query cw Ack Cw QueryRep CW NAK Cw Tag PC+EPC RN16 +CRC16 Interrogator cw Query Cw QueryRep CW QueryRep Cw QueryRep CW INo ReplyI Collision Detected Single Reply Tag RN16 RN16 Fig.2.C1G2 protocol
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-1 • Tag inventory and access

基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-2 Tag inventory and access The MAC protocol for the C1G2 system is based on Slotted ALOHA, where each frame has a number of slots and each active tag will reply in a randomly selected slot per frame. When a reader(interrogator)wishes to read a set of tags,it first powers up and transmits a continuous wave(CW)to energize the tags.It then initiates a series of frames,varying the number of slots in each frame to best accommodate the number of tags.After all tags are read,the reader powers down.We refer to an individual frame as a Query Round,and the series of Query Rounds between power down periods as a Query Cycle. Query Cycle Query Round Query Round cee0。 Query Round
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-2 • Tag inventory and access – The MAC protocol for the C1G2 system is based on Slotted ALOHA, where each frame has a number of slots and each active tag will reply in a randomly selected slot per frame. – When a reader (interrogator) wishes to read a set of tags, it first powers up and transmits a continuous wave (CW) to energize the tags. It then initiates a series of frames, varying the number of slots in each frame to best accommodate the number of tags. After all tags are read, the reader powers down. We refer to an individual frame as a Query Round, and the series of Query Rounds between power down periods as a Query Cycle. Query Round Query Round …… Query Round Query Cycle

基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-3 Tag inventory and access - For each Query Round,the reader can optionally transmit a Select command which limits the number of active tags by providing a bit mask.Then a Ouery command is transmitted which contains the uplink frequency and data encoding,the o parameter determining the number of slots for the following frame,and a Target parameter. Interrogator Select cw Query cw Ack Cw QueryRep Cw NAK Cw Tag RN16 PC+EPC +CRC16 Interrogator Query CW QueryRep Cw QueryRep Cw QueryRep INo Reply I Collision Detected Single Reply Tag RN16 Fig.2.C1G2 protocol
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-3 • Tag inventory and access – For each Query Round, the reader can optionally transmit a Select command which limits the number of active tags by providing a bit mask. Then a Query command is transmitted which contains the uplink frequency and data encoding, the Q parameter determining the number of slots for the following frame, and a Target parameter
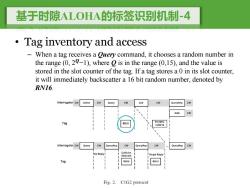
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-4 Tag inventory and access 一 When a tag receives a Ouery command,it chooses a random number in the range (0,20-1),where is in the range (0,15),and the value is stored in the slot counter of the tag.If a tag stores a 0 in its slot counter, it will immediately backscatter a 16 bit random number,denoted by RN16. Interrogator Cw Select Cw Query cw Ack Cw QueryRep Cw NAK CW Tag RN16 PC+EPC +CRC16 Interrogator Cw Query CW QueryRep Cw QueryRep Cw QueryRep INo Reply I Collision Detected Single Reply Tag RN16 Fig.2.C1G2 protocol
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-4 • Tag inventory and access – When a tag receives a Query command, it chooses a random number in the range (0, 2�−1), where Q is in the range (0,15), and the value is stored in the slot counter of the tag. If a tag stores a 0 in its slot counter, it will immediately backscatter a 16 bit random number, denoted by RN16
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 非传感器感知技术.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 自动识别技术与RFID(RFID防冲突协议与无源感知技术).pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 传感器感知技术.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 智能感知技术概述.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 物联网概述.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)课程介绍 Introduction(谢磊).pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)专题三 边缘智能(边缘计算时代的人工智能).pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)专题一 MapReduce的概念、原理与应用.pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 并行数值算法(稠密矩阵运算).pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 并行数值算法(基本通信操作).pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 并行算法的一般设计过程.pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 并行算法的基本设计技术.pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 并行算法的一般设计方法.pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 并行算法的设计基础.pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 并行计算硬件结构基础(并行计算性能评测).pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)专题二 云计算的概念、技术与应用.pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 并行计算硬件结构基础——当代并行机系统(SMP、MPP和Cluster).pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 并行计算硬件结构基础(并行计算机系统及其结构模型).pdf
- 南京大学:《并行处理技术——分布式与并行计算 Distributed and Parallel computing(并行计算——结构、算法、编程)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)引论 Introduction(谢磊).pdf
- 计算机科学与技术(参考文献)Focus and Shoot - Efficient Identification over RFID Tags in the Specified Area.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)专题——从识别到感知(基于RFID的可标记无源感知机制研究).pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 传感器技术(传感器网络).pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 定位系统(定位技术).pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)专题——物联网定位机制(概念、原理与前沿技术)以及基于位置的服务.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)专题——基于RFID的感知机制研究(RFID as a Sensing Tool).pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 物联网信息安全与隐私保护.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)Efficient Tag Identification in Mobile RFID Systems.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)P-MTI - Physical-layer Missing Tag Identification via Compressive Sensing.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)Probabilistic Optimal Tree Hopping for RFID Identification.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)Season Shelving Interference and Joint Identification in Large-scale RFID Systems.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)Using Analog Network Coding to Improve the RFID Reading Throughput.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)An Efficient Protocol for RFID Multigroup Threshold-based Classification.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)Counting RFID Tags Efficiently and Anonymously.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)Energy Efficient Algorithms for the RFID Estimation Problem.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)Every Bit Counts - Fast and Scalable RFID Estimation.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)ZOE - Fast Cardinality Estimation for Large-Scale RFID Systems.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)Location, Localization, and Localizability.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)Survey of Wireless Indoor Positioning Techniques and Systems.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)Wi-Fi雷达 - 从RSSI到CSI.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)基于位置服的务(架构与研究进展).pdf
