南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)堆与堆排序

计算机问题求解一论题2-12 堆与堆排序 2016年05月05日
计算机问题求解 – 论题2-12 - 堆与堆排序 2016年05月05日
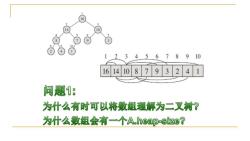
16 10 12345678910 1614108793241 问题1: 为什么有时可以将数组理解为二叉树? 为什么数组会有一个A.heap-size?

间题2: 堆与我们上次讨论的队列与 栈最突出的差别是什么? 其特征与对象的内容相关, 一定是源于具体应用
其特征与对象的内容相关, 一定是源于具体应用

堆(偏序树)性质 ·树T满足偏序树性质当且仅当树中任一结点的键值不小于 (或不大于)其子结点(如果有)的键值。 ·此性质在数组实现中的表示: Max-heap: A[PARENTO(i)】≥A[] oMin-heap: APARENT(i)】≤A[] 如果我们要定义堆的 ADT,在其数据部分, 我们应该给出什么约束?
堆(偏序树)性质 树T 满足偏序树性质 当且仅当 树中任一结点的键值不小于 (或不大于)其子结点(如果有)的键值。 此性质在数组实现中的表示: Max-heap: Min-heap: 如果我们要定义堆的 ADT,在其数据部分, 我们应该给出什么约束?
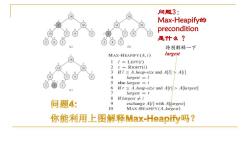
问题3: Max-Heapify的 precondition 是什么? b 特别解释一下 MAX-HEAPIFY(A,i) largest 16 11 LEFT(i) 2 r=RIGHT(i) 3ifl≤A.heap-size and A[W¥A[i] 4 largest =I 5 else largest =i (c) 6 if r A.heap-size and A[rl>A[largest] 7 largest =r 8 if largest≠i 问题4: 9 exchange A[i]with Allargest] 10 MAX-HEAPIFY (A,largest) 你能利用上图解释Max-Heapifyl吗?
特别解释一下 largest 问题3: Max-Heapify的 precondition 是什么?

Worst-case Analysis for Max-Heapify 过程Max-Heapify中不包含循环,所以,如果不递归,其 代价是O(1)。 口如果考虑比较运算的次数,每“下沉”一层,执行2次比较。 ·递归:T(m)≤T(2n/3)+Θ(1) 问题5: 为什么? The solution to this recurrence,by case 2 of the master theorem (Theorem 4.1). is T(n)=0(lg n).Altematively,we can characterize the running time of MAX- HEAPIFY on a node of height h as O(h)
Worst-case Analysis for Max-Heapify 过程Max-Heapify中不包含循环,所以,如果不递归,其 代价是O(1)。 如果考虑比较运算的次数,每“下沉”一层,执行2次比较。 递归:
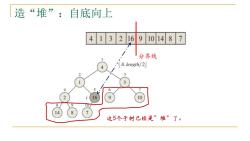
造“堆”:自底向上 413269 101487 分界线 A.length/2] 3 6 2 16 9 10 14 8 这5个子树已经是”堆”了
这5个子树已经是”堆”了。 分界线 造“堆”:自底向上
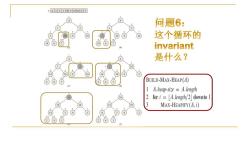
A4326910487 问题6: 2 16 9 10 2 16 9 10 这个循环的 10 10 8 7 4 8 (b) invariant 4 是什么? 0 16 10 16 9 3 ② 2 BUILD-MAX-HEAP(A) 1 A.heap-size =A.length 16 2 for i =A.length/2 downto 1 10 MAX-HEAPIFY (A,i) 9 2 (0

Built--Max-Heap正确性证明 At the start of each iteration of the for loop of lines 2-3,each node i+1, i+2.....n is the root of a max-heap. Initialization:Prior to the first iteration of the loop,i=n/2.Each node n/2+1,n/2+2.....n is a leaf and is thus the root of a trivial max-heap. Maintenance:To see that each iteration maintains the loop invariant,observe that the children of node i are numbered higher than i.By the loop invariant,there- fore,they are both roots of max-heaps.This is precisely the condition rered for the call MAX-HEAPIFY(A,i)to make node i a the MAX-HEAPIFY call preserves the property th 为什么算法是 are all roots of max-heaps.Decrementing i in th downto1,而不是 the loop invariant for the next iteration. upto length/2? Termination:At termination,i=0.By the loop invarian is the root of a max-heap.In particular,node 1 is
Built-Max-Heap正确性证明 为什么算法是 downto 1,而不是 upto length/2?

A Poor Upper Bound We an compute a simple upper boundonthe ngtime of BUILD-MAX- HEAP as follows.Each call to MAX-HEAPIFY costs (g)time,and BUILD- MAX-HEAP makes (n)such calls.Thus,the running time is O(n).This upper bound,thougis ot asymptotically tight. 间题7: 为什么这个Bound不很好?
A Poor Upper Bound
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)基本数据结构.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)分治法与递归.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)函数.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)关系及其基本性质.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)什么样的推理是正确的.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)为什么计算机能解题.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)不同的程序设计方法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Hashing方法.pdf
- Go To Statement Considered Harmful.pdf
- What is System Hang and How to Handle it?.pdf
- How Far We Have Progressed in the Journey? An Examination of Cross-Project Defect Prediction.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)关于问题求解的几个思考.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)随机算法的概念.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)群与拉格郎日定理.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)线性规划.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)矩阵计算.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)平面图与图着色.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Dijkstra算法正确性.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)图的计算机表示以及遍历.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)动态规划.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)如何将算法告诉计算机.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)布尔代数.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)常用的证明方法及其逻辑正确性.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)排序与选择.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)数据与数据结构.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)有限与无限.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)树及搜索树.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)概率分析与随机算法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)离散概率基础.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法方法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法正确性.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法的基本结构.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法的效率.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)组合与计数.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)计算思维引导.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)递归及其数学基础.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)集合及其运算.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)动态规划.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)贪心算法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)用于动态等价关系的数据结构.pdf
