上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 38_Exergy of CV systems

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 38 Cengel Chapter 8 Exergy-A measure of work potential Spring,4/30/2019 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 MAMMMAAN http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 38 Spring, 4/30/2019 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Cengel Chapter 8 Exergy – A measure of work potential http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html

Open Systems Exergy Analysis Definition of Useful Work for Open Systems: W mout Surroundings @ToPo Reservoir @T Assumptions: ● Surroundings are at fixed To and po System interacts only with surroundings and one or more heat reservoirs 上游充通大 April 30,2019 2 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 2 Open Systems Exergy Analysis Definition of Useful Work for Open Systems: Surroundings @ To , po Assumptions: • Surroundings are at fixed To and po • System interacts only with surroundings and one or more heat reservoirs . W . Qj . min . mout B A CV . Qo Reservoir @ Tj

Derivation of exergy balance equation for CV sys. 1st law,energy balance: -0,w号 dt out 2nd law,entropy balance: -是+∑是+∑msm+ dt T。 out Solve entropy balance equation for Q,and then substitute in energy balance equation: -工o[aIs+2n- dt out +0-8mh++-2m+ +g2 out 2 out 上游通大学 April 30,2019 3 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 3 Derivation of exergy balance equation for CV sys. 1 st law, energy balance: 2 nd law, entropy balance: Solve entropy balance equation for Qo and then substitute in energy balance equation: 2 2 CV o j in out j in out in out dE v v Q Q W m h gz m h gz dt 2 2 CV o j in in out out tot o j j in out dS Q Q m s m s dt T T CV CV o o j in o in out o out o tot j in out j 2 2 j in out j in out in out dE dS T T Q m T s m T s T dt dt T v v Q W m h gz m h gz 2 2

Derivation of exergy balance equation for CV sys. Useful Work: Solving for work term,and rearranging combining: w-m hg-ta mahst) +o-}监+会- dt Some of the work may be done by or against the atmosphere and is not useful: We=Wca-P。 dVev dt The definition of useful work is then, ma++g-T-mn+号g-t out destruction +-} dEcv-Po dScv of exergy due to irreversibilities within dt the system. 上游充通大学 April 30,2019 4 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 4 Derivation of exergy balance equation for CV sys. Solving for work term, and rearranging & combining: Some of the work may be done by or against the atmosphere and is not useful: The definition of useful work is then, 2 2 act in o out o in out in out o CV CV j o o tot j j v v W m h gz T s m h gz T s 2 2 T dE dS Q 1 T T T dt dt CV use act o dV W W p dt Useful Work: 2 2 use in o out o in out in out o CV CV CV j o o o tot j j v v W m h gz T s m h gz T s 2 2 T dE dV dS Q 1 p T T T dt dt dt destruction of exergy due to irreversibilities within the system

Useful Work for SSSF Open Systems Open system:Assume SSSF (Steady State Steady Flow 成-Σg-T-2h片+g ,v2 o-}- Further assumptions: ●SSSF and reversible wmm-空-g--2+5g以-2o-) 上游通大学 April 30,2019 5 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 5 Useful Work for SSSF Open Systems Open system: Assume SSSF (Steady State Steady Flow ) Further assumptions: • SSSF and reversible 2 2 use,SSSF in o out o in out in out o j o tot j j v v W m h gz T s m h gz T s 2 2 T Q 1 T T 2 2 o rev,use,SSSF in o out o j in out j j in out v v T W m h gz T s m h gz T s Q 1 2 2 T
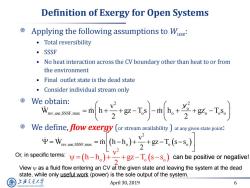
Definition of Exergy for Open Systems Applying the following assumptions to Wuse: ·Total reversibility ·SSSF No heat interaction across the CV boundary other than heat to or from the environment Final outlet state is the dead state Consider individual stream only We obtain: an4g时ja+学+以-T We define,flow exergy (or stream availability)at any given state point: 中=Wwm=mhh,)+2+g-工6-s,) emsy=-h,)十y+gz-T,s-s,)canb View y as a fluid flow entering an CV at the given state and leaving the system at the dead state,while only useful work(power)is the sole output of the system. 上游充通大学 April 30,2019 6 HANGHAI JAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 6 Definition of Exergy for Open Systems 2 2 o rev,use,SSSF,max o o o o o v v W m h gz T s m h gz T s 2 2 Applying the following assumptions to Wuse: • Total reversibility • SSSF • No heat interaction across the CV boundary other than heat to or from the environment • Final outlet state is the dead state • Consider individual stream only We obtain: We define, flow exergy (or stream availability ) at any given state point: 2 rev,use,SSSF,max o o o v W m h h gz T s s 2 2 o o o v h h gz T s s 2 Or, in specific terms: can be positive or negative! View as a fluid flow entering an CV at the given state and leaving the system at the dead state, while only useful work (power) is the sole output of the system

Change in specific flow exergy for one individual stream across CV inlet and outlet states: △Ψ12=Ψ2-Ψ1 Aye=,-h,)+(-)+g(a-Z)-T(s,-s) Generalizing for multiple inlets and outlets,we define total change in exergy across CV boundary: △中cy=∑loout-∑inVn out in a-Ta out Relationship between flow exergy and useful work for CV: n dt out dc-P。at o dt =0 for SSSF assumption 上游气通大粤 April 30,2019 7 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 7 Change in specific flow exergy for one individual stream across CV inlet and outlet states: Generalizing for multiple inlets and outlets, we define total change in exergy across CV boundary: Relationship between flow exergy and useful work for CV: 2 2 12 2 1 2 1 12 2 2 2 1 1 o 1 1 h h v v g z z T s s 2 CV out out in in out in 2 2 CV out o in o out in out in m m v v m h gz T s m h gz T s 2 2 o CV CV CV use in in out out j o tot o o in out j j T dE dV dS W m m Q 1 T p T T dt dt dt 0 for SSSF assumption

Example 38.1:Exergy for Open Systems Steam Given: T1=400C CV P1=30 bars Surroundings:T=300 K,po=1 bar Find: e Shaft work output per kg of steam Maximum possible work output per kg of steam for the given inlet and outlet states T2=120C P2=1 bar Irreversibilities of the expansion process Theoretical work output per kg of steam for isentropic expansion process to final pressure Assumptions: SSSF ● △KE=△PE=0 。Adiabatic 上游充通大 April 30,2019 8 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 8 Example 38.1: Exergy for Open Systems Given: Find: • Shaft work output per kg of steam • Maximum possible work output per kg of steam for the given inlet and outlet states • Irreversibilities of the expansion process • Theoretical work output per kg of steam for isentropic expansion process to final pressure Assumptions: • SSSF • ΔKE= ΔPE=0 • Adiabatic . WT CV Steam T1=400oC p1=30 bars T2=120oC p2=1 bar Surroundings:To=300 K,po=1 bar

Continue Example 38.1 Steam Solution: T1=400C P=30 bars ·From steam tables: h1=3230.9kJ/kg s=6.9212kJ/kg·K) h2=2716.6kJ/kg s2=7.4668kJ/(kg·K) T2=120C p2=1 bar 1st law,energy balance: --++差 dt W=minhin-mouhout Mass balaee:i=m。=i w,=h-h,=(3230.9-2716.6)=5143 g 上游通大学 April 30,2019 9 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 9 Continue Example 38.1 Solution: • From steam tables: • 1 st law, energy balance: CV dE dt 2 in v Q W m h 2 gz 2 out out in v m h 2 gz out in in out in in out out T 1 2 Mass balance : m m m W m h m h kJ kJ w h h 3230.9 2716.6 514.3 kg kg 1 1 2 2 h 3230.9 kJ kg s 6.9212 kJ (kg K) h 2716.6 kJ kg s 7.4668 kJ (kg K) . WT CV Steam T1=400oC p1=30 bars T2=120oC p2=1 bar
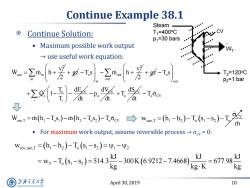
Continue Example 38.1 Steam Continue Solution: T=400C P=30 bars Maximum possible work output use useful work equation: 成+芳--h+- T2=120C P2=1 bar +Σ-}装n兴 dSg-Tocv w1=h-Is)-mh,-Ts,)-Iw→wer=(,-h)-T6-s,)T m For maximum work output,assume reversible processocv=0: wev,c,T=(h-h2)-T(S-S2)=41-Ψ2 =w,-T,6-5,)=5143300K(6.9212-7468) kJ =677.9 kJ kg g.K kg 上游充通大 April 30,2019 10 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
April 30, 2019 10 Continue Example 38.1 Continue Solution: • Maximum possible work output → use useful work equation: • For maximum work output, assume reversible process → σcv = 0: 2 use in v W m h 2 gz 2 o out in in v T s m h 2 gz o out out i T s Q o CV i i T dE 1 T dt CV o dV p dt CV o dS T dt o CV use,T 1 o 1 2 o 2 o CV T W m h T s m h T s T . WT CV Steam T1=400oC p1=30 bars T2=120oC p2=1 bar CV w h h T s s T use,T 1 2 o 1 2 o m rev,use,T 1 2 o 1 2 1 2 T o 1 2 w h h T s s kJ kJ kJ w T s s 514.3 300K 6.9212 7.4668 677.98 kg kg K kg
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 37_Concept of exergy and apply to CM systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 36_Heat transfer and Work of internal reversible, ss flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 35_Isentropic processes, Isentropic efficiencies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 34_Entropy balance to open systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 33_Entropy increase principle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 28_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 27_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 25-26_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 22_Transient analysis of Energy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 20-21_Illustrations_3 Heat exchangers, throttling devices, System integration.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 19_Illustrations_2 Compressors, pumps.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 18_Illustrations_1 Nozzles, diffusers, turbines.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 17_Control volume analysis - energy conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 16_Control volume analysis - mass conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 15_Polytropic process.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 14_cv, cp, Δu, Δh of ideal gas and applied to close system.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 13_Equation of state and ideal gas model.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 39-40_vapor power cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 41-42_superheat and reaheat.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 43-44_Vapor-compression refrigeration, Heat pump systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 45_Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 46_Diesel cycle and dual cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 47_Compressor, compression with intercooling.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 48_Review and Final Exam.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)全美经典学习指导系列——工程热力学.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Challenges to the Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics(8th Ed).pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics, 7th Edition.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Fundamentals.of.Engineering.Thermodynamics.8th.edition.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)THE MECHANICAL THEORY OF HEAT(R Clausius).pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach 8th Ed.pdf
- 《热力学 Thermodynamics》课程教学资源(书籍文献)中国物理学前辈——胡刚复.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《医用物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)流体力学(Fluid Mechanics).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)我要飛得更高.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)活在“天宮”——太空生活的行、眠、食.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)“戴”著竹蜻蜓飛翔.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)人類的飛天夢——載人航太飛船.doc
