南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法正确性

计算机问题求解一论题2-2 -算法的正确性 2015年3月03日
计算机问题求解 – 论题2-2 - 算法的正确性 2015年3月03日

As discussed in Chapter 1,an algorithmic problem can be concisely divided into two parts: 1.a specification of the set of legal inputs;and 2.the relationship between the inputs and the desired outputs. 这段话和我们今天的主题什么关系?
这段话和我们今天的主题什么关系?

问题1: 人们似乎对于计算机 “犯错比对于人犯错更 加苛刻,这是为什么呢?
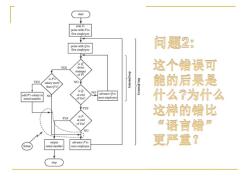
start note point with P to finst employee point wih O to 问题2: fing employee is? YES drect 这个错误可 marager of p is P's YES salary moce NO dool puaul doo 1 能的后果是 than 0's? s0 NO add p's salary to NO at end advance O to noted number of Sst? next employee 什么?为什么 YES 这样的错比 YES isp at end cf五tn %语言错 NO u中ut advance P to 更严重? noted rumber next employce 如p

问题3: 书上的对文本中出现“money 一词的句子计数的例子出现了什 么样的错误,你能说出它的性质 与前一个例子有什么不同吗?

几种不同的错误 “语言错” 口很容易被语言处理软件发现,甚至自动纠正。 “语义错” 口合格的程序员很少会犯这类错误。 解题逻辑错误 )“粗心”造成的错误。 常见(相对来说) “真正的”逻辑错误。 不常见,但这个是真的“伤脑筋”!
几种不同的错误 “语言错” 很容易被语言处理软件发现,甚至自动纠正。 “语义错” 合格的程序员很少会犯这类错误。 解题逻辑错误 “粗心”造成的错误。 常见(相对来说) “真正的”逻辑错误。 不常见,但这个是真的“伤脑筋”!

问题4: “Computers Do Not Err!' 你如何理解这句话?

Test and debugging A designer might try out an algorithm on several typical and atypical inputs and not find the error. In fact,a programmer will normally test a program on numerous inputs,sometimes called test sets,and will gradually rid it of its language errors and most of its logical errors. Most algorithmic problems have infinite sets of legal inputs,and hence infinitely many candidate test sets,each of which has the potential of exposing a new error
Test and debugging A designer might try out an algorithm on several typical and atypical inputs and not find the error. In fact, a programmer will normally test a program on numerous inputs, sometimes called test sets, and will gradually rid it of its language errors and most of its logical errors. Most algorithmic problems have infinite sets of legal inputs, and hence infinitely many candidate test sets, each of which has the potential of exposing a new error

|Debugging的局限性 Logical errors,someone once said,are like mermaids.The mere fact that you haven't seen one doesn't mean they don't exist. As someone once put it,testing and debugging cannot be used to demonstrate the absence of errors in software,only their presence. “someone”believed to be Dijkstra: Program testing can be used to show the presence of bugs,but never to show their absence! Also,Dijkstra believed to say: Programming is one of the most difficult branches of applied mathematics; the poorer mathematicians had the better remain pure mathematicians
Debugging 的局限性 “someone” believed to be Dijkstra: Program testing can be used to show the presence of bugs, but never to show their absence! Also, Dijkstra believed to say: Programming is one of the most difficult branches of applied mathematics; the poorer mathematicians had the better remain pure mathematicians

关于debugging的思考 ■为什么我们可以: The process of repeatedly executing an algorithm,or running a program,with the intention of finding and eliminating errors is called debugging?
关于debugging的思考 为什么我们可以: The process of repeatedly executing an algorithm, or running a program, with the intention of finding and eliminating errors is called debugging?
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法方法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)离散概率基础.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)概率分析与随机算法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)树及搜索树.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)有限与无限.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)数据与数据结构.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)排序与选择.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)常用的证明方法及其逻辑正确性.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)布尔代数.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)如何将算法告诉计算机.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)堆与堆排序.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)基本数据结构.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)分治法与递归.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)函数.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)关系及其基本性质.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)什么样的推理是正确的.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)为什么计算机能解题.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)不同的程序设计方法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Hashing方法.pdf
- Go To Statement Considered Harmful.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法的基本结构.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法的效率.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)组合与计数.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)计算思维引导.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)递归及其数学基础.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)集合及其运算.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)动态规划.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)贪心算法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)用于动态等价关系的数据结构.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)B树.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)图的基本概念.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)图的计算机表示以及遍历.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)树.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)单源最短通路算法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)多源最短通路算法 All-Pair Shortest Paths.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)图中的连通度和距离.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)旅行问题(图旅行).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)图中的匹配与覆盖(图中的匹配与因子分解).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)最大流算法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)图论的其它专题(平面图与图着色).pdf
