上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 45_Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 45 Chapter 9 Gas Power Cycles Spring,5/9/2019 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 目e http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日G
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 45 Spring, 5/9/2019 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Chapter 9 Gas Power Cycles http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
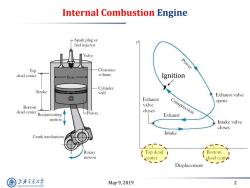
Internal Combustion Engine Spark plug or fuel injector Valve Power Top Clearance dead center volume Bore Ignition Cylinder Stroke wall Exhaust valve Exhaust opens Bottom valve dead center closes Compression Reciprocating LPiston Exhaust motion Intake valve closes Intake Crank mechanism Rotary Top dead 1 Bottom I motion center dead centr Displacement 上游充通大 May9,2019 2 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 2 Internal Combustion Engine Ignition

Air Standard Cycles Air standard cycles are idealized cycles based on the following approximations: >A fixed amount of air modeled as an ideal gas is the working fluid. >The combustion process is replaced by a heat transfer from an external source. There are no exhaust and intake processes as in an actual engine. The cycle is completed by a constant-volume heat transfer process taking place while the piston is at the bottom dead center position. >All processes are internally reversible. Cold air-standard analysis >The specific heats are assumed constant at their ambient temperature values. 上游气通大学 May9,2019 3 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 3 Air Standard Cycles Air standard cycles are idealized cycles based on the following approximations: A fixed amount of air modeled as an ideal gas is the working fluid. The combustion process is replaced by a heat transfer from an external source. There are no exhaust and intake processes as in an actual engine. The cycle is completed by a constant-volume heat transfer process taking place while the piston is at the bottom dead center position. All processes are internally reversible. Cold air-standard analysis The specific heats are assumed constant at their ambient temperature values

Continue Air Standard Cycles Cycles under consideration: Carnot cycle -maximum cycle efficiency Otto cycle-Spark-ignition engine (SI engine) Diesel cycle-Compression-ignition engine (CI engine) Dual cycle-modern CI engine Brayton cycle -gas turbines .Other cycles for interests: ·Stirling cycle ·Ericsson cycle 上游气通大粤 May9,2019 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 4 Continue Air Standard Cycles Cycles under consideration: • Carnot cycle – maximum cycle efficiency • Otto cycle – Spark-ignition engine (SI engine) • Diesel cycle – Compression-ignition engine (CI engine) • Dual cycle – modern CI engine • Brayton cycle – gas turbines • Other cycles for interests: • Stirling cycle • Ericsson cycle
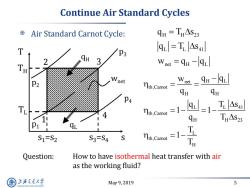
Continue Air Standard Cycles Air Standard Carnot Cycle: qH=TH△S23 T QL=T AS41 P3 Wnet qr-qL P2 Wnet th.Camnot Waet qu-qL. QH P4 4 nth.Camot =1--1-IAs THAS23 QL T S1=S2 S3=S4 Tth,Camot =1- Question: How to have isothermal heat transfer with air as the working fluid? 上游充通大 May9,2019 5 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 5 Continue Air Standard Cycles Air Standard Carnot Cycle: H H 23 L L 41 net H L q T s q T s w q q Question: How to have isothermal heat transfer with air as the working fluid? s s 1=s2 s3=s4 T TH TL 1 2 3 4 qL p3 p2 p4 p1 qH wnet net H L th,Carnot H H L L 41 th,Carnot H H 23 L th,Carnot H w q q q q q T s 1 1 q T s T 1 T
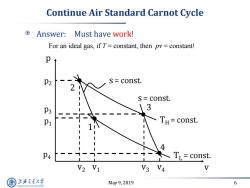
Continue Air Standard Carnot Cycle Answer:Must have work! For an ideal gas,if T=constant,then py constant! p P2 s=const. S=const. P3 13 TH=const. 4 P4 TL=const. V1 V3 V4 上游通大学 May9,2019 6 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 6 Continue Air Standard Carnot Cycle Answer: Must have work! v p 1 2 3 4 p3 p2 p4 p1 TL = const. v2 v1 v3 v4 TH = const. s = const. s = const. For an ideal gas, if T = constant, then pv = constant!
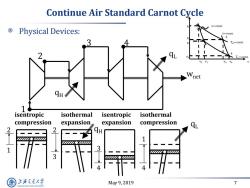
Continue Air Standard Carnot Cycle s=const Physical Devices: s=const. TH=const. TL=const. V2 V1 V3 V4 1 isentropic isothermal isentropic isothermal compression expansion expansion compression QL 2 2 QH 1 1 3 4 上降文通大学 May9,2019 7 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 7 Continue Air Standard Carnot Cycle Physical Devices: 2 3 4 wnet isentropic compression isentropic expansion isothermal compression isothermal expansion 1 1 2 3 2 4 3 4 1 qL qL qH qH v p 1 2 3 4 p3 p2 p4 p1 TL = const. v2 v1 v3 v4 TH = const. s = const. s = const

Internal (ignition)Combustion Engines Spark ignition (SD: combustion initiated by spark air and fuel can be added together Light and lower in cost,used in automobiles Compression ignition (CD: combustion initiated by auto ignition requires fuel injection to control ignition large power,heavy trucks,locomotives,ships 上游通大学 May9,2019 8 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 8 Internal (ignition) Combustion Engines Spark ignition (SI): • combustion initiated by spark • air and fuel can be added together • Light and lower in cost, used in automobiles Compression ignition (CI): • combustion initiated by auto ignition • requires fuel injection to control ignition • large power, heavy trucks, locomotives, ships

Spark ignition (SI): Spark Plug Cutaway Connector (to plug wire) CONVENTIONAL SPARK IGNITION Ceramic Insulator Spark- initiated flame Gasket Electrode 上游充通大学 May9,2019 9 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 9 Spark ignition (SI):
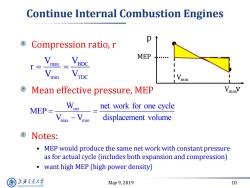
Continue Internal Combustion Engines p Compression ratio,r MEP… r= max min min Mean effective pressure,MEP Vmav W MEP et net work for one cycle max min displacement volume Notes: o MEP would produce the same net work with constant pressure as for actual cycle (includes both expansion and compression) o want high MEP (high power density) 上游充通大 May9,2019 10 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
May 9, 2019 10 Continue Internal Combustion Engines Compression ratio, r Mean effective pressure, MEP Notes: • MEP would produce the same net work with constant pressure as for actual cycle (includes both expansion and compression) • want high MEP (high power density) max BDC min TDC V V r V V net max min W net work for one cycle MEP V V displacement volume v p MEP Vmin Vmax
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 43-44_Vapor-compression refrigeration, Heat pump systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 41-42_superheat and reaheat.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 39-40_vapor power cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 38_Exergy of CV systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 37_Concept of exergy and apply to CM systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 36_Heat transfer and Work of internal reversible, ss flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 35_Isentropic processes, Isentropic efficiencies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 34_Entropy balance to open systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 33_Entropy increase principle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 28_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 27_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 25-26_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 22_Transient analysis of Energy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 20-21_Illustrations_3 Heat exchangers, throttling devices, System integration.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 19_Illustrations_2 Compressors, pumps.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 18_Illustrations_1 Nozzles, diffusers, turbines.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 17_Control volume analysis - energy conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 46_Diesel cycle and dual cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 47_Compressor, compression with intercooling.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 48_Review and Final Exam.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)全美经典学习指导系列——工程热力学.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics(8th Ed).pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics, 7th Edition.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Fundamentals.of.Engineering.Thermodynamics.8th.edition.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)THE MECHANICAL THEORY OF HEAT(R Clausius).pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach 8th Ed.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)中国物理学前辈——胡刚复.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《医用物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)流体力学(Fluid Mechanics).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)我要飛得更高.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)活在“天宮”——太空生活的行、眠、食.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)“戴”著竹蜻蜓飛翔.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)人類的飛天夢——載人航太飛船.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)白衣天使的翅膀.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)征服蓝天,像鸟一样地飞翔.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)是什么造就了“飞鱼”——菲尔普斯?.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)讓電子飛.pdf
